
Nuremberg Airport, German: Albrecht Dürer Flughafen Nürnberg, is the international airport of the Franconian metropolitan area of Nuremberg and the second-busiest airport in Bavaria after Munich Airport. The year 2018, with 4.5 million, was the year with the highest passenger volume to date at this airport. It is Germany's 9th busiest airport in 2022. It is located approximately 5 km north of Nuremberg's city centre and offers flights within Germany as well as to European metropolitan and leisure destinations, especially along the Mediterranean Sea, on the Canary Islands and in Egypt.

Nürnberg Hauptbahnhof or Nuremberg Central Station is the main railway station serving the city of Nuremberg in Germany. It is the largest station in north Bavaria and belongs to the 20 stations in the highest category of importance allocated by DB Station&Service.

The Nuremberg S-Bahn is an S-Bahn network covering the region of Nuremberg, Fürth and Erlangen which started operations in 1987 and is now integrated into the Greater Nuremberg Transport Association. The full length of the five current lines is about 277.6 kilometres.

The Nuremberg–Ingolstadt high-speed railway is a 78-kilometre-long (48 mi) high-speed railway running between the cities of Nuremberg and Ingolstadt in Bavaria, Germany. It branches off the Nuremberg–Regensburg railway and runs parallel to the A9 Autobahn to Ingolstadt, where it joins the Munich–Treuchtlingen railway at Ingolstadt Nord station.

The München-Nürnberg-Express is a RegionalExpress train service in the southern German state of Bavaria, connecting the two main cities of the state, Munich and Nuremberg. With its maximum speed of 200 km/h (125 mph), the train is currently the fastest regional train service in Germany. The train was formerly known under the project name FRESH, expanding to FRanken-Express über die Schnellfahrstrecke in die LandesHauptstadt.

Allersberg-Express was the brand name for the RegionalBahn train service between Nuremberg and Allersberg in Bavaria in southern Germany, operated by Deutsche Bahn. It started operations on 10 December 2006 and is one of the few regional trains to run on a German high-speed line. The total journey time was about fifteen minutes; the train was subject to the fare structure of the Verkehrsverbund Großraum Nürnberg. The Allersberg-Express was also called the R9 Express on VGN network web site. With the December 2020 schedule change, the Allersberg Express was retitled S5 of the Nuremberg S-Bahn. It is now served with Alstom Coradia Continental trainsets.

Allersberg (Rothsee) is a railway station situated at km 25.4 of the Nuremberg–Ingolstadt high-speed railway.

Ingolstadt Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the Bavarian city of Ingolstadt, situated in southern Germany. Ingolstadt station is an important junction in the Deutsche Bahn network. It has 7 platform tracks and is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 2 station.

The Nuremberg Transport Museum is based in Nuremberg, Germany, and consists of the Deutsche Bahn's own DB Museum and the Museum of Communications. It also has two satellite museums at Koblenz-Lützel and Halle. The Nuremberg Transport Museum is one of the oldest technical history museums in Europe.

Ansbach station is the central transportation hub in the town of Ansbach in southern Germany. It is here that two main lines cross: the Nürnberg–Crailsheim and Treuchtlingen–Würzburg railways.

The Nuremberg-Bamberg line is a German railway connecting the Bavarian city of Nuremberg with Bamberg via Fürth, Erlangen, Forchheim. It is part of the northern section of the Ludwig South-North Railway. It runs along the Regnitz Valley and is one of the important German transport routes. Since 2010 line S1 of the Nuremberg S-Bahn uses the entirety of the line from Nuremberg to Bamberg.

The Nuremberg–Würzburg Railway is a German trunk line railway in northern Bavaria, connecting the city of Nuremberg with Würzburg, the two largest cities in Franconia, and passing through Fürth, Neustadt an der Aisch and Kitzingen. In addition to hourly Regional-Express trains and numerous freight trains, it is served by Intercity-Express trains during the day at half-hourly intervals with some gaps.
The Nuremberg–Schwandorf railway is a 93.7 km long railway from Nuremberg, running along the Pegnitz river, to Hersbruck and continuing via Neukirchen bei Sulzbach-Rosenberg and Amberg to Schwandorf in the German state of Bavaria. It runs parallel to the Nuremberg–Cheb line between Nuremberg and Pommelsbrunn and this section is known as the Left Pegnitz line. It was opened in 1859 and is one of the oldest railways in Germany.
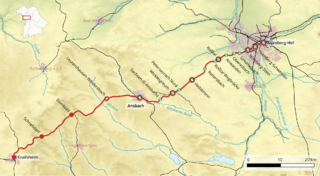
The Nuremberg–Crailsheim railway is a major railway in the north of the German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg, which links Nuremberg, Ansbach and Crailsheim. The line has the current timetable number of 891.7 and is an important German railway line. The Nuremberg–Ansbach section is used as an alternative route when problems occur for long-distance services between Nuremberg and Würzburg and Nuremberg and Treuchtlingen and to relieve the Nuremberg–Würzburg railway of some of its freight traffic.

The Schwandorf–Furth im Wald railway is a 67 km long mainline railway in the German state of Bavaria. It runs from Schwandorf via Cham to Furth im Wald. It is part of a long-distance connection between Germany and the Czech Republic.

National Express Germany is a railway operator in Germany. A subsidiary of Mobico Group, it commenced trading in December 2015.

The VAG Class DT3 is an electric multiple unit (EMU) train type operated by the Verkehrs-Aktiengesellschaft Nürnberg on the Nuremberg U-Bahn system. It is the first type of rolling stock on the Nuremberg U-Bahn that has gangways between the individual cars.

The VAG Class G1 is an electric multiple unit (EMU) train type operated by the Verkehrs-Aktiengesellschaft Nürnberg on the Nuremberg U-Bahn system. They are replacing the VAG Class DT1 and VAG Class DT2 currently in service on Nuremberg U-Bahn line U1. On 20 August 2020, the first of three G1 trains entered into the revenue service.


















