Related Research Articles

Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and is a PFAS that has numerous applications. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemours, a spin-off from DuPont, which originally discovered the compound in 1938.

A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Fluid bearings are bearings in which the load is supported by a thin layer of rapidly moving pressurized liquid or gas between the bearing surfaces. Since there is no contact between the moving parts, there is no sliding friction, allowing fluid bearings to have lower friction, wear and vibration than many other types of bearings. Thus, it is possible for some fluid bearings to have near-zero wear if operated correctly.

A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free rotation around a fixed axis; or, it may prevent a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts. Most bearings facilitate the desired motion by minimizing friction. Bearings are classified broadly according to the type of operation, the motions allowed, or the directions of the loads (forces) applied to the parts.
Tribology is the science and engineering of understanding friction, lubrication and wear phenomena for interacting surfaces in relative motion. It is highly interdisciplinary, drawing on many academic fields, including physics, chemistry, materials science, mathematics, biology and engineering. The fundamental objects of study in tribology are tribosystems, which are physical systems of contacting surfaces. Subfields of tribology include biotribology, nanotribology and space tribology. It is also related to other areas such as the coupling of corrosion and tribology in tribocorrosion and the contact mechanics of how surfaces in contact deform. Approximately 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world is due to the impact of friction and wear in the transportation, manufacturing, power generation, and residential sectors.

A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing, is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe.
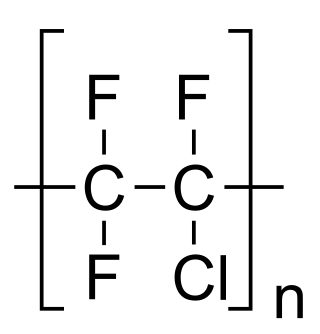
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE or PTFCE) is a thermoplastic chlorofluoropolymer with the molecular formula (CF2CClF)n, where n is the number of monomer units in the polymer molecule. It is similar to polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE), except that it is a homopolymer of the monomer chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE) instead of tetrafluoroethene. It has the lowest water vapor transmission rate of any plastic.

Rolling resistance, sometimes called rolling friction or rolling drag, is the force resisting the motion when a body rolls on a surface. It is mainly caused by non-elastic effects; that is, not all the energy needed for deformation of the wheel, roadbed, etc., is recovered when the pressure is removed. Two forms of this are hysteresis losses, and permanent (plastic) deformation of the object or the surface. Note that the slippage between the wheel and the surface also results in energy dissipation. Although some researchers have included this term in rolling resistance, some suggest that this dissipation term should be treated separately from rolling resistance because it is due to the applied torque to the wheel and the resultant slip between the wheel and ground, which is called slip loss or slip resistance. In addition, only the so-called slip resistance involves friction, therefore the name "rolling friction" is to an extent a misnomer.
A hermetic seal is any type of sealing that makes a given object airtight. The term originally applied to airtight glass containers, but as technology advanced it applied to a larger category of materials, including rubber and plastics. Hermetic seals are essential to the correct and safe functionality of many electronic and healthcare products. Used technically, it is stated in conjunction with a specific test method and conditions of use. Colloquially, the exact requirements of such a seal varies with the application.
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene is a subset of the thermoplastic polyethylene. Also known as high-modulus polyethylene (HMPE), it has extremely long chains, with a molecular mass usually between 3.5 and 7.5 million amu. The longer chain serves to transfer load more effectively to the polymer backbone by strengthening intermolecular interactions. This results in a very tough material, with the highest impact strength of any thermoplastic presently made.

Engineering plastics are a group of plastic materials that have better mechanical or thermal properties than the more widely used commodity plastics.

Heat-shrink tubing is a shrinkable plastic tube used to insulate wires, providing abrasion resistance and environmental protection for stranded and solid wire conductors, connections, joints and terminals in electrical wiring. It can also be used to repair the insulation on wires or to bundle them together, to protect wires or small parts from minor abrasion, and to create cable entry seals, offering environmental sealing protection. Heat-shrink tubing is ordinarily made of polyolefin, which shrinks radially when heated, to between one-half and one-sixth of its diameter.

Vespel is the trademark of a range of durable high-performance polyimide-based plastics made by DuPont.

Filler materials are particles added to resin or binders that can improve specific properties, make the product cheaper, or a mixture of both. The two largest segments for filler material use is elastomers and plastics. Worldwide, more than 53 million tons of fillers are used every year in application areas such as paper, plastics, rubber, paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants. As such, fillers, produced by more than 700 companies, rank among the world's major raw materials and are contained in a variety of goods for daily consumer needs. The top filler materials used are ground calcium carbonate (GCC), precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), kaolin, talc, and carbon black. Filler materials can affect the tensile strength, toughness, heat resistance, color, clarity, etc. A good example of this is the addition of talc to polypropylene. Most of the filler materials used in plastics are mineral or glass based filler materials. Particulates and fibers are the main subgroups of filler materials. Particulates are small particles of filler that are mixed in the matrix where size and aspect ratio are important. Fibers are small circular strands that can be very long and have very high aspect ratios.
Dry lubricants or solid lubricants are materials that, despite being in the solid phase, are able to reduce friction between two surfaces sliding against each other without the need for a liquid oil medium.
Anti-scratch coating is a type of protective coating or film applied to an object's surface for mitigation against scratches. Scratches are small surface-level cuts left on a surface following interaction with a sharper object. Anti-scratch coatings provide scratch resistances by containing tiny microscopic materials with scratch-resistant properties. Scratch resistance materials come in the form of additives, filters, and binders. Besides materials, scratch resistances is impacted by coating formation techniques. Scratch resistance is measured using the Scratch-hardness test. Commercially, anti-scratch coatings are used in the automotive, optical, photographic, and electronics industries, where resale and/or functionality is impaired by scratches. Anti-scratch coatings are of growing importance as traditional scratch resistance materials like metals and glass are replaced with low-scratch resistant plastics.
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is any of a class of polyurethane plastics with many properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease, and abrasion. Technically, they are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of linear segmented block copolymers composed of hard and soft segments.
Novel polymeric alloy (NPA) is a polymeric alloy composed of polyolefin and thermoplastic engineering polymer with enhanced engineering properties. NPA was developed for use in geosynthetics. One of the first commercial NPA applications was in the manufacturer of polymeric strips used to form Neoloy® cellular confinement systems (geocells).
IPX 2000 Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene is an engineered polyethylene compound developed to maintain many traits of UHMW, while increasing abrasion resistance, UV stability and decreasing friction and thermal expansion. IPX UHMW was developed in the early 2000s by material scientists at Interstate Plastics in Sacramento, CA and was first brought to market in 2005 by Interstate Plastics, under the trademark IPX. The acronym IPX-UHMW-PE stands for Interstate Plastics eXtra ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene.
A composite bearing is a bearing made from a combination of materials such as a resin reinforced with fibre and this may also include friction reducing lubricants and ingredients.
References
- 1 2 3 "Rulon". San Diego Plastics, Inc. Retrieved 2008-01-23..
- 1 2 "High Performance Fluoropolymer Materials" (PDF). Saint-Gobain Performance Plastics Corporation. 2005. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-10-15. Retrieved 2010-10-11.
- ↑ "Rulon AR". Saint-Gobain Performance Plastics Corporation. Archived from the original on 2010-05-29. Retrieved 2010-10-11.