Related Research Articles

Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the Krishna River surrounded by the hills of the Eastern Ghats, known as the Indrakeeladri Hills. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Kanaka Durga Temple. It geographically lies on the center spot of Andhra Pradesh. The city has been described as the commercial, political, cultural and educational capital of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of NTR district. The Prakasam Barrage across the Krishna River connects the NTR and Guntur districts.

Coastal Andhra or Kosta Andhra is a geographic region in the States and union territories of India of Andhra Pradesh. Vijayawada is the largest city in this region. Region share borders with Uttarandhra, Rayalaseema and Telangana. It was part of Madras State before 1953 and Andhra State from 1953 to 1956. According to the 2011 census, it has an area of 91,915 square kilometres (35,489 sq mi) which is 57.99% of the total state area and a population of 34,193,868 which is 69.20% of Andhra Pradesh state population. This area includes the coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh on the Circar Coast between the Eastern Ghats and the Bay of Bengal, from the northern border with Odisha to Rayalaseema in the south.

The West Godavari district is a coastal district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh with an administrative headquarters in Bhimavaram. As of the 2011 Census of India, the district has an area of 2,178 km2 (841 sq mi) and a population of 1,779,935. It is bounded by the Krishna district and Bay of Bengal to the south, East Godavari district to the east, and Eluru district, Kolleru Lake and Upputeru Drain to the northwest.

General Sir Arthur Thomas Cotton was a British army officer and irrigation engineer who worked in the Madras Presidency.

Nizam Sagar Dam is an Indian dam named after the Nizam of Hyderabad. It is a reservoir constructed across the Manjira River, a tributary of the Godavari River, between Achampet and BanjePally villages of the Kamareddy district in Telangana, India. It is located at about 144 km (89 mi) north-west of Hyderabad. Nizam Sagar is the oldest dam in the state of Telangana.

Prakasamdistrict is one of the twelve districts in the coastal Andhra region of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It was formed in 1970 and reorganised on 4 April 2022. The headquarters of the district is Ongole. It is located on the western shore of Bay of Bengal and is bounded by Bapatla district and Palnadu districts in the north, Nandyal district in the west, Kadapa and Nellore districts in the south. A part of north west region also borders with Nagarkurnool district of Telangana. It is the largest district in the state with an area of 14,322 km2 (5,530 sq mi) and had a population of 22,88,026 as per 2011 Census of India.
Budameru is a rivulet in Krishna district which originates in the hills surrounding Mylavaram and empties itself into Kolleru Lake. Budameru is also known as The Sorrow of Vijayawada. In order to control the floods, the river was dammed at Velagaleru village and a diversion channel named, Budameru Diversion Channel (BDC) was constructed from Velagaleru to join Krishna River upstream of Prakasam Barrage.

River Vamsadhara or River Banshadhara is an important east flowing river between Rushikulya and Godavari, in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh states in India.

The Prakasam Barrage stretches 1223.5 m across the Krishna River connecting Vijayawada, NTR and Mangalagiri Tadepalle Municipal Corporation, Guntur districts in Andhra Pradesh, India. The barrage serves also as a road bridge and spans over a lake. The three canals associated with the barrage run through the city of Vijayawada, crossing it and giving it a Venetian appearance.
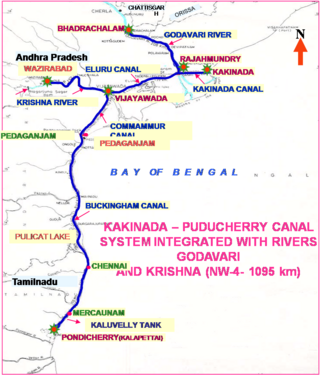
National Waterway 4 (NW-4) is a 1,095 kilometres (680 mi) long waterway in India. It has been declared as an Indian National Waterway and is currently under development. It connects the Indian states of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and the union territory of Puducherry. The NW-4 runs along the Coromandal Coast through Kakinada, Eluru, Commanur, Buckingham Canals and also through part of Krishna and Godavari rivers in South India. It was declared a National Waterway on 24 November 2008 under the Provisions of National Waterways Bill, 2006. It is being developed by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), and was scheduled for completion by 2013. The National Waterways Act, 2016 has extended the length of NW-4 from 1,095 km (680 mi) to 2,890 km (1,800 mi) by connecting the Krishna and Godavari Rivers. The Project would be undertaken in 3 phases with first phase beginning in October, 2017 and to be completed by June, 2019

