Related Research Articles
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to various fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 14th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Freemasonry is the oldest fraternity in the world and among the oldest continued organizations in history.

The Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite of Freemasonry is a rite within the broader context of Freemasonry. It is the most widely practiced Rite in the world. In some parts of the world, and in the Droit Humain, it is a concordant body and oversees all degrees from the 1st to 33rd degrees, while in other areas, a Supreme Council oversees the 4th to 33rd degrees.

A Masonic lodge, also called a private lodge or constituent lodge, is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry.
In Anglo-American Freemasonry, York Rite, sometimes referred to as the American Rite, is one of several Rites of Freemasonry. It is named after York, in Yorkshire, England; where the legend of the Rite, was first practiced.
The history of Freemasonry encompasses the origins, evolution and defining events of the fraternal organisation known as Freemasonry. It covers three phases. Firstly, the emergence of organised lodges of operative masons during the Middle Ages, then the admission of lay members as "accepted" or "speculative" masons, and finally the evolution of purely speculative lodges, and the emergence of Grand Lodges to govern them. The watershed in this process is generally taken to be the formation of the first Grand Lodge in London in 1717. The two difficulties facing historians are the paucity of written material, even down to the 19th century, and the misinformation generated by masons and non-masons alike from the earliest years.
Hundreds of conspiracy theories about Freemasonry have been described since the late 18th century. Usually, these theories fall into three distinct categories: political, religious, and cultural. Many conspiracy theories have connected the Freemasons with worship of the devil; these ideas are based on different interpretations of the doctrines of those organizations.
A Grand Lodge, also called Grand Orient or by another similar title, is the overarching governing body of a fraternal or other similarly organized group in a given area, usually a city, state, or country.
Anti-Masonry is "avowed opposition to Freemasonry", which has led to multiple forms of religious discrimination, violent persecution, and suppression in some countries as well as in various organized religions. However, there is no homogeneous anti-Masonic movement. Anti-Masonry consists of radically differing criticisms from frequently incompatible political institutions and organized religions that oppose each other, and are hostile to Freemasonry in some form.

The House of the Temple is a Masonic temple in Washington, D.C., United States, that serves as the headquarters of the Scottish Rite of Freemasonry, Southern Jurisdiction, U.S.A.

The Royal Order of Scotland is an appendant order within the structures of Freemasonry. Membership is an honour extended to Freemasons by invitation. The Grand Lodge of the Royal Order of Scotland is headquartered in Edinburgh, with a total of 88 subordinate Provincial Grand Lodges; of these, the greatest concentration is in the British Isles, with the rest located in countries around the world.
While many Christian denominations either allow or take no stance on their members joining Freemasonry, others discourage or prohibit their members from joining the fraternity.

The Knights Templar, full name The United Religious, Military and Masonic Orders of the Temple and of St John of Jerusalem, Israel, Rhodes and Malta, is a fraternal order affiliated with Freemasonry. Unlike the initial degrees conferred in a regular Masonic Lodge, which only require a belief in a Supreme Being regardless of religious affiliation, the Knights Templar is one of several additional Masonic Orders in which membership is open only to Freemasons who profess a belief in Christianity. One of the obligations entrants to the order are required to declare is to protect and defend the Christian faith. The word "United" in its full title indicates that more than one historical tradition and more than one actual order are jointly controlled within this system. The individual orders 'united' within this system are principally the Knights of the Temple, the Knights of Malta, the Knights of St Paul, and only within the York Rite, the Knights of the Red Cross.
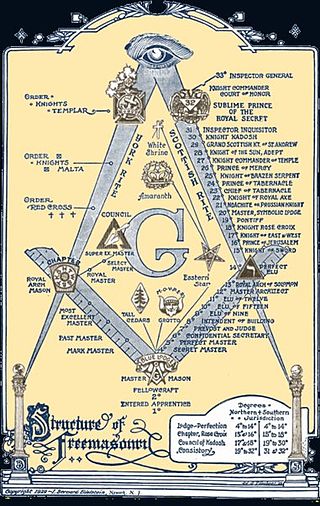
There are many organisations and orders which form part of the widespread fraternity of Freemasonry, each having its own structure and terminology. Collectively these may be referred to as Masonic bodies, Masonic orders, Concordant bodies or appendant bodies of Freemasonry.

