A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern.

The Santa Ana River is the largest river entirely within Southern California in the United States. It rises in the San Bernardino Mountains and flows for most of its length through San Bernardino and Riverside counties, before cutting through the northern Santa Ana Mountains via Santa Ana Canyon and flowing southwest through urban Orange County to drain into the Pacific Ocean. The Santa Ana River is 96 miles (154 km) long, and its drainage basin is 2,650 square miles (6,900 km2) in size.
Streamflow, or channel runoff, is the flow of water in streams and other channels, and is a major element of the water cycle. It is one runoff component, the movement of water from the land to waterbodies, the other component being surface runoff. Water flowing in channels comes from surface runoff from adjacent hillslopes, from groundwater flow out of the ground, and from water discharged from pipes. The discharge of water flowing in a channel is measured using stream gauges or can be estimated by the Manning equation. The record of flow over time is called a hydrograph. Flooding occurs when the volume of water exceeds the capacity of the channel.

The Klamath Basin is the region in the U.S. states of Oregon and California drained by the Klamath River. It contains most of Klamath County and parts of Lake and Jackson counties in Oregon, and parts of Del Norte, Humboldt, Modoc, Siskiyou, and Trinity counties in California. The 15,751-square-mile (40,790 km2) drainage basin is 35% in Oregon and 65% in California. In Oregon, the watershed typically lies east of the Cascade Range, while California contains most of the river's segment that passes through the mountains. In the Oregon-far northern California segment of the river, the watershed is semi-desert at lower elevations and dry alpine in the upper elevations. In the western part of the basin, in California, however, the climate is more of temperate rainforest, and the Trinity River watershed consists of a more typical alpine climate.

San Juan Creek, also called the San Juan River, is a 29-mile (47 km) long stream in Orange and Riverside Counties, draining a watershed of 133.9 square miles (347 km2). Its mainstem begins in the southern Santa Ana Mountains in the Cleveland National Forest. It winds west and south through San Juan Canyon, and is joined by Arroyo Trabuco as it passes through San Juan Capistrano. It flows into the Pacific Ocean at Doheny State Beach. San Juan Canyon provides a major part of the route for California State Route 74.

Aliso Creek is a 19.8-mile (31.9 km)-long, mostly urban stream in south Orange County, California. Originating in the Cleveland National Forest in the Santa Ana Mountains, it flows generally southwest and empties into the Pacific Ocean at Laguna Beach. The creek's watershed drains 34.9 square miles (90 km2), and it is joined by seven main tributaries. As of 2018, the watershed had a population of 144,000 divided among seven incorporated cities.

Arroyo Trabuco is a 22-mile (35 km)-long stream in coastal southern California in the United States. Rising in a rugged canyon in the Santa Ana Mountains of Orange County, the creek flows west and southwest before emptying into San Juan Creek in the city of San Juan Capistrano. Arroyo Trabuco's watershed drains 54 square miles (140 km2) of hilly, semi-arid land and lies mostly in Orange County, with a small portion extending northward into Riverside County. The lower section of the creek flows through three incorporated cities and is moderately polluted by urban and agricultural runoff.

San Diego Creek is a 16-mile (26 km) urban waterway flowing into Upper Newport Bay in Orange County, California in the United States. Its watershed covers 112.2 square miles (291 km2) in parts of eight cities, including Irvine, Tustin, and Costa Mesa. From its headwaters in Laguna Woods the creek flows northwest to its confluence with Peters Canyon Wash, where it turns abruptly southwest towards the bay. Most of the creek has been converted to a concrete flood control channel, but it also provides important aquatic and riparian habitat along its course and its tidal estuary.
Moro Canyon is a canyon and seasonal stream near Laguna Beach, Orange County, California in the Crystal Cove State Park. Moro Canyon Creek originates at the summit of the San Joaquin Hills and flows southwest, under Pacific Coast Highway to empty into the Pacific Ocean at Moro Beach.
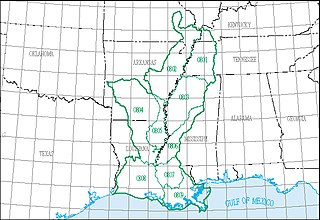
The Lower Mississippi water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

The Great Lakes water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

The Rio Grande water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
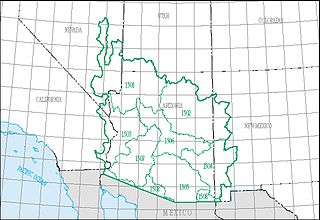
The Lower Colorado water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
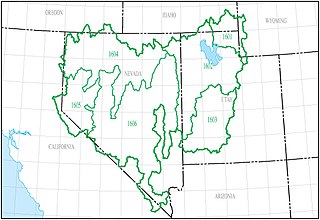
The Great Basin water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.
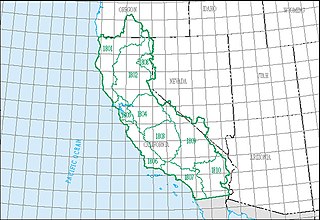
The California water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey in the United States hydrologic unit system, which is used to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.

In order to advantage hydrologists, ecologists and water-resource managers in the study of "water, its properties and laws, and its distribution over the earth's surface" in the United States, the United States Geological Survey created a hierarchical system of hydrologic units.

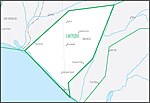
Ventura–San Gabriel Coastal water resource basin is one of three hydrologic basins within the Southern California Coastal water resource subregion and is one of approximately 2,200 water resource basins in the United States hydrologic unit system. The Ventura–San Gabriel Coastal water resource basin is a third-level subdivision of the United States hydrologic unit system.

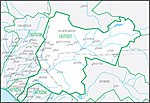
Northern Mojave–Mono Lake water resource subregion is one of 10 water resource subregions within the California water resource region and is one of 222 water resource subregions in the federally organized United States hydrologic unit system.

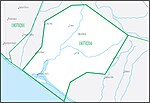
Laguna–San Diego Coastal water resource basin is one of three hydrologic basins within the Southern California Coastal water resource subregion and is one of approximately 2,200 water resource basins in the United States hydrologic unit system.