The Polavaram Project is an under construction multi-purpose irrigation project on the Godavari River in the Eluru District and East Godavari District in Andhra Pradesh. The project has been accorded National project status by the Central Government of India. Its reservoir back water spreads up to the Dummugudem Anicut and approx 115 km on Sabari River side. Thus back water spreads into parts of Chhattisgarh and Odisha States. It gives major boost to tourism sector in Godavari Districts as the reservoir covers the famous Papikonda National Park, Polavaram hydro electric project (HEP) and National Waterway 4 are under construction on left side of the river. It is located 40 km to the upstream of Sir Arthur Cotton Barrage in Rajamahendravaram City and 25 km from Rajahmundry Airport.
The Pulichintala Project is a multi-purpose water management project for irrigation, hydropower generation, and flood control in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. It is a crucial irrigation facility for farmers in four coastal districts: West Godavari, Krishna, Guntur, Palanadu, and Prakasam, covering over 13 lakh acres. It has 24 gates and a balancing reservoir with a capacity of 46 Tmcft at 175 feet (53 m) MSL full reservoir level (FRL).

Rajiv Dummugudem Lift Irrigation Scheme is a lift irrigation scheme under execution which are located near Dummugudem, Khammam district in Telangana, India. There are three lift irrigation schemes by names Rajiv Dummugudem lift irrigation scheme, Indirasagar Rudrammakota Dummugudem lift irrigation scheme and Dummugudem to Sagar tail pond canal project. Rajiv Dummugudem lift irrigation scheme starting at 17°54′05″N80°52′45″E is planned to supply irrigation water for 200,000 acres in Khammam and Warangal districts drawing Godavari River water from the Dummugudem pond. Indira Dummugudem lift irrigation scheme starting at 17°33′49″N81°14′49″E is planned to supply irrigation water for 200,000 acres in Khammam, Krishna and West Godavari districts drawing Godavari River water from the back waters of Polavaram reservoir.

The Tungabhadra Dam, also known as Pampa Sagar, is a water reservoir constructed across the Tungabhadra River in the city of Hosapete in Vijayanagara district, Karnataka, India. It is a multipurpose dam serving irrigation, electricity generation, flood control, etc. for the state. It is one of the only two non-cement dams in India, the other being the Mullaperiyar Dam in Kerala. The dam is built of surki mortar, a combination of mud and limestone, commonly used at the time of its construction.

The Duvvada–Vijayawada section is a railway line connecting Duvvada in the city of Visakhapatnam and Vijayawada, both in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. The main line is part of the Howrah–Chennai main line. The track from Duvvada to Thadi is under the administrative jurisdiction of East Coast Railway zone, and the rest of the line from Anakapalle to Vijayawada is under the administrative jurisdiction of South Central Railway zone.
Kalingarayan Anicut is a barrage on the Bhavani river in Erode district, Tamil Nadu. It is located before Kooduthurai where Bhavani meets with Kaveri in Bhavani, Erode.
Pattiseema Lift Irrigation Project is a river interlinking project which connects Godavari River to Krishna River. This project has thereby become the first of such irrigation type projects in the country to be completed in time without any budget enhancements. It also holds a record in Limca Book of Records. The project was Inaugurated by the Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh Nara Chandrababu Naidu in March 2016 while the project was completed in one year record of time.
Vykuntapuram Barrage is an Indian barrage and water storage project. It is under construction on Krishna River 23 kilometers upstream of existing Prakasam Barrage with FRL 25M. It is designed to store 10 TMC of flood water coming from the Vyra and Munneru rivers. The backwater of this dam will extend beyond Pokkunuru to the toe of Pulichintala dam. Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister Nara chandrababu Naidu laid the foundation stone for this project on 13 February 2019.
Jogulamba Barrage is a proposed barrage across Krishna River with full pond level (FPL) 274m. It would be located at Veltoor village, Peddamandadi mandal, Wanaparthy district, Telangana, India. This barrage is proposed to divert 3 TMC of water via lift to Yedula Reservoir being built as part of Palamuru-Rangareddy Lift Irrigation Scheme. This would also provide water for Dindi Lift Irrigation Project and Mahatma Gandhi Kalwakurthy Lift Irrigation Scheme.
References
- ↑ "Veerapandian discusses canals beautification with GIIC team". The Hindu. 25 March 2016. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- 1 2 A Manual of the Kistna District, in the Presidency of Madras: Compiled for the Government of Madras. Lawrence Asylum Press. 1883. p. 262. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- ↑ "Vijayawada Through the ages" . Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- ↑ "PRAKASAM BARRAGE". irrigationap.cgg.gov.in. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- ↑ "Page 154 - LIST OF INSCRIPTIONS ON TOMBS OR MONUMENTS IN MADRAS VOLUME I". www.e-books-chennaimuseum.tn.gov.in. Retrieved 9 September 2016.