
Bristol County is a county in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. As of the 2020 census, the population was 579,200. The shire town is Taunton. Some governmental functions are performed by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, others by the county, and others by local towns and cities.

Dighton is a town in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 8,101 at the 2020 census. The town is located on the western shore of the Taunton River in the southeastern part of the state.

North Attleborough, alternatively spelled North Attleboro, is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 30,834 at the 2020 United States Census.

Rehoboth is a historic town in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1643, Rehoboth is one of the oldest towns in Massachusetts. The population was 12,502 at the 2020 census. Rehoboth is a mostly rural community with many historic sites, including 53 historic cemeteries.

Seekonk is a town in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States, on the Massachusetts border with Rhode Island. It was incorporated in 1812 from the western half of Rehoboth. The population was 15,531 at the 2020 census. In 1862, under a U.S. Supreme Court decision resolving a longstanding border dispute between Massachusetts and Rhode Island, a portion of Tiverton, Rhode Island was awarded to Massachusetts to become part of Fall River, while two-thirds of Seekonk was awarded to Rhode Island.

Swansea is a town in Bristol County in southeastern Massachusetts, United States. It is located at the mouth of the Taunton River, just west of Fall River, 47 miles (76 km) south of Boston, and 12 miles (19 km) southeast of Providence, Rhode Island. The population was 17,144 at the 2020 census. The villages of Hortonville, Barneyville and Ocean Grove are located in the town.

Taunton is a city and county seat of Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. Taunton is situated on the Taunton River, which winds its way through the city on its way to Mount Hope Bay, 10 miles (16 km) to the south. At the 2020 census, the city had a population of 59,408. Shaunna O'Connell is the mayor of Taunton.

Massachusetts's 4th congressional district is located mostly in southern Massachusetts. It is represented by Democrat Jake Auchincloss. Auchincloss was first elected in 2020.

The Greater Attleboro Taunton Regional Transit Authority (GATRA) oversees and coordinates public and medical transportation in the areas of Attleboro and Taunton, Massachusetts and 24 nearby areas. It operates daily fixed bus routes, commuter shuttle services and Dial-A-Ride services for seniors and persons with disabilities within communities in Bristol, Norfolk, and Plymouth counties. GATRA is based at the Bloom Bus Terminal in Taunton.
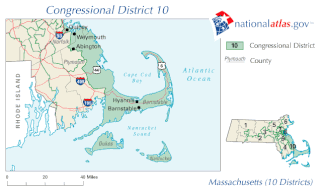
Massachusetts's 10th congressional district is an obsolete district that was active during 1795–2013. It was first located in the District of Maine during 1795–1803, then located in several different areas of Massachusetts. It was most recently eliminated in 2013 as district lines were redrawn to accommodate the loss of the seat due to reapportionment as a result of the 2010 census.

The South Coast of Massachusetts is the region of southeastern Massachusetts consisting of the southern part of Bristol and Plymouth counties, bordering Buzzards Bay, and includes the cities of Fall River, New Bedford, the southeastern tip of East Taunton and nearby towns. The Rhode Island towns of Tiverton and Little Compton, located in Newport County, are often included within the South Coast designation due to regional similarities with adjacent communities.
The Massachusetts Highway Department was the highway department in the U.S. state of Massachusetts from 1991 until the formation of the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) in 2009.
Seekonk High School is a public high school operated by Seekonk Public Schools in Seekonk, Massachusetts, United States. It serves the district's grade 9–12 student population. The school's mission statement is "All students will achieve their maximum potential by becoming responsible, productive citizens and life-long learners."

Norton is a town in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States, and contains the villages of Norton Center and Chartley. The population was 19,202 at the 2020 census. Home of Wheaton College, Norton hosted the Dell Technologies Championship, a tournament of the PGA Tour held annually on the Labor Day holiday weekend at the TPC Boston golf club until 2018.

Dighton-Rehoboth Regional High School is a high school in North Dighton, Massachusetts, United States. it is part of the Dighton-Rehoboth School District which also serves the neighboring town, Rehoboth, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1961.
The 155th Massachusetts General Court, consisting of the Massachusetts Senate and the Massachusetts House of Representatives, met from January 1, 1947, to June 18, 1948, during the governorship of Robert F. Bradford, in Boston.
The Southeastern Massachusetts Law Enforcement Council, sometimes called "SEMLEC," is a regional mutual aid facilitator formed by thirty police agencies in southeastern Massachusetts. It pools resources to provide SWAT, mobile operations, search and rescue, dive teams, color guards, and other units throughout the area.
Elections to the Massachusetts Senate were held on November 4, 1908, to elect 40 State Senators to the 130th Massachusetts General Court. Candidates were elected at the district level, with many districts covering multiple towns or counties.

The Old Colony Street Railway Company was a horse-drawn and electric streetcar railroad operated on the streets of Boston, Massachusetts and communities south of the city. Founded in 1881 as the Brockton Street Railway Company, via lease and merger it became a primary mass transit provider for southeastern Massachusetts and Rhode Island. Its immediate successor was the Bay State Street Railway, and its modern successor is the state-run Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA).














