Related Research Articles

Knud Johan Victor Rasmussen was a Greenlandic-Danish polar explorer and anthropologist. He has been called the "father of Eskimology" and was the first European to cross the Northwest Passage via dog sled. He remains well known in Greenland, Denmark and among Canadian Inuit.

Baffin Island, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada, the second largest island in the Americas, and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is 507,451 km2 (195,928 sq mi) with a population density of 0.03/km2; the population was 13,039 according to the 2021 Canadian census; and it is located at 68°N70°W. It also contains the city of Iqaluit, which is the capital of Nunavut.

Sir Martin Frobisher was an English sailor and privateer who made three voyages to the New World looking for the North-west Passage. He probably sighted Resolution Island near Labrador in north-eastern Canada, before entering Frobisher Bay and landing on present-day Baffin Island. On his second voyage, Frobisher found what he thought was gold ore and carried 200 tons of it home on three ships, where initial assaying determined it to be worth a profit of £5.20 per ton. Encouraged, Frobisher returned to Canada with an even larger fleet and dug several mines around Frobisher Bay. He carried 1,350 tons of the ore back to England, where, after years of smelting, it was realized that the ore was a worthless rock containing the mineral hornblende. As an English privateer, he plundered riches from French ships. He was later knighted for his service in repelling the Spanish Armada in 1588.

Frobisher Bay is an inlet of the Davis Strait in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the southeastern corner of Baffin Island. Its length is about 230 km (140 mi) and its width varies from about 40 km (25 mi) at its outlet into the Davis Strait to roughly 20 km (12 mi) towards its inner end.
Indigenous peoples in Canada are the indigenous peoples within the boundaries of Canada. They comprise the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis. Although "Indian" is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors "Indian" and "Eskimo" have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them to be pejorative. "Aboriginal" as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the Constitution Act, 1982, though in some circles that word is also falling into disfavour.

Vilhjalmur Stefansson was an Arctic explorer and ethnologist. He was born in Manitoba, Canada.

Bathurst Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in Nunavut, Canada. It is a member of the Arctic Archipelago. The area of the island is estimated at 16,042 km2 (6,194 sq mi), 115 to 117 mi long and from 63 mi (101 km) to 72 mi (116 km) to 92.9 mi (149.5 km) wide, making it Canada's 13th largest island. It is located between Devon Island and Cornwallis Island in the east, and Melville Island in the west. Four small islands of Cameron, Vanier, Massey and Alexander lie in its northwest.

Diamond Jenness, was one of Canada's greatest early scientists and a pioneer of Canadian anthropology.

The Royal Canadian Geographical Society is a Canadian nonprofit educational organization. It has dedicated itself to spreading a broader knowledge and deeper appreciation of Canada, including its people, places, natural and cultural heritage, as well as its environmental, social and economic challenges.
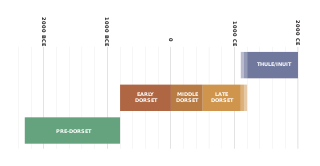
The history of Nunavut covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Eskimo thousands of years ago to present day. Prior to the colonization of the continent by Europeans, the lands encompassing present-day Nunavut were inhabited by several historical cultural groups, including the Pre-Dorset, the Dorsets, the Thule and their descendants, the Inuit.
Based on archeological finds, Brooman Point Village is an abandoned village in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the central High Arctic near Brooman Point of the Gregory Peninsula, part of the eastern coast of Bathurst Island. Brooman was both a Late Dorset culture Paleo-Eskimo village as well as an Early Thule culture village. Both the artifacts and the architecture, specifically longhouses, are considered important historical remains of the two cultures. The site shows traces of Palaeo-Eskimo occupations between about 2000 BC and 1 AD, but the major prehistoric settlement occurred from about 900 to 1200 AD.

Inuit are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of North America, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, Yukon (traditionally), Alaska, and Chukotsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut.

