
Schenkenschanz is a small community in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany that was incorporated into the town of Kleve (Cleves) in 1969. Schenkenschanz is site of the former Schenkenschans fortress that was of significance in the Dutch Revolt.

Schenkenschanz is a small community in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany that was incorporated into the town of Kleve (Cleves) in 1969. Schenkenschanz is site of the former Schenkenschans fortress that was of significance in the Dutch Revolt.
Schenkenschanz is a village within Kleve and home to about 100 inhabitants (2013). [1] Most of its 38 hectares is not protected against flooding and part of a nature preserve. Schenkenschanz is located about 5 km north of the center of Kleve. Until 1972 it could only be reached by ferry service across the nearby old Rhine arm, while today the Kleve-Griethausen bridge provides a road connection.
The area of Schenkenschanz is subject to the influence of the Rhine river due to flooding, erosion, formation of islands and changes in the course of the river. Schenkenschanz had military significance when it was the point that split the Rhine river into two arms, the southern Waal and the northern Nederrijn.
Flooding by the Rhine in 1995 forced a complete evacuation of the village.

After the Dutch Republic had declared its independence from Spain in 1581, Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester commissioned Maarten Schenck van Nydeggen to erect a fortress at the Waal/Nederrijn fork in 1586. [1] As Schenkenschans (Schenk's fortification) it was built as star fortress with extensive fortification works on both sides of the river representing at its time one of the strongest fortifications in Europe. It controlled the river access to the Netherlands.
During the Dutch War of Independence the fortress was unsuccessfully besieged in 1599 by Spanish forces. It was however captured by them in 1635 only to succumb to the Dutch forces led by Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange in the long and bitter siege of 1636.
During the Franco-Dutch War French troops under Louis XIV attacked the fortress successfully in 1672. [2] Two years later Brandenburg-Prussian troops took over, dismantled the fortress [2] and returned the place to the Dutch in 1679.
By the end of the 17th century Rhine water flowed more and more into the Waal while the Nederrijn at Schenkenschanz was sanding up. The creation of the Pannerdens Kanaal in 1701/09 repositioned the fork between the two rivers west to Millingen aan de Rijn and Schenkenschanz lost its military significance.
About 1800 Schenkenschanz became French again. [1] After the turmoil of the Napoleonic wars, Schenkenschanz become part of the Rhine Province, Prussia at the 1816 Congress of Vienna. [1]

Nijmegen is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and tenth largest of the Netherlands as a whole, located on the Waal river close to the German border. Nijmegen is the oldest city in the Netherlands, the second to be recognized as such in Roman times, and in 2005 celebrated 2,000 years of existence.

The Rhine is one of the major European rivers. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein, Swiss-Austrian, and Swiss-German borders. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border, after which it flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally in Germany the Rhine turns into a predominantly westerly direction and flows into the Netherlands where it eventually empties into the North Sea. It drains an area of 9,973 sq km and its name derives from the Celtic Rēnos. There are also two German states named after the river, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate.

The IJssel is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer, a North Sea natural harbour. It more immediately flows into the east-south channel around the Flevopolder, Flevoland which is kept at 3 metres below sea level. This body of water is then pumped up into the IJsselmeer.

Kleve is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century onwards, Cleves was capital of a county and later a duchy. Today, Cleves is the capital of the district of Cleves in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The city is home to one of the campuses of the Rhine-Waal University of Applied Sciences.
Kleve or Kreis Kleve is a Kreis in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighbouring districts are Borken, Wesel, and Viersen in Germany, and the Dutch provinces of Limburg and Gelderland.

The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War, was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. In its early stages, France was allied with Münster and Cologne, as well as England. The 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War are considered related conflicts.

The Pannerdens Kanaal is a canal in the Netherlands that was dredged between 1701 and 1709 to cut off a large, shallow bend of the river Rhine and so improve river traffic and water regulation.

The Bijlands Kanaal is a canal in the Dutch province of Gelderland, near the Dutch-German border. It is currently by far the most important river-stretch of the Rhine when that major river enters the Netherlands.

The Dutch Waterline was a series of water-based defences conceived by Maurice of Nassau in the early 17th century, and realised by his half brother Frederick Henry. Combined with natural bodies of water, the Waterline could be used to transform Holland, the westernmost region of the Netherlands and adjacent to the North Sea, almost into an island. In the 19th century, the Line was extended to include Utrecht.

Operation Veritable was the northern part of an Allied pincer movement that took place between 8 February and 11 March 1945 during the final stages of the Second World War. The operation was conducted by Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery's Anglo-Canadian 21st Army Group, primarily consisting of the First Canadian Army under Lieutenant-General Harry Crerar and the British XXX Corps under Lieutenant-general Brian Horrocks.
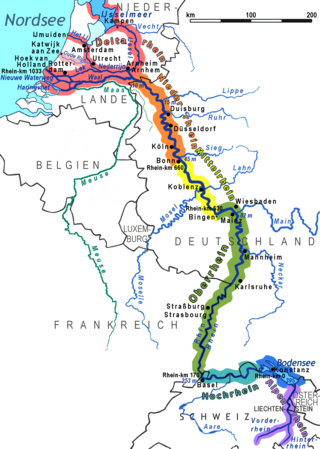
The Lower Rhine flows from Bonn, Germany, to the North Sea at Hook of Holland, Netherlands ; alternatively, Lower Rhine may refer to the part upstream of Pannerdens Kop, excluding the Nederrijn.

The Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta is a river delta in the Netherlands formed by the confluence of the Rhine, the Meuse and the Scheldt rivers. In some cases, the Scheldt delta is considered a separate delta to the Rhine–Meuse delta. The result is a multitude of islands, branches and branch names that may at first sight look bewildering, especially as a waterway that appears to be one continuous stream may change names as many as seven times, e.g. Rhine → Bijlands Kanaal → Pannerdens Kanaal → Nederrijn → Lek → Nieuwe Maas → Het Scheur → Nieuwe Waterweg. Since the Rhine contributes most of the water, the shorter term Rhine Delta is commonly used. However, this name is also used for the delta where the Alpine Rhine flows into Lake Constance, so it is clearer to call the larger one Rhine–Meuse delta, or even Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, as the Scheldt ends in the same delta. By some calculations, the delta covers 25,347 km2 (9,787 sq mi), making it the largest in Europe.

The siege of Schenkenschans was a major siege of the Eighty Years' War. In a successful campaign the Army of Flanders, commanded by Spanish general Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria, captured Schenkenschans along with a number of important towns, reversing recent Dutch gains and opening the Dutch Republic to a possible invasion. The Dutch Stadtholder, Fredrick Henry, pushed the republic's military efforts to their limit to recapture the fortress of Schenkenschans to counter the threat to the exposed Dutch heartland. He succeeded in doing so after a costly nine month siege.

The siege of Kehl lasted from 26 October 1796 to 9 January 1797. Habsburg and Württemