SYMPL is an obsolete programming language developed by the Control Data Corporation (CDC) for use on the CDC 6000 series computer systems in the 1970s and 1980s. It was based on a subset of CDC's version of JOVIAL, as an alternative to assembly language. A number of important CDC software products were implemented in SYMPL, including compilers, libraries, a full-screen editor, and major subsystems.
SYMPL is a compiled, imperative, and procedural language. Compared to the Fortran of the day, SYMPL supports:
A distinct feature of SYMPL, also found in JOVIAL tables, is that arrays of multi-item variables can be specified with either a "serial" or "parallel" memory layout. A "serial" layout has array entries following one another in memory as is usual in most computer languages. A "parallel" layout groups each of the individual items within each of the array entries together. For example, if each array entry has items x, y, and z, a parallel layout would group x[0]...x[n] together in memory, followed by y[0]...y[n], and then z[0]...z[n]. This has the effect of potentially speeding up access to all the same items across the array - as they are all contiguous with one another.
Simplifications compared to JOVIAL include: no fixed point data type, no table structures, and no COMPOOL concept. Though in lieu of COMPOOLs, a CDC-specific system text capability allows encapsulation of common data declarations.
In computer science, an array is a data structure consisting of a collection of elements, of same memory size, each identified by at least one array index or key. An array is stored such that the position of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called one-dimensional array.
In computer science, an abstract data type (ADT) is a mathematical model for data types, defined by its behavior (semantics) from the point of view of a user of the data, specifically in terms of possible values, possible operations on data of this type, and the behavior of these operations. This mathematical model contrasts with data structures, which are concrete representations of data, and are the point of view of an implementer, not a user.
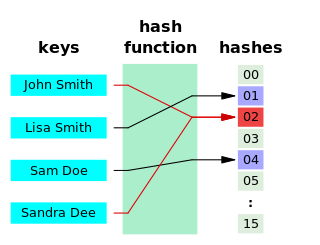
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values, though there are some hash functions that support variable length output. The values returned by a hash function are called hash values, hash codes, digests, or simply hashes. The values are usually used to index a fixed-size table called a hash table. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called hashing or scatter storage addressing.
Pascal is an imperative and procedural programming language, designed by Niklaus Wirth as a small, efficient language intended to encourage good programming practices using structured programming and data structuring. It is named after French mathematician, philosopher and physicist Blaise Pascal.

Lua is a lightweight, high-level, multi-paradigm programming language designed primarily for embedded use in applications. Lua is cross-platform, since the interpreter of compiled bytecode is written in ANSI C, and Lua has a relatively simple C API to embed it into applications.

In computer science and computer programming, a data type is a collection or grouping of data values, usually specified by a set of possible values, a set of allowed operations on these values, and/or a representation of these values as machine types. A data type specification in a program constrains the possible values that an expression, such as a variable or a function call, might take. On literal data, it tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data. Most programming languages support basic data types of integer numbers, floating-point numbers, characters and Booleans.
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a type to every term. Usually the terms are various language constructs of a computer program, such as variables, expressions, functions, or modules. A type system dictates the operations that can be performed on a term. For variables, the type system determines the allowed values of that term. Type systems formalize and enforce the otherwise implicit categories the programmer uses for algebraic data types, data structures, or other components.
JOVIAL is a high-level programming language based on ALGOL 58, specialized for developing embedded systems. It was a major system programming language through the 1960s and 1970s.

The syntax of the C programming language is the set of rules governing writing of software in the C language. It is designed to allow for programs that are extremely terse, have a close relationship with the resulting object code, and yet provide relatively high-level data abstraction. C was the first widely successful high-level language for portable operating-system development.
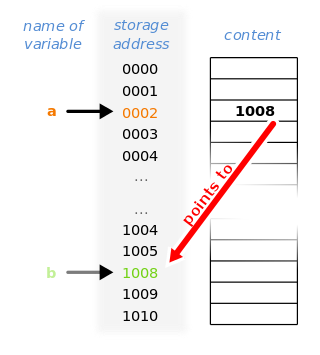
In computer science, a pointer is an object in many programming languages that stores a memory address. This can be that of another value located in computer memory, or in some cases, that of memory-mapped computer hardware. A pointer references a location in memory, and obtaining the value stored at that location is known as dereferencing the pointer. As an analogy, a page number in a book's index could be considered a pointer to the corresponding page; dereferencing such a pointer would be done by flipping to the page with the given page number and reading the text found on that page. The actual format and content of a pointer variable is dependent on the underlying computer architecture.
In computer science, a union is a value that may have any of several representations or formats within the same position in memory; that consists of a variable that may hold such a data structure. Some programming languages support special data types, called union types, to describe such values and variables. In other words, a union type definition will specify which of a number of permitted primitive types may be stored in its instances, e.g., "float or long integer". In contrast with a record, which could be defined to contain both a float and an integer; in a union, there is only one value at any given time.
In computer science, a record is a basic data structure. Records in a database or spreadsheet are usually called "rows".
In computing, aliasing describes a situation in which a data location in memory can be accessed through different symbolic names in the program. Thus, modifying the data through one name implicitly modifies the values associated with all aliased names, which may not be expected by the programmer. As a result, aliasing makes it particularly difficult to understand, analyze and optimize programs. Aliasing analysers intend to make and compute useful information for understanding aliasing in programs.

CMS-2 is an embedded systems programming language used by the United States Navy. It was an early attempt to develop a standardized high-level computer programming language intended to improve code portability and reusability. CMS-2 was developed primarily for the US Navy’s tactical data systems (NTDS).
The computer programming languages C and Pascal have similar times of origin, influences, and purposes. Both were used to design their own compilers early in their lifetimes. The original Pascal definition appeared in 1969 and a first compiler in 1970. The first version of C appeared in 1972.

In the C programming language, data types constitute the semantics and characteristics of storage of data elements. They are expressed in the language syntax in form of declarations for memory locations or variables. Data types also determine the types of operations or methods of processing of data elements.
Systems Programming Language, often shortened to SPL but sometimes known as SPL/3000, was a procedurally-oriented programming language written by Hewlett-Packard for the HP 3000 minicomputer line and first introduced in 1972. SPL was used to write the HP 3000's primary operating system, Multi-Programming Executive (MPE). Similar languages on other platforms were generically referred to as system programming languages, confusing matters.
In computer programming, a branch table or jump table is a method of transferring program control (branching) to another part of a program using a table of branch or jump instructions. It is a form of multiway branch. The branch table construction is commonly used when programming in assembly language but may also be generated by compilers, especially when implementing optimized switch statements whose values are densely packed together.
This comparison of programming languages (array) compares the features of array data structures or matrix processing for various computer programming languages.
In computer programming, a function or subroutine is a sequence of program instructions that performs a specific task, packaged as a unit. This unit can then be used in programs wherever that particular task should be performed.