
Tipu Sultan, commonly referred to as Sher-e-Mysore or "Tiger of Mysore", was a ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery. He expanded the iron-cased Mysorean rockets and commissioned the military manual Fathul Mujahidin. The economy of Mysore reached a zenith during his reign. He deployed rockets against advances of British forces and their allies during the Anglo-Mysore Wars, including the Battle of Pollilur and Siege of Srirangapatna.

Hubli is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. The twin cities Hubli–Dharwad form the second largest city in the state by area and population and the largest city in North Karnataka. Hubli is in Dharwad district of Karnataka and is the taluk headquarters of Hubli City and Hubli Rural. Although it hosts the HDMC office, the district headquarters is in Dharwad.

Raghavendra Tirtha, also referred as Raghavendra Swami, was a Vaishnava scholar, theologian, and saint. He was also known as Sudha Parimalacharya. His diverse oeuvre include commentaries on the works of Madhva, Jayatirtha, and Vyasatirtha, interpretation of the Principal Upanishads from the standpoint of Dvaita and a treatise on Purva Mimamsa. He served as the pontiff of the matha at Kumbakonam from 1621 to 1671. Raghavendra Tirtha was also an accomplished player of the veena and he composed several songs under the name of Venu Gopala. His memorial at Mantralayam attracts lakhs of visitors every year.

The Fourth Anglo-Mysore War was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore against the British East India Company and the Hyderabad Deccan in 1798–99.

Dharwad, also known as Dharwar, is a city located in the northwestern part of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of the Dharwad district of Karnataka and forms a contiguous urban area with the city of Hubballi. It was merged with Hubballi in 1962 to form the twin cities of Hubballi-Dharwad. It covers an area of 213 km2 (82 sq mi) and is located 430 km (270 mi) northwest of Bangalore, on NH-48, between Bangalore and Pune.

Dakṣiṇāmnāya Śrī Śāradā Pīṭham or Śri Śṛṅgagiri Maṭha ; Sanskrit: मठ, maṭha) is one amongst the four cardinal pīthams following the Daśanāmi Sampradaya - the peetham or matha is said to have been established by acharya Śrī Ādi Śaṅkara to preserve and propagate Sanātana Dharma and Advaita Vedānta, the doctrine of non-dualism. Located in Śringerī in Chikmagalur district in Karnataka, India, it is the Southern Āmnāya Pītham amongst the four Chaturāmnāya Pīthams, with the others being the Dvārakā Śāradā Pītham (Gujarat) in the West, Purī Govardhana Pīṭhaṃ (Odisha) in the East, Badri Jyotishpīṭhaṃ (Uttarakhand) in the North. The head of the matha is called Shankarayacharya, the title derives from Adi Shankara.

Bijapur district, officially known as Vijayapura district, is a district in the state of Karnataka in India. The city of Bijapur is the headquarters of the district, and is located 530 km northwest of Bangalore. Bijapur is well known for the great monuments of historical importance built during the Adil Shahi dynasty.

Kittur, historically known as Kittoor, is a town and a taluk in the Belagavi district of the Indian state of Karnataka. It was part of Bailhongal taluka but was declared as an independent taluka on 23 October 2012 by the Chief Minister of Karnataka on the inauguration of Kittur Utsav. It is 177th Taluk of Karnataka State. It is a place of historical importance because of the armed rebellion of Kittur Chennamma (1778–1829), Rani of the State of Kittur against the British East India Company, during which a British Commissioner, St John Thackeray was killed.

Dharwad or Dharawada is an administrative district of the state of Karnataka in southern India. The administrative headquarters of the district is the city of Dharwad, also known as Dharwar. Dharwad is located 425 km northwest of Bangalore and 421 km southeast of Pune, on the main highway between Chennai and Pune, the National Highway 4 (NH4).
Bankapura is a panchayat town in Haveri district in the state of Karnataka, India. It is in Shiggaon taluk, is just 2.5 km from the Pune-Bangalore national highway NH-4, 22 km from Haveri town. Bankapura is about 45 km from Hubli-Dharwad. An historical site, Bankapura is famous for the Nagareshwara temple, Bankapura fort, The Bankapura Peacock Sanctuary. Baada, the birthplace of Kanakadasa is near to Bankapura.
Shiggaon is a municipal town in Haveri district in the Indian state of Karnataka.

Athani is a town in the Belagavi district of Karnataka, India. It is 140 kilometers from the city of Belagavi, 70 kilometers from Vijayapura, 55 kilometers from Miraj, 100 kilometers from Kolhapur, and 624 kilometers from Bengaluru.
Yergol is a panchayat village in the southern state of Karnataka, India. It is located in the Yadgir Taluka of Yadgir district in Karnataka. It has a famous temple of Shri Gavisiddeshwara Samsthana Matha, Sanji Bheemaraya Devastana, Sri Ramachandra Tirtha Brindavana of Uttaradi Matha, Ramalingeshwara Devastana.

