
Person County is a county located in the U.S. state of North Carolina. The population was 39,097 as of the 2020 census. The county seat is Roxboro.

Roxboro is a city and the county seat of Person County in the U.S. state of North Carolina. The population was 8,134 at the 2020 census. The city is 30 miles (48 km) north of Durham and is a part of the four-county Durham–Chapel Hill Metropolitan Statistical Area, which has a population of 649,903 as of the 2020 Census. The Durham–Chapel Hill MSA is a part of the larger Raleigh–Durham–Cary Combined Statistical Area, which has a population of 2,043,867 as of the 2020 Census.

Nevada Solar One is a concentrated solar power plant, with a nominal capacity of 64 MW and maximum steam turbine power output up to 72 MW net (75 MW gross), spread over an area of 400 acres (160 ha). The projected CO2 emissions avoided is equivalent to taking approximately 20,000 cars off the road. The project required an investment of $266 million USD, and the project officially went into operation in June 2007. Electricity production is estimated to be 134 GWh (gigawatt hours) per year.
The Black Fox Nuclear Power Plant was a nuclear power plant proposed by the Public Service Company of Oklahoma (PSO) in May 1973. It was cancelled in 1982.

Hyco Lake is a reservoir in Person and Caswell counties, North Carolina. It is the area's main destination for fishing, boating, water skiing, wake boarding, and recreation and is the larger of Person County's two lakes, the other being Mayo Lake. The lake was formed from the Hyco River and has three main tributaries; North Hyco Creek, South Hyco Creek, and Cobbs Creek. Interest in the lake for vacation homes has created numerous homes along its shores with relatively high property values. Over 1500 homes have been constructed around the lake with approximately 800 occupied year-round. It runs through the following municipalities: Semora, Leasburg, and the city of Roxboro located about ten miles (16 km) from the lake.

Rockport Generating Station is a coal-fired power plant, located along the Ohio River in Ohio Township, Spencer County, Indiana, in the United States, near Rockport. The power plant is located along U.S. Route 231, approximately one mile north of the William H. Natcher Bridge, spanning the Ohio River. It is operated by Indiana Michigan Power, a subsidiary of American Electric Power.

Geothermal energy was first used for electric power production in the United States in 1960. The Geysers in Sonoma and Lake counties, California was developed into the largest geothermal steam electrical plant in the world, at 1,517 megawatts. Other geothermal steam fields operate in the western US and Alaska.

Coal generated about 19.5% of the electricity at utility-scale facilities in the United States in 2022, down from 38.6% in 2014 and 51% in 2001. In 2021, coal supplied 9.5 quadrillion British thermal units (2,800 TWh) of primary energy to electric power plants, which made up 90% of coal's contribution to U.S. energy supply. Utilities buy more than 90% of the coal consumed in the United States. There were over 200 coal powered units across the United States in 2022. Coal plants have been closing since the 2010s due to cheaper and cleaner natural gas and renewables. Due to measures such as scrubbers air pollution from the plants kills far fewer people nowadays, but deaths in 2020 from PM 2.5 have been estimated at 1600. Environmentalists say that political action is needed to close them faster, to also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and better limit climate change.
The William States Lee III Nuclear Station was a planned two-unit nuclear power plant in Cherokee County, South Carolina. Duke Energy filed the Combined Construction and Operating License (COL) application for the plant on December 13, 2007 to the NRC. On December 19, 2016, the NRC issued two Combined Licenses authorizing Duke to build and operate two AP1000 reactors at the site.
The 5 megawatt (MW) Kimberlina Solar Thermal Energy Plant in Bakersfield, California is the first commercial solar thermal power plant to be built by Areva Solar. Completed in 2008, the Kimberlina renewable energy solar boiler uses Compact Linear Fresnel Reflector (CLFR) technology to generate superheated steam. Each solar boiler has a group of 13 narrow, flat mirrors, that individually track and focus the sun's heat onto overhead pipes carrying water. The water boils directly into steam. The steam can then spin a turbine to generate electricity or be used as industrial steam for food, oil and desalination processes. The Kimberlina solar boiler currently achieves 750-degree F superheated steam. The next generation solar boiler under construction is designed to achieve 900-degree F superheated steam.

Capital Power is a North American independent power generation company based in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It develops, acquires, owns and operates power generation facilities using a variety of energy sources.
The Montague Nuclear Power Plant was a proposed nuclear power plant to be located in Montague, Massachusetts. The plant was to consist of two 1150 MWe General Electric boiling water reactors. The project was proposed in 1973 and canceled in 1980, after $29 million was spent on the project.
The Erie Nuclear Power Plant was a proposed nuclear power plant to be located 9 miles (14 km) southeast of Sandusky, Ohio. It was proposed in 1976 by Ohio Edison for the Central Area Power Coordination (CAPCO). The plant was to consist of two Babcock & Wilcox 1,267 megawatt reactors. Unit 1 was scheduled to be complete in 1986, Unit 2 in 1988. Preliminary work was canceled in 1980 due to new federal requirements placed on nuclear plants that make their construction more expensive and by a drop in anticipated customer energy demand.

The DeSoto Next Generation Solar Energy Center is a photovoltaic power station in Arcadia, DeSoto County, in the U.S. state of Florida, owned by Florida Power & Light (FPL). President Barack Obama attended the plant's commissioning on October 27, 2009. It has a nameplate capacity of 25 megawatts (MW), and produces an estimated 42,000 megawatt hours (MW·h) of electricity per year.
Holaniku at Keahole Point is a 2MW micro-scaled concentrated solar power plant in the Kona District of the island of Hawaiʻi. It is located in the Natural Energy Laboratory of Hawaii at Keahole Point.
The 21 megawatt Blythe Photovoltaic Power Plant is a photovoltaic (PV) solar project in California. It is located in Blythe, California, in Riverside County about 200 miles (320 km) east of Los Angeles. Commercial operation began in December 2009. Electricity generated by the power plant is being sold to Southern California Edison under a 20-year power purchase agreement. Another 20 MW plant called NRG Solar Blythe II came online in April 2017.
The 12 megawatt (MW) Wyandot Solar Facility is a solar photovoltaic power plant completed in 2010, located in Salem Township, Wyandot County, Ohio. This system uses 159,200 panels spread over 83.9 acres (34.0 ha).
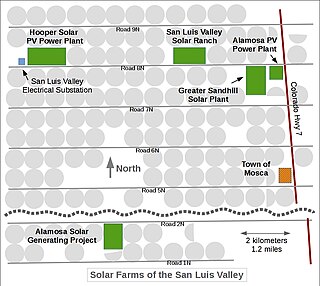
The Hooper Solar PV Power Plant is a 50 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station in the San Luis Valley, located near the town of Mosca, Colorado. It was the largest solar facility in the state when it came online at the end of 2015. The electricity is being sold to Public Service of Colorado, a subsidiary of Xcel Energy, under a long-term power purchase agreement.
The Fusion Pilot Plant is a program initiated in 2021 by the United States Department of Energy to construct a pilot plant capable of producing net electrical fusion power by the 2030s. In September 2022, $50 million was earmarked by the Department of Energy for development of a pilot fusion power plant. The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine was involved in kicking off the program and advised it become a United States public-private partnership.










