Related Research Articles

Iwo Jima, officially romanized and pronounced Iōtō, is one of the Japanese Volcano Islands, which lie south of the Bonin Islands and together with them make up the Ogasawara Archipelago. Together with the Izu Islands, they make up Japan's Nanpō Islands. Although 1,200 km (750 mi) south of Tokyo on Honshu, Iwo Jima is administered as part of the Ogasawara Subprefecture of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government.

A volcanologist, or volcano scientist, is a geologist who focuses on understanding the formation and eruptive activity of volcanoes. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, sometimes active ones, to observe and monitor volcanic eruptions, collect eruptive products including tephra, rock and lava samples. One major focus of inquiry in recent times is the prediction of eruptions to alleviate the impact on surrounding populations and monitor natural hazards associated with volcanic activity. Geologists who research volcanic materials that make up the solid Earth are referred to as igneous petrologists.

Nevado del Ruiz, also known as La Mesa de Herveo is a volcano on the border of the departments of Caldas and Tolima in Colombia, being the highest point of both. It is located about 130 km (81 mi) west of the capital city Bogotá. It is a stratovolcano composed of many layers of lava alternating with hardened volcanic ash and other pyroclastic rocks. Volcanic activity at Nevado del Ruiz began about two million years ago, during the Early Pleistocene or Late Pliocene, with three major eruptive periods. The current volcanic cone formed during the present eruptive period, which began 150,000 years ago.

Bezymianny is an active stratovolcano in Kamchatka, Russia. Bezymianny volcano had been considered extinct until 1955. Activity started in 1955, culminating in a dramatic eruption on 30 March 1956. This eruption, similar to that of 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens, produced a large horseshoe-shaped crater that was formed by collapse of the summit and an associated lateral blast. Subsequent episodic but ongoing lava dome growth, accompanied by intermittent explosive activity and pyroclastic flows, has largely filled the 1956 crater. The most recent eruption of lava flows occurred in February 2013. An explosive eruption on 20 December 2017 released an ash plume rising to a height of 15 kilometres (49,000 ft) above sea level, which drifted for 320 kilometres (200 mi) NE. The volcano erupted similarly on 28 May 2022, again spewing an ash plume over 15 kilometres (49,000 ft) high. On April 7, 2023, Russia reported Bezymianny had erupted explosively again and the Federal Agency for Air Transport, Rosaviatsiya, issued a Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) and raised the aviation Color Code Red. The eruption formed a column of ash that rose to a height of 12 kilometres (39,000 ft) and was drifting to the southeast slowly. The ash plume stretched out across a distance of 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi).

The Soufrière Hills is an active, complex stratovolcano with many lava domes forming its summit on the Caribbean island of Montserrat. After a long period of dormancy, the Soufrière Hills volcano became active in 1995 and continued to erupt through 2010. Its last eruption was in 2013. Its eruptions have rendered more than half of Montserrat uninhabitable, destroying the capital city, Plymouth, and causing widespread evacuations: about two-thirds of the population have left the island. Chances Peak in the Soufrière Hills was the highest summit on Montserrat until the mid-1990s, but it has since been eclipsed by various rising and falling volcanic domes during the recent volcanic activity.

Shiveluch, also called Sheveluch, which originates from the name "suelich" which means "smoking mountain" in Itelmen is the northernmost active volcano in Kamchatka Krai, Russia. It and Karymsky are Kamchatka's largest, most active and most continuously erupting volcanoes, as well as one of the most active on the planet. Shiveluch erupts around 0.015 km3 (0.0036 cu mi) of magma per year, which causes frequent and large hot avalanches and lava dome formations at the summit. Volcanic ash emissions from this volcano often disrupt air traffic connecting the Asian and North American continents.