Dhondia Wagh was a military soldier and adventurer in 18th century India. He started his career in the service of Hyder Ali, the ruler of Mysore. During the Third Anglo-Mysore War, he deserted Ali's successor Tipu Sultan, and subsequently raided territories on the Maratha-Mysore border. After the Marathas forced him to retreat, he sought refuge from Tipu and converted to Islam, changing his name to Malik Jahan Khan. After Tipu's death in the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War, he raised a force comprising soldiers from the former Mysore Army, and took control of northern part of the Mysore Kingdom. He styled himself as Ubhaya-Lokadheeshwara. The British East India Company as well as the Maratha Peshwa sent armies to check his rising power. He was ultimately defeated and killed by a British force led by Arthur Wellesley.

Sri Uttaradi Math, is one of the main monasteries (matha) founded by Madhvacharya with Padmanabha Tirtha as its head to preserve and propagate Dvaita Vedanta (Tattvavada) outside Tulunadu region. Uttaradi Math is one of the three primary Dvaita monasteries or Mathatraya that descended from Madhvacharya in the lineage of Padmanabha Tirtha through Jayatirtha. After Jayatirtha and Vidyadhiraja Tirtha, Uttaradi Matha continued in the lineage of Kavindra Tirtha and later in the lineage of Vidyanidhi Tirtha. The Moola Rama and Moola Sita idols worshipped in the Uttaradi Matha have a long history and are revered among adherents.
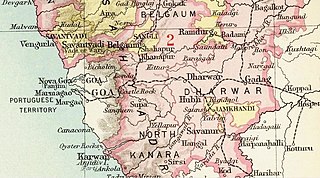
Savanur State, Nawab of Savanur was one of the princely states in British India. The last ruler of the state acceded to the Dominion of India on 8 March 1948, becoming part of the Bombay State. Later in 1956, it transferred to Mysore State in what is now Karnataka.
Murari Rao Ghorpade (1699-1779), known simply as Murari Rao, was an army general in the Maratha Army from Gooty who administered the fort of Tiruchirappalli and surrounding areas from 1741 to 1743. His administration marks the only period of Maratha occupation in Tiruchirappalli. Murari Rao occupied Tiruchirappalli at the head of a strong Maratha army after defeating and imprisoning the Carnatic general Chanda Sahib. However, he was forced to relinquish the fort by Asaf Jah. The Nizam sieged Trichinopoly for four months, and after receiving no reinforcements, Murari Rao was eventually bought off by the Nizam and handed the fort over to him on 29 August 1743. Murari Rao was a disciple and an ardent devotee of Satyabodha Tirtha Swami of Uttaradi Matha. Murari Rao Ghorpade was the founder of the Ghati Subramanya Temple and the Makalidurga Fort.

Sri Satyatma Tirtha, is an Indian Hindu philosopher, guru, scholar, spiritual leader, saint and the present pontiff of Uttaradi Math. He is the 42nd pontiff of Uttaradi Math since Madhvacharya, the chief proponent and the one who rejuvenated the Dvaita philosophy (Tattvavada). Satyatma Tirtha founded Vishwa Madhwa Maha Parishat, a non-profit, religious and social organization in 1998.

Haripant Phadke, known as Hari Pant was a general of the Maratha Confederacy. Hari Pant became a general during the siege of Badami on 20 May 1786 against the Kingdom of Mysore. He became general of 50,000 and won the war in Maratha-Mysore War.

Satyabodha Tirtha was an Indian philosopher, scholar, yogi, mystic and saint. He was the 25th pontiff of Uttaradi Math and served the pontificate from March 1744 - 9 March 1783. Satyabodha Tirtha was a great yogi and was honoured by both Hindu and Muslim rulers of his time. Satyabodha Tirtha enjoyed a good fame as a miracle-man. Almost all the princes of the South India used to worship him and were his ardent disciples. Murari Rao of Gooty, Raghoji Bhosale and Fateh Singh Rao Gaekwad, were his great disciples. Satyabodha Tirtha Swamiji's mission of peace has played a prominent role during this time. He earned a reputation as the greatest of Madhva saints of his time for his un-rivaled scholarship, miraculous achievements and dynamism as the pontiff of the Uttaradi Math. So many were his achievements and so well was he liked, admired and respected by people of all castes and creeds, rich and poor, that the Uttaradi Math in Savanur got the name as Satyabodha Math after him. Satyabodha Tirtha is believed to be the incarnation of Markandeya.




















