Related Research Articles
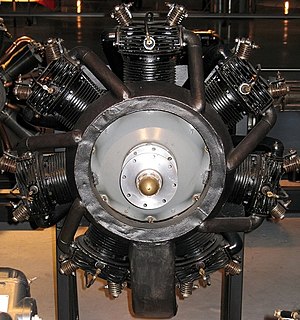
The Warner Scarab is an American seven-cylinder radial aircraft engine, that was manufactured by the Warner Aircraft Corporation of Detroit, Michigan in 1928 through to the early 1940s. In military service the engine was designated R-420.

The Alvis Leonides Major was a British air-cooled 14-cylinder radial aero engine developed by Alvis from the earlier nine-cylinder Leonides.

The Jacobs R-755 is a seven-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft manufactured in the United States by the Jacobs Aircraft Engine Company.

The Ivchenko AI-14 is a nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial piston engine designed in the Soviet Union to power aircraft.

The Kinner R-5 is an American five cylinder radial engine for light general and sport aircraft of the 1930s.

The Continental O-470 engine is a family of carbureted and fuel-injected six-cylinder, horizontally opposed, air-cooled aircraft engines that was developed especially for use in light aircraft by Continental Motors. Engines designated "IO" are fuel-injected.

The Rotax 503 is a 37 kW (50 hp), inline 2-cylinder, two-stroke aircraft engine, built by BRP-Rotax GmbH & Co. KG of Austria for use in ultralight aircraft.
The Rotax 447 is a 41.6 hp (31 kW), inline 2-cylinder, two-stroke aircraft engine, built by BRP-Rotax GmbH & Co. KG of Austria for use in ultralight aircraft.
The Rotax 532 is a 48 kW (64 hp) two-stroke, two-cylinder, rotary valve engine, liquid-cooled, gear reduction-drive engine that was formerly manufactured by BRP-Rotax GmbH & Co. KG. It was designed for use on ultralight aircraft.
The Lycoming O-340 is a family of four-cylinder horizontally opposed, carburetor-equipped aircraft engines, that was manufactured by Lycoming Engines in the mid-1950s.
The Hirth F-23 is a twin cylinder, horizontally-opposed, two stroke, carburetted or optionally fuel injected aircraft engine designed for use on ultralight aircraft.
The Hirth F-263 is a twin cylinder, in-line, two stroke, carburetted aircraft engine that was designed for use on ultralight aircraft. The engine was discontinued about 2001.
The Hirth 2704 and 2706 are a family of in-line twin cylinder, two stroke, carburetted aircraft engines, with optional fuel injection, designed for use on ultralight aircraft and especially two seat ultralight trainers, single seat gyrocopters and small homebuilts.
The Hirth 3701 is an in-line three-cylinder, two-stroke, carburetted aircraft engine, with optional fuel injection, designed for use on ultralight aircraft and small homebuilts.
The Kawasaki 440, also called the T/A 440, is a Japanese twin-cylinder, in-line, two-stroke engine that was designed for snowmobiles and produced by Kawasaki Heavy Industries until the early 1980s.
The 2si 460 is a family of in-line twin-cylinder, two-stroke, single ignition, aircraft engines that were designed for ultralight aircraft.
The Nelson H-63, known in the US military designation system as the YO-65, is an American dual ignition, four-cylinder, horizontally opposed, two-stroke aircraft engine that was developed by the Nelson Engine Company for use in helicopters and light aircraft. The engine designation means horizontally opposed 63 cubic inch displacement.
The Franklin O-500 was an American air-cooled aircraft engine that first ran in the mid-1940s. The engine was of six-cylinder, horizontally-opposed layout and displaced 500 cu in (8 L). The power output was 215 hp (160 kW).
The Franklin O-425 was an American air-cooled aircraft engine that first ran in the mid-1940s. The engine was of six-cylinder, horizontally-opposed layout and displaced 425 cu in (7 L). The power output was between 240 hp (179 kW) and 285 hp (213 kW) depending on variant. The O-405-13 (6V6-300-D16FT) of 1955 was a vertically mounted, turbocharged and fan cooled version for helicopters.

The Fiat A.53 was a seven-cylinder, air-cooled radial piston engine developed in Italy in the 1930s as a powerplant for aircraft.