Mount Rinjani is an active volcano in Indonesia on the island of Lombok. Administratively the mountain is in the Regency of North Lombok, West Nusa Tenggara. It rises to 3,726 metres (12,224 ft), making it the second highest volcano in Indonesia. It is also the highest point in the Indonesian province of West Nusa Tenggara. Adjacent to the volcano is a 6-by-8.5-kilometre caldera, which is filled partially by the crater lake known as Segara Anak or Anak Laut, due to the color of its water, as blue as the sea (laut). This lake is approximately 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) above sea level and estimated to be about 200 metres (660 ft) deep; the caldera also contains hot springs. The lake and mountain are sacred to the Sasak people and Hindus, and are the site of religious rituals. UNESCO made Mount Rinjani Caldera a part of the Global Geoparks Network in April 2018. Its catastrophic eruption in 1257 was the largest volcanic eruption in the last 2000 years.
The Decade Volcanoes are 16 volcanoes identified by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior (IAVCEI) as being worthy of particular study in light of their history of large, destructive eruptions and proximity to densely populated areas. The Decade Volcanoes project encourages studies and public-awareness activities at these volcanoes, with the aim of achieving a better understanding of the volcanoes and the dangers they present, and thus being able to reduce the severity of natural disasters.

Ulawun is a basaltic and andesitic stratovolcano in West New Britain Province, on the island of New Britain in Papua New Guinea.

Anak Krakatau is a volcanic island in Indonesia. On 29 December 1927, Anak Krakatau first emerged from the caldera formed in 1883 by the explosive volcanic eruption that destroyed the island of Krakatoa. There has been sporadic eruptive activity at the site since the late 20th century, culminating in a large underwater collapse of the volcano, which caused a deadly tsunami in December 2018. There has been subsequent activity since. Owing to its young age the island is one of several in the area that are of interest to, and the subject of extensive study by volcanologists.

Babuyan Claro Volcano, also known as Mount Pangasun, is an active volcano located on Babuyan Island, the northernmost of the Babuyan group of islands in Luzon Strait, north of the main island of Luzon in the Philippines. It is classified as one of the active volcanoes of the country with the last confirmed eruption in 1860.

The Smithsonian Institution's Global Volcanism Program (GVP) documents Earth's volcanoes and their eruptive history during the Quaternary Period of Earth's geologic history, with particular emphasis on volcanic activity during the Holocene Epoch. The mission of the GVP is to document, understand, and disseminate information about global volcanic activity.
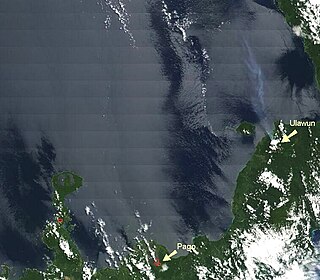
The volcano Pago is located East of Kimbe, West New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea. Pago is a young post-caldera cone within the Witori Caldera. The Buru Caldera cuts the SW flank of the Witori volcano. Biggest eruptions were at 4000±200 BC, VEI 6, 10 cubic kilometres (2.5 mi.3); 1370±100 BC, VEI6, 30 km3 (7 mi.3); and 710±75 AD, VEI 6, 20 km3 (5 mi.3) of tephra.

Mount Agung, a volcano on the island of Bali in Indonesia, erupted five times in late November 2017, causing thousands to evacuate, disrupting air travel and causing environmental damage. As of 27 November 2017, the alert level was at its highest and evacuation orders were in place.

Janine Krippner is a physical volcanologist from New Zealand who uses remote sensing to study pyroclastic flows and is a popular science communicator.
References
- ↑ "Sally Kuhn Sennert – Mineral Sciences". mineralsciences.si.edu. Retrieved 2018-08-16.
- 1 2 "Ask Sally Kuhn Sennert (Global Volcanism Program) your questions!". WIRED. Retrieved 2018-08-16.
- 1 2 3 Sennert, Sally. "Sally Susan Kuhn Sennert Curriculum vitae" (PDF). National Museum of Natural History.
- ↑ Sennert, Sally. "Sally Kuhn Sennert". LinkedIn.
- ↑ Klemetti, Erik. "GVP's Sally Kuhn Sennert answers your questions!". Big Think. Retrieved 2018-08-16.