
HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia.

Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph.

Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APOB gene. It is commonly used to detect risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
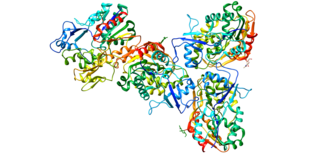
Lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase is an enzyme, in many animals including humans, that converts free cholesterol into cholesteryl ester, which is then sequestered into the core of a lipoprotein particle, eventually making the newly synthesized HDL spherical and forcing the reaction to become unidirectional since the particles are removed from the surface. The enzyme is bound to high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) (alpha-LCAT) and LDLs (beta-LCAT) in the blood plasma. LCAT deficiency can cause impaired vision due to cholesterol corneal opacities, anemia, and kidney damage. It belongs to the family of phospholipid:diacylglycerol acyltransferases.

Apolipoprotein C-IV, also known as apolipoprotein C4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APOC4 gene.

Lanosterol synthase (EC 5.4.99.7) is an oxidosqualene cyclase (OSC) enzyme that converts (S)-2,3-oxidosqualene to a protosterol cation and finally to lanosterol. Lanosterol is a key four-ringed intermediate in cholesterol biosynthesis. In humans, lanosterol synthase is encoded by the LSS gene.

Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, mitochondrial, also known as acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACAT1 gene.

Sterol regulatory element-binding protein cleavage-activating protein, also known as SREBP cleavage-activating protein or SCAP, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCAP gene.
Diglyceride acyltransferase, DGAT, catalyzes the formation of triglycerides from diacylglycerol and fatty acyl-CoA. The reaction catalyzed by DGAT is considered the terminal and only committed step in triglyceride synthesis. The conversion is essential for intestinal absorption and adipose tissue formation.
Sterol O-acyltransferase is an intracellular protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum that forms cholesteryl esters from cholesterol.

Apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide 1 also known as C->U-editing enzyme APOBEC-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APOBEC1 gene.

Sterol O-acyltransferase 1, also known as SOAT1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOAT1 gene.

Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACOT8 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA7 gene.

Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BAAT gene.

Very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SLC27A2 gene.

Bile acyl-CoA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SLC27A5 gene.

Apolipoprotein F is a protein that in humans is encoded for by the APOF gene. The product of this gene is one of the minor apolipoproteins found in plasma. This protein forms complexes with lipoproteins and may be involved in transport and/or esterification of cholesterol.

CYP8B1 also known as sterol 12-alpha-hydroxylase is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CYP8B1 gene.

Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, cytosolic, also known as cytosolic acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACAT2 gene


















