A charge-coupled device (CCD) is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time. CCDs move charge between capacitive bins in the device, with the shift allowing for the transfer of charge between bins.

In digital imaging, a pixel, pel, or picture element is a physical point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable element in an all points addressable display device; so it is the smallest controllable element of a picture represented on the screen.

A thermographic camera is a device that forms a heat zone image using infrared radiation, similar to a common camera that forms an image using visible light. Instead of the 400–700 nanometre range of the visible light camera, infrared cameras operate in wavelengths as long as 14,000 nm (14 µm). Their use is called thermography.
LBCAST is a type of photo sensor which the manufacturer claims is simpler and thus smaller and faster than CMOS sensors. It was developed over ten years by Nikon, in parallel with other manufacturer's development of CMOS, and resulted in shipping product in 2003.
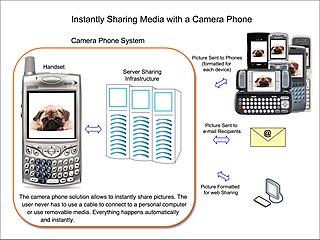
A camera phone is a mobile phone which is able to capture photographs and often record video using one or more built-in digital cameras. The first camera phone was sold in 2000 in Japan, a Sharp J-SH04 J-Phone model, although some argue that the SCH-V200 and Kyocera VP-210 Visual Phone, both introduced months earlier in South Korea and Japan respectively, are the first camera phones.

High-speed photography is the science of taking pictures of very fast phenomena. In 1948, the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) defined high-speed photography as any set of photographs captured by a camera capable of 69 frames per second or greater, and of at least three consecutive frames. High-speed photography can be considered to be the opposite of time-lapse photography.
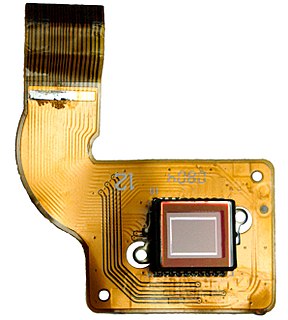
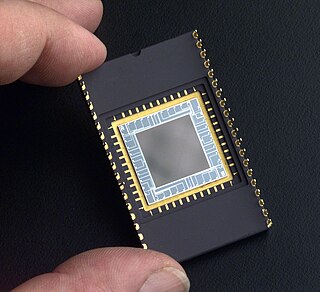
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, digital imaging tends to replace analog imaging.

In photography, a color filter array (CFA), or color filter mosaic (CFM), is a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the pixel sensors of an image sensor to capture color information.
OmniVision Technologies Inc. is a corporation that designs and develops advanced digital imaging technologies and products for use in mobile phones, notebooks, netbooks and webcams, security and surveillance cameras, entertainment, digital still and video cameras, automotive and medical imaging systems. Headquartered in Santa Clara, California, OmniVision Technologies has offices in the USA, Western Europe and Asia, including a design center and testing facility in Shanghai, China.

Note: If you came here to get a quick understanding of numbers like 1/2.3, skip ahead to table of sensor formats and sizes. For a simplified discussion of image sensors see image sensor.

Rolling shutter is a method of image capture in which a still picture or each frame of a video is captured not by taking a snapshot of the entire scene at a single instant in time but rather by scanning across the scene rapidly, either vertically or horizontally. In other words, not all parts of the image of the scene are recorded at exactly the same instant. This produces predictable distortions of fast-moving objects or rapid flashes of light. This is in contrast with "global shutter" in which the entire frame is captured at the same instant.
Canesta is a fabless semiconductor company that was founded in April, 1999, by Cyrus Bamji, Abbas Rafii, and Nazim Kareemi.

A back-illuminated sensor, also known as backside illumination sensor, is a type of digital image sensor that uses a novel arrangement of the imaging elements to increase the amount of light captured and thereby improve low-light performance.
Aptina Imaging Corporation was a company that sold CMOS imaging products. Their CMOS sensors were used in Nikon V1, Nikon J1, Nikon V2. By 2009 year Aptina had a 16% share of the CMOS image sensors market, with revenue estimated at $671 million. The company was acquired in 2014 by ON Semiconductor
Bedabrata Pain is an Indian scientist turned film director, producer and screenwriter. Bedabrata Pain was also a member of the team that invented the CMOS image sensor. Bedabrata Pain has also won National Film Award for Best Debut Film of a Director for Chittagong.
An oversampled binary image sensor is an image sensor with non-linear response capabilities reminiscent of traditional photographic film. Each pixel in the sensor has a binary response, giving only a one-bit quantized measurement of the local light intensity. The response function of the image sensor is non-linear and similar to a logarithmic function, which makes the sensor suitable for high dynamic range imaging.

The Photron FASTCAM ULTIMA 512 is a 512 × 512 high-speed camera. It is part of the Photron FASTCAM line of cameras. Photron FASTCAM ULTIMA 512 was introduced in 2001.

The Fujifilm X-Trans is a CMOS sensor developed by Fujifilm and used in its Fujifilm X-series cameras. Unlike most CMOS sensors featuring a conventional Bayer filter array, X-Trans sensors have a unique 6 by 6 pattern of photosites. Fujifilm claims that this layout can minimise moiré effects, and increase resolution by eliminating the need for a low-pass filter.




















