
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a landlocked state of Germany, occupying its southeastern corner. With an area of 70,550.19 square kilometres (27,239.58 sq mi) Bavaria is the largest German state by land area comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With 13 million inhabitants, it is Germany's second-most-populous state after North Rhine-Westphalia. Bavaria's main cities are Munich, Nuremberg, and Augsburg.
The Christian Social Union in Bavaria is a Christian-democratic and conservative political party in Germany. Having a regionalist identity, the CSU operates only in Bavaria while its larger counterpart, the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), operates in the other fifteen states of Germany. It differs from the CDU by being somewhat more conservative in social matters, following the Catholic social teaching. The CSU is considered the de facto successor of the Weimar-era Catholic Bavarian People's Party.

Franconia is a region in Germany, characterised by its culture and language, and may be roughly associated with the areas in which the East Franconian dialect group, colloquially referred to as "Franconian", is spoken. There are several other Franconian dialects, but only the East Franconian ones are colloquially referred to as "Franconian".

The Palatinate, historically also Rhenish Palatinate or Lower Palatinate (Unterpfalz), is a region in southwestern Germany. It occupies roughly the southernmost quarter of the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate (Rheinland-Pfalz), covering an area of 5,451 square kilometres (2,105 sq mi) with about 1.4 million inhabitants. Its residents are known as Palatines.
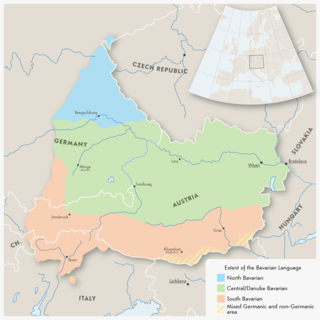
Austro-Bavarian is a major group of Upper German varieties spoken in the southeast of the German language area, much of Bavaria, most of Austria and South Tyrol in Italy, as well as Samnaun in Switzerland. Before 1945, Austro-Bavarian was also prevalent in parts of the southern Czech Republic and western Hungary. Bavarian forms a continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional variants.

The Upper Palatinate is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany, located in the east of Bavaria.

The Iller (help·info) is a river of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It is a right tributary of the Danube, 146 kilometres (91 mi) long.
The Regen is a river in Bavaria, Germany, and a left tributary of the Danube, at Regensburg, Germany. The source of its main headstream, the Great Regen, is in the Bohemian Forest on the territory of the Czech Republic, near Železná Ruda. The river crosses the border after a few kilometres, at Bayerisch Eisenstein. The name in German evolved from the name in Latin, but its meaning is unknown. The Romans called the river variously Regana, Reganus (masculine), and Reganum (neuter).

The Ilz is a river running through the Bavarian Forest, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Danube and 40 km (25 mi) in length, during which it travels down a height difference of ~140m.

The Landtag of Bavaria, officially known in English as the Bavarian State Parliament, is the unicameral legislature of the state of Bavaria in Germany. The parliament meets in the Maximilianeum in Munich.

Bavarian Alps is a summarizing term of several mountain ranges of the Northern Limestone Alps in the German state of Bavaria.

Bavarians are an ethnographic group of Germans of the Bavaria region, a state within Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as the Bavarian language, native to Altbayern, roughly the territory of the Electorate of Bavaria in the 17th century.

Central Bavarian, also known as Central Austro-Bavarian, form a subgroup of Bavarian dialects in large parts of Austria and the German state of Bavaria along the Danube river, on the northern side of the Eastern Alps. They are spoken in the 'Old Bavarian' regions of Upper Bavaria, Lower Bavaria and in the adjacent parts of the Upper Palatinate region around Regensburg, in Upper and Lower Austria, in Vienna, in the state of Salzburg, as well as in the northern and eastern parts of Styria and Burgenland.

The Duchy of Bavaria was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (duces) under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.

The Innviertel is a traditional Austrian region southeast of the Inn river. It forms the western part of the state of Upper Austria and borders the German state of Bavaria. The Innviertel is one of the four traditional "quarters" of Upper Austria, the others being Hausruckviertel, Mühlviertel, and Traunviertel.

The Vils is a river in Bavaria, Germany, it is a right tributary of the Danube.

The Naab is a river in Bavaria, Germany, and is a left tributary of the Danube. Including its main source river Waldnaab, it is 196.6 km (122 mi) long.

The Kingdom of Bavaria was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. The Bavarian Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach became the first King of Bavaria in 1805 as Maximilian I Joseph. The crown would go on being held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of Bavaria's present-day borders were established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federated state of the new empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. In 1918, Bavaria became a republic after the German Revolution, and the kingdom was thus succeeded by the current Free State of Bavaria.

The Rednitz is a 46 km (29 mi) long river in Franconia, Germany, tributary of the Regnitz. The Rednitz is formed by the confluence of the rivers Franconian Rezat and Swabian Rezat, in Georgensgmünd. The Rednitz flows north through Roth bei Nürnberg, Schwabach and the southwestern quarters of Nuremberg. The Rednitz joins the Pegnitz to form the Regnitz in Fürth.

The Günz is a river in Bavaria, Germany.