Freemasonry has had a complex relationship with women for centuries. A few women were involved in Freemasonry before the 18th century, despite de jure prohibitions in the Premier Grand Lodge of England.
Christopher L. Hodapp is an American author and filmmaker, noted for his writings about Freemasonry, fraternalism, the Knights Templar, secret societies and conspiracy theories. He is the founding editor in chief of the Journal of The Masonic Society, the associate director of the Masonic Library and Museum of Indiana, and Public Relations Director for the Grand Lodge F&AM of Indiana.
The Philalethes Society is a Masonic research society based in North America. The society was founded on October 1, 1928, by a group of Masonic authors led by Cyrus Field Willard. Willard was a former reporter for the Boston Globe and the founder of a utopian commune on Puget Sound. Philalethes was designed to serve the needs of those in search of deeper insight into the history, rituals and symbolism of Freemasonry.

The Grand Lodge of Free & Accepted Masons of Indiana is one of two statewide organizations that oversee Masonic lodges in the state of Indiana. It was established on January 13, 1818. In 2016 the number of Freemasons in the Grand Lodge of Indiana was 55,553 amongst its 394 separate lodges, currently making it the sixth largest Masonic jurisdiction in the U.S. The Grand Lodge of Indiana's offices and archives are located in the Indianapolis Masonic Temple. The historically black Most Worshipful Prince Hall Grand Lodge of Indiana F&AM is the second regular Masonic grand lodge in the state, and it was originally established in 1856 as the Independent Union Grand Lodge of Free and Accepted Masons of the State of Indiana. The two grand lodges agreed to mutual recognition in May 1998, and they jointly share sovereignty over the Masonic fraternity in Indiana.

Masonic ritual is the scripted words and actions that are spoken or performed during the degree work in a Masonic lodge. Masonic symbolism is that which is used to illustrate the principles which Freemasonry espouses. Masonic ritual has appeared in a number of contexts within literature including in "The Man Who Would Be King", by Rudyard Kipling, and War and Peace, by Leo Tolstoy.
The history of Freemasonry in Mexico can be traced to at least 1806 when the first Masonic lodge was formally established in the nation.
References
- ↑ The Complete Idiot's Guide to Freemasonry, Penguin Books
- ↑ "Dr. S. Brent Morris". www.usasciencefestival.org. Archived from the original on 2015-02-05.
- ↑ "Nifty Fifty". Archived from the original on 2010-05-24. Retrieved 2010-05-17. retrieved 2010-16-05
- ↑ Press Release from Pietre-Stones Review of Freemasonry
- ↑ S. Brent Morris' CV
- ↑ S. Brent Morris at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- ↑ Reviews of Magic Tricks, Card Shuffling and Dynamic Computer Memories:
- Steve Abbott, The Mathematical Gazette, doi : 10.2307/3621515, JSTOR 3621515
- H. Don Allen, The Mathematics Teacher, JSTOR 27970723
- James Lawrence, "A Book for the Mathemagician", Math Horizons, JSTOR 25678459
- Miroslav Lovrić, Zbl 0902.00004
- ↑ Reviews of Freemasonry on Both Sides of the Atlantic:
- Bruce Chabot, Journal of Social History, JSTOR 3790101
- Jeanne Halgren Kilde, The Journal of American History, doi : 10.2307/3660896, JSTOR 3660896
- Michael Bradley McCoy, Pennsylvania History: A Journal of Mid-Atlantic Studies, JSTOR 27778629
- Andrew Prescott, The Slavonic and East European Review, JSTOR 4214189
- Mark C. Wallace, The Scottish Historical Review, JSTOR 25529814
- ↑ Review of American Masonic Periodicals: The Papers of the Bibliographical Society of America, JSTOR 24295633
- ↑ Review of International Masonic Periodicals: The Papers of the Bibliographical Society of America, JSTOR 24293963
- ↑ Review of Why Thirty-Three?: Shawn Eyer, Philalethes,