
Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol or polyphenol and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts.

Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively.
Calorie restriction mimetics (CRM), also known as energy restriction mimetics, are a hypothetical class of dietary supplements or drug candidates that would, in principle, mimic the substantial anti-aging effects that calorie restriction (CR) has on many laboratory animals and humans. CR is defined as a reduction in calorie intake of 20% to 50% without incurring malnutrition or a reduction in essential nutrients. An effective CRM would alter the key metabolic pathways involved in the effects of CR itself, leading to preserved youthful health and longer lifespan without the need to reduce food intake. The term was coined by Lane, Ingram, Roth of the National Institute on Aging in a seminal 1998 paper in the Journal of Anti-Aging Medicine, the forerunner of Rejuvenation Research. A number of genes and pathways have been shown to be involved with the actions of CR in model organisms and these represent attractive targets for drug discovery and for developing CRM. However, no effective CRM have been identified to date.
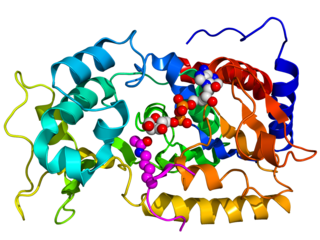
Sirtuins are a family of signaling proteins involved in metabolic regulation. They are ancient in animal evolution and appear to possess a highly conserved structure throughout all kingdoms of life. Chemically, sirtuins are a class of proteins that possess either mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase or deacylase activity, including deacetylase, desuccinylase, demalonylase, demyristoylase and depalmitoylase activity. The name Sir2 comes from the yeast gene 'silent mating-type information regulation 2', the gene responsible for cellular regulation in yeast.
Leonard Pershing Guarente is an American biologist best known for his research on life span extension in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, roundworms, and mice. He is a Novartis Professor of Biology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.

David Andrew Sinclair is an Australian-American biologist and academic known for his research and controversial claims on aging and epigenetics. Sinclair is a tenured professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School.

Ursolic acid, is a pentacyclic triterpenoid identified in the epicuticular waxes of apples as early as 1920 and widely found in the peels of fruits, as well as in herbs and spices like rosemary and thyme.

Free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFAR2), also known as G-protein coupled receptor 43 (GPR43), is a rhodopsin-like G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) encoded by the FFAR2 gene. In humans, the FFAR2 gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 19 at position 13.12 (19q13.12).

Sirtuin 1, also known as NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIRT1 gene.

Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) is a protein that in mammals is encoded by the FGF21 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family and specifically a member of the endocrine subfamily which includes FGF23 and FGF15/19. FGF21 is the primary endogenous agonist of the FGF21 receptor, which is composed of the co-receptors FGF receptor 1 and β-Klotho.
Sirtris Pharmaceuticals, Inc. was a biotechnology company based in Cambridge, MA that developed therapies for type 2 diabetes, cancer, and other diseases. Conceived in 2004 by Harvard University biologist David Sinclair and Andrew Perlman, and founded that year by Sinclair and Perlman, along with Christoph Westphal, Richard Aldrich, Richard Pops, and Paul Schimmel, the company was focused on developing Sinclair's research into activators of sirtuins, work that began in the laboratory of Leonard P. Guarente where Sinclair worked as a post-doc before starting his own lab.
Sirtuin-activating compounds (STAC) are chemical compounds having an effect on sirtuins, a group of enzymes that use NAD+ to remove acetyl groups from proteins. They are caloric restriction mimetic compounds that may be helpful in treating various aging-related diseases.
Christoph Westphal is an American biomedical businessman.
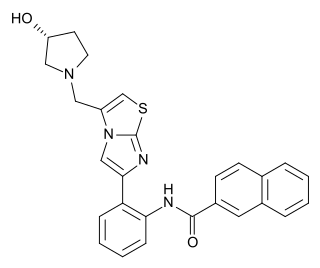
SRT-2183 is a drug in development by Sirtris Pharmaceuticals intended as a small-molecule activator of the sirtuin subtype SIRT1. It has similar activity in animal studies to another SIRT1 activator SRT-1720, but is closer in potency to resveratrol. In animal studies it was found to improve insulin sensitivity and lower plasma glucose levels in fat, muscle and liver tissue, and increased mitochondrial and metabolic function. However, the claim that SRT-2183 is a SIRT1 activator has been questioned and further defended.

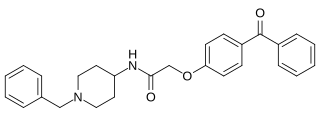
SRT-1460 is a drug in development by Sirtris Pharmaceuticals intended as a small-molecule activator of the sirtuin subtype SIRT1. It has similar activity in animal studies to the known SIRT1 activator resveratrol, but is closer in potency to SRT-1720. In animal studies it was found to improve insulin sensitivity and lower plasma glucose levels in fat, muscle and liver tissue, and increased mitochondrial and metabolic function. However, the claim that SRT1460 is a SIRT1 activator has been questioned and further defended.

MicroRNA 34a (miR-34a) is a microRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR34A gene.
AdipoRon is a selective, orally active, synthetic small-molecule agonist of the adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1) and adiponectin receptor 2 (AdipoR2). It activates AMPK and PPARα signaling and ameliorates insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and glucose intolerance in db/db mice. Moreover, AdipoRon has been found to extend the lifespans of db/db mice fed a high-fat diet, as well as improve exercise endurance. The compound was discovered by Japanese researchers in 2013 via screening of a compound library, and is the first orally active, small-molecule agonist of the adiponectin receptors to be identified.
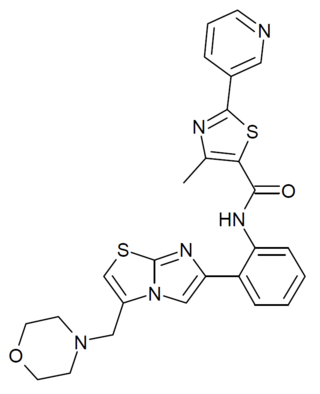
SRT-2104 is an experimental drug that was studied by Sirtris Pharmaceuticals as a small-molecule activator of the sirtuin subtype SIRT1. The compound progressed to Phase II human trials for Type II diabetes before development was discontinued, however it continues to be widely used in animal research into the functions of SIRT1.

SRT-3025 is an experimental drug that was studied by Sirtris Pharmaceuticals as a small-molecule activator of the sirtuin subtype SIRT1. It has been investigated as a potential treatment for osteoporosis, and anemia.

STAC-9 is an experimental drug that was developed by GlaxoSmithKline as a small-molecule activator of the sirtuin subtype SIRT1, with potential applications in the treatment of diabetes.















