
In molecular biology, a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule, resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. Thus, an mRNA that contains a riboswitch is directly involved in regulating its own activity, in response to the concentrations of its effector molecule. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins, catalyze reactions, or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules.
In molecular biology and bioinformatics, the consensus sequence is the calculated sequence of most frequent residues, either nucleotide or amino acid, found at each position in a sequence alignment. It represents the results of multiple sequence alignments in which related sequences are compared to each other and similar sequence motifs are calculated. Such information is important when considering sequence-dependent enzymes such as RNA polymerase.

The ykkC/yxkD leader is a conserved RNA structure found upstream of the ykkC and yxkD genes in Bacillus subtilis and related genes in other bacteria. The function of this family is unclear for many years although it has been suggested that it may function to switch on efflux pumps and detoxification systems in response to harmful environmental molecules. The Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis sequence AE013027 overlaps with that of purine riboswitch suggesting that the two riboswitches may work in conjunction to regulate the upstream gene which codes for TTE0584 (Q8RC62), a member of the permease family.

The sucA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure found in bacteria of the order Burkholderiales. RNAs within this motif are always found in the presumed 5' UTR of sucA genes. sucA encodes a subunit of an enzyme that participates in the citric acid cycle by synthesizing succinyl-CoA from 2-oxoglutarate. A part of the conserved structure overlaps predicted Shine-Dalgarno sequences of the downstream sucA genes. Because of the RNA motif's consistent gene association and a possible mechanism for sequestering the ribosome binding site, it was proposed that the sucA RNA motif corresponds to a cis-regulatory element. Its relatively complex secondary structure could indicate that it is a riboswitch. However, the function of this RNA motif remains unknown.

The Downstream-peptide motif refers to a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in the cyanobacterial genera Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus and one phage that infects such bacteria. It was also detected in marine samples of DNA from uncultivated bacteria, which are presumably other species of cyanobacteria.
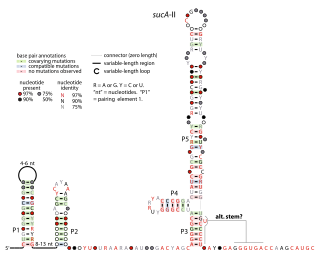
The sucA-II RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. It is consistently found in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of sucA genes, which encode Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase enzymes that participate in the citric acid cycle. Given this arrangement, sucA-II RNAs might regulate the downstream sucA gene. This genetic arrangement is similar to the previously reported sucA RNA motif. However, sucA-II RNAs are found only in bacteria classified within the genus Pseudomonas, whereas the previously reported motif is found only in betaproteobacteria.

The sucC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure discovered using bioinformatics. sucC RNAs are found in the genus Pseudomonas. They ae consistently found in possible 5' untranslated regions of sucC genes. These genes encode Succinyl coenzyme A synthetase, and are hypothesised to be regulated by the sucC RNAs. sucC genes participate in the citric acid cycle, and another gene involved in the citric acid cycle, sucA, is also predicted to be regulated by a conserved RNA structure.

The aspS RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. aspS motifs are found in a specific lineage of Actinomycetota.
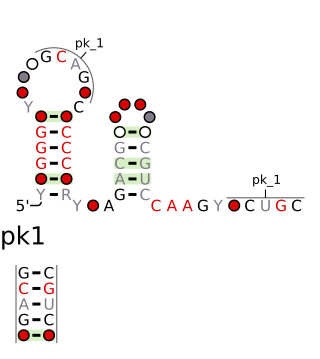
The chrB-a RNA motif and chrB-b RNA motif refer to a related, conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The structures of these motifs are similar, and some genomic locations are predicted to exhibit both motifs. The chrB-b motif has an extra pseudoknot that is not consistently found in chrB-a examples. It was proposed that the two motifs could be unified into one common structure, with additional information.
The gltS RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. gltS motifs are found in the bacterial lineage Vibrionaceae.
The ldcC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. ldcC motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and two species of Spirochaetota.
The leuA-Halobacteria RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. leuA-Halobacteria motifs are found in Halobacteriaceae, a lineage of archaea.
The narK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. narK motif RNAs are found in Beta- and Gammaproteobacteria.

The NLPC-P60 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. NLPC-P60 motif RNAs are found in Streptomyces.

The Poribacteria-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The Poribacteria-1 motif is found only in the candidate bacterial phylum known as Poribacteria, and all 6 Poribacteria-1 RNAs are actually found in one organism, Candidatus Poribacteria sp. WGA-4E. All but one of these RNAs occur within roughly 6 kilobases of genomic DNA, and each of the 5 RNAs occurs between a different pair of protein-coding genes. This arrangement could suggest that the motif functions on the level of single-stranded DNA as attC sites that are part of an integron. It is also possible that Poribacteria-1 RNAs are cis-regulatory elements that regulate genes that happen to often be nearby to one another, or that the RNAs function in trans as small RNAs.
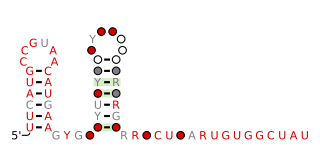
The queA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. queA motif RNAs have not yet been found in any classified organism; they are known from metagenomic sequences.
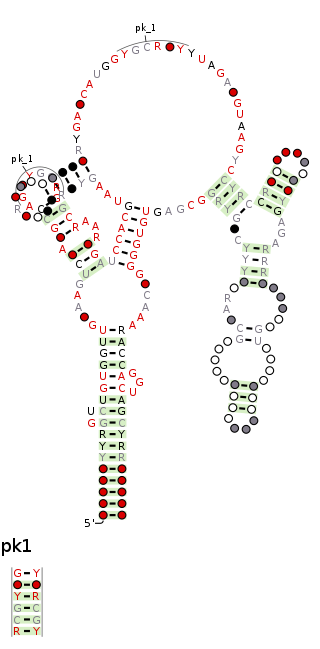
The raiA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. raiA motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota and Bacillota, and have many conserved features—including conserved nucleotide positions, conserved secondary structures and associated protein-coding genes—in both of these phyla. Some conserved features of the raiA RNA motif suggest that they function as cis-regulatory elements, but other aspects of the motif suggest otherwise.

The sul1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Energetically stable tetraloops often occur in this motif. sul1 motif RNAs are found in Alphaproteobacteria.

The terC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. terC motif RNAs are found in Pseudomonadota, within the sub-lineages Alphaproteobacteria and Pseudomonadales.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.