Franklin's lost expedition was a failed British voyage of Arctic exploration led by Captain Sir John Franklin that departed England in 1845 aboard two ships, HMS Erebus and HMS Terror, and was assigned to traverse the last unnavigated sections of the Northwest Passage in the Canadian Arctic and to record magnetic data to help determine whether a better understanding could aid navigation. The expedition met with disaster after both ships and their crews, a total of 129 officers and men, became icebound in Victoria Strait near King William Island in what is today the Canadian territory of Nunavut. After being icebound for more than a year Erebus and Terror were abandoned in April 1848, by which point two dozen men, including Franklin, had died. The survivors, now led by Franklin's second-in-command, Francis Crozier, and Erebus's captain, James Fitzjames, set out for the Canadian mainland and disappeared, presumably having perished.

Copper Inuit, also known as Inuinnait and Kitlinermiut, are a Canadian Inuit group who live north of the tree line, in what is now the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut and in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. Most of them historically lived in the area around Coronation Gulf, on Victoria Island, and southern Banks Island.
Count Eigil Knuth was a Danish explorer, archaeologist, sculptor and writer. He is referred to as the Nestor of Danish polar explorers. His archaeological investigations were made in Peary Land and adjacent areas of High Arctic Greenland. Knuth was made a Knight of the Dannebrog.

The Canadian Arctic Expedition 1913–1916 was a scientific expedition in the Arctic Circle organized and led by Vilhjalmur Stefansson. The expedition was originally to be sponsored by the (US) National Geographic Society and the American Museum of Natural History. Canada took over the sponsorship because of the potential for discovery of new land and Stefansson, who though born in Canada was now an American, re-established his Canadian citizenship. The expedition was divided into a Northern Party led by Stefansson, and a Southern Party led by R M. Anderson.
Patricia D. Sutherland is a Canadian archaeologist, specialising in the Arctic. She is an adjunct professor at Carleton University, an Honorary Research Fellow at the University of Aberdeen, and sole proprietor of Northlands Research. Much of her recent research has focused on evidence of a lengthy Norse presence on Baffin Island in the 11th to 13th centuries CE and trade between them and the now-extinct Dorset people of the region. Sutherland's theory that there were Europeans on Baffin Island hundreds of years before the Norse settled Greenland at the start of the 11th century is controversial.

There is a long historical tradition of research on Inuit clothing across many fields. Since Europeans first made contact with the Inuit in the 16th century, documentation and research on Inuit clothing has included artistic depictions, academic writing, studies of effectiveness, and museum collections. Historically, European images of Inuit were sourced from the clothing worn by Inuit who travelled to Europe, clothing brought to museums by explorers, and from written accounts of travels to the Arctic.

Kodlunarn Island, known as Qallunaaq in Inuktitut and originally named Countess of Warwick Island, is a small island located in Frobisher Bay in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. During the 1570s, explorer Martin Frobisher led expeditions to the island to mine what he believed was gold ore. The ore turned out to be worthless, and the island was ignored by explorers until Charles Francis Hall, inspired by oral history accounts from the Inuit of Frobisher Bay, visited the site in 1861 to investigate the remains of Frobisher's expeditions. Notable features of the island include two large mining trenches and the remains of a stone house built by Frobisher in 1578. Kodlunarn Island was designated a National Historic Site of Canada in 1964.
David Charles Woodman is a Canadian mariner, author, and arctic researcher. He is known for his research on Franklin's Lost Expedition, having led or participated in nine expeditions to King William Island between 1992 and 2004, searching for relics, records, and the wrecks of the ships HMS Terror and HMS Erebus, and establishing the important role of Inuit oral testimony in the search.
References
- ↑ Wright, Shelley (2014). Our Ice Is Vanishing / Sikuvut Nunguliqtuq: A History of Inuit, Newcomers, and Climate Change. McGill-Queen's Native and Northern Series. Vol. 75. Montreal: McGill-Queens University Press. p. 27. ISBN 9780773596108.
- ↑ "Royal Canadian Geographical Society Massey Medal 2000". Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved May 3, 2011.