Related Research Articles

The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) is an independent intergovernmental organisation supported by most of the nations of Europe. It is based at three sites: Shinfield Park, Reading, United Kingdom; Bologna, Italy; and Bonn, Germany. It operates one of the largest supercomputer complexes in Europe and the world's largest archive of numerical weather prediction data.

Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since the 19th century.

Aerobiology is a branch of biology that studies the passive transport of organic particles, such as bacteria, fungal spores, very small insects, pollen grains and viruses. Aerobiologists have traditionally been involved in the measurement and reporting of airborne pollen and fungal spores as a service to those with allergies. However, aerobiology is a varied field, relating to environmental science, plant science, meteorology, phenology, and climate change.

The Meteorological Office, abbreviated as the Met Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather and climate service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and is led by CEO Penelope Endersby, who took on the role as Chief Executive in December 2018 and is the first woman to do so. The Met Office makes meteorological predictions across all timescales from weather forecasts to climate change.
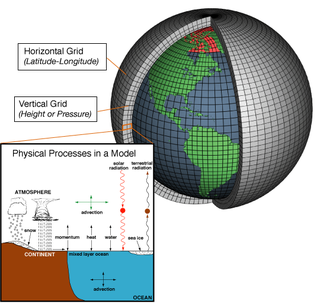
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs.

An air quality index (AQI) is an indicator developed by government agencies to communicate to the public how polluted the air currently is or how polluted it is forecast to become. As air pollution levels rise, so does the AQI, along with the associated public health risk. Children, the elderly and individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular problems are typically the first groups affected by poor air quality. When the AQI is high, governmental bodies generally encourage people to reduce physical activity outdoors, or even avoid going out altogether. When wildfires result in a high AQI, the use of a mask outdoors and an air purifier indoors are also encouraged.

The Finnish Meteorological Institute is the government agency responsible for gathering and reporting weather data and forecasts in Finland. It is a part of the Ministry of Transport and Communications but it operates semi-autonomously.

The Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute is the Dutch national weather forecasting service, which has its headquarters in De Bilt, in the province of Utrecht, central Netherlands.
The National Atmospheric Release Advisory Center (NARAC) is located at the University of California's Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. It is a national support and resource center for planning, real-time assessment, emergency response, and detailed studies of incidents involving a wide variety of hazards, including nuclear, radiological, chemical, biological, and natural emissions.
CALPUFF is an advanced, integrated Lagrangian puff modeling system for the simulation of atmospheric pollution dispersion distributed by the Atmospheric Studies Group at TRC Solutions.

The Czech Hydrometeorological Institute is the central state office of the Czech Republic in the fields of air quality, meteorology, climatology and hydrology. It is an organization established by the Ministry of the Environment of the Czech Republic. The head office and centralized workplaces of the CHMI, including the data processing, telecommunication and technical services, are located at the Institute's own campus in Prague.
TAMDAR is a weather monitoring system that consists of an in situ atmospheric sensor mounted on commercial aircraft for data gathering. It collects information similar to that collected by radiosondes carried aloft by weather balloons. It was developed by AirDat LLC, which was acquired by Panasonic Avionics Corporation in April 2013 and was operated until October 2018 under the name Panasonic Weather Solutions. It is now owned by FLYHT Aerospace Solutions Ltd.
Carmen Nicole Moelders is an American atmospheric scientist. Her work is mainly focused on hydrometeorology, mesoscale meteorology, cloud physics, land-atmosphere interaction, air pollution, wildfire modeling, and wind power modeling.
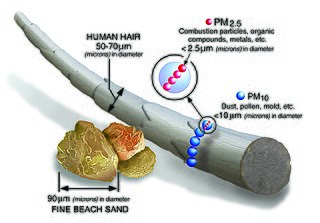
Particulates or atmospheric particulate matter are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The term aerosol commonly refers to the particulate/air mixture, as opposed to the particulate matter alone. Sources of particulate matter can be natural or anthropogenic. They have impacts on climate and precipitation that adversely affect human health, in ways additional to direct inhalation.

The history of numerical weather prediction considers how current weather conditions as input into mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather and future sea state has changed over the years. Though first attempted manually in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of the computer and computer simulation that computation time was reduced to less than the forecast period itself. ENIAC was used to create the first forecasts via computer in 1950, and over the years more powerful computers have been used to increase the size of initial datasets and use more complicated versions of the equations of motion. The development of global forecasting models led to the first climate models. The development of limited area (regional) models facilitated advances in forecasting the tracks of tropical cyclone as well as air quality in the 1970s and 1980s.
The Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory model (HYSPLIT) is a computer model that is used to compute air parcel trajectories to determine how far and in what direction a parcel of air, and subsequently air pollutants, will travel. HYSPLIT is also capable of calculating air pollutant dispersion, chemical transformation, and deposition. The HYSPLIT model was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Air Resources Laboratory and the Australian Bureau of Meteorology Research Centere in 1998. The model derives its name from the usage of both Lagrangian and Eulerian approaches.
Air pollution forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the composition of the air pollution in the atmosphere for a given location and time. An algorithm prediction of the pollutant concentrations can be translated into air quality index, same as actual measurements.
Silam or SILAM may refer to:
Particulate pollution is pollution of an environment that consists of particles suspended in some medium. There are three primary forms: atmospheric particulate matter, marine debris, and space debris. Some particles are released directly from a specific source, while others form in chemical reactions in the atmosphere. Particulate pollution can be derived from either natural sources or anthropogenic processes.
References
- ↑ Sofiev, M.; Siljamo, P.; Valkama, I.; Ilvonen, M.; Kukkonen, J. (February 2006). "A dispersion modelling system SILAM and its evaluation against ETEX data". Atmospheric Environment. 40 (4): 674–685. Bibcode:2006AtmEn..40..674S. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.09.069.
- ↑ "System for Integrated modeLling of Atmospheric coMposition". silam.fmi.fi.