
The Auckland Islands are an archipelago of New Zealand, lying 465 km (289 mi) south of the South Island. The main Auckland Island, occupying 460 km2 (180 sq mi), is surrounded by smaller Adams Island, Enderby Island, Disappointment Island, Ewing Island, Rose Island, Dundas Island, and Green Island, with a combined area of 570 km2 (220 sq mi). The islands have no permanent human inhabitants.

Macquarie Island is an island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, about halfway between New Zealand and Antarctica. Regionally part of Oceania and politically a part of Tasmania, Australia, since 1900, it became a Tasmanian State Reserve in 1978 and was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1997.

Auckland Island is the main island of the eponymous uninhabited archipelago in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the New Zealand subantarctic area. It is inscribed in the UNESCO World Heritage list together with the other New Zealand Subantarctic Islands in the region.

Campbell Island / Motu Ihupuku is an uninhabited subantarctic island of New Zealand, and the main island of the Campbell Island group. It covers 112.68 square kilometres (43.51 sq mi) of the group's 113.31 km2 (43.75 sq mi), and is surrounded by numerous stacks, rocks and islets like Dent Island, Folly Island, Isle de Jeanette-Marie, and Jacquemart Island, the latter being the southernmost extremity of New Zealand. The island is mountainous, rising to over 500 metres (1,640 ft) in the south. A long fiord, Perseverance Harbour, nearly bisects it, opening out to sea on the east coast.
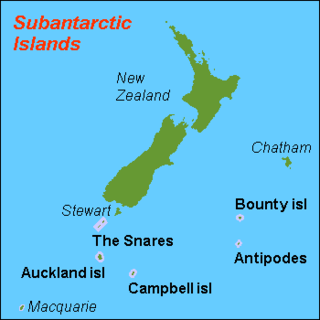
The New Zealand Subantarctic Islands comprise the five southernmost groups of the New Zealand outlying islands. They are collectively designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Antipodes Subantarctic Islands tundra ecoregion, within the tundra biome, includes five remote island groups in the Pacific Ocean south of New Zealand: the Bounty Islands, Auckland Islands, Antipodes Islands and Campbell Island groups of New Zealand, and Macquarie Island of Australia.

The Campbell Islands are a group of subantarctic islands, belonging to New Zealand. They lie about 600 km south of Stewart Island. The islands have a total area of 113 km2 (44 sq mi), consisting of one big island, Campbell Island, and several small islets, notably Dent Island, Isle de Jeanette Marie, Folly Island, Jacquemart Island, and Monowai Island. Ecologically, they are part of the Antipodes Subantarctic Islands tundra ecoregion. The islands are one of five subantarctic island groups collectively designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.

Adams Island is the second largest island of New Zealand's Auckland Islands archipelago.

Enderby Island is part of New Zealand's uninhabited Auckland Islands archipelago, south of mainland New Zealand. It is situated just off the northern tip of Auckland Island, the largest island in the archipelago.

Ewing Island is an uninhabited island, part of the Auckland Islands group, a subantarctic chain that forms part of the New Zealand outlying islands. It lies in the north-east of the group, close to the mouth of Port Ross, immediately to the south of the larger Enderby Island and off the north-eastern tip of the main Auckland Island.

The New Zealand outlying islands are nine offshore island groups that are part of New Zealand, with all but Solander Islands lying beyond the 12nm limit of the mainland's territorial waters. Although considered integral parts of New Zealand, seven of the nine island groups are not part of any administrative region or district, but are instead each designated as an Area Outside Territorial Authority. The two exceptions are the Chatham Islands, which are covered by their own special territorial authority, and the Solander Islands, which are part of the Southland Region and Southland District.

The austral snipes, also known as the New Zealand snipes or tutukiwi, are a genus, Coenocorypha, of tiny birds in the sandpiper family, which are now only found on New Zealand's outlying islands. There are currently three living species and six known extinct species, with the Subantarctic snipe having three subspecies, including the Campbell Island snipe discovered as recently as 1997. The genus was once distributed from Fiji, New Caledonia and Norfolk Island, across New Zealand and southwards into New Zealand's subantarctic islands, but predation by introduced species, especially rats, has drastically reduced their range.
Enderby Island Cattle are a breed of cattle that existed in a wild state in isolation on Enderby Island, New Zealand for over 80 years. Only about seven specimens remain today, after a rescue expedition by the Rare Breeds Conservation Society of New Zealand (RBCSNZ), and a culling program to protect the native flora and fauna of Enderby Island. There have since been intensive efforts at breeding the cattle, involving both in vitro fertilisation and cloning, and there is an ongoing program to perpetuate the breed in captivity.

Disappointment Island is one of seven uninhabited islands in the Auckland Islands archipelago, in New Zealand. It is 475 kilometres (295 mi) south of the country's main South Island and 8 kilometres (5 mi) from the northwest end of Auckland Island. It is home to a large colony of white-capped albatrosses: about 65,000 pairs – nearly the entire world's population – nest there. Also on the island is the Auckland rail, endemic to the archipelago; once thought to be extinct, it was rediscovered in 1966.

The Rare Breeds Conservation Society of New Zealand (RBCSNZ) was founded in 1988 to conserve, record and promote rare livestock breeds with the aim of maintaining genetic diversity within livestock species. The area of coverage is broad, and includes poultry as well as camelids, cattle, chinchillas, deer, donkeys, goats, horses, pigs, rabbits and sheep.

A castaway depot is a store or hut placed on an isolated island to provide emergency supplies and relief for castaways and victims of shipwrecks.

The Sub-Antarctic Islands Scientific Expedition of 1907 was organised by the Philosophical Institute of Canterbury. The main aim of the expedition was to extend the magnetic survey of New Zealand by investigating Campbell Island and the Auckland Islands, but botanical, biological and zoological surveys were also conducted.

Pleurophyllum hookeri, also known as the silver-leaf daisy or sage-green rosette herb, is a herbaceous plant in the family Asteraceae, a megaherb native to the subantarctic Auckland and Campbell Islands of New Zealand and Australia’s Macquarie Island. It grows up to 900 mm in height and has crimson button flowers and long, silky, silver leaves, with a large carrot-like tuber and long roots. It also has the unusual feature of a vertically contractile stem, most of which is underground, which serves to keep the leaf rosette close to the ground surface and the plant anchored securely against the very strong winds typical of subantarctic islands. Prior to the successful eradication of introduced mammals on Macquarie Island in 2011, it had been threatened there by black rats and European rabbits.

The Auckland snipe, also known as the Auckland Island snipe, is a small bird in the sandpiper family. It is the isolated nominate subspecies of the subantarctic snipe that is endemic to the Auckland Islands, a subantarctic island group south of New Zealand in the Southern Ocean.

Megaherbs are a group of herbaceous wildflowers growing in the New Zealand subantarctic islands and on the other subantarctic islands. They are characterised by their great size, with huge leaves and very large and often unusually coloured flowers, which have evolved as an adaptation to the harsh weather conditions on the islands. They suffer from overgrazing due to introduced mammals.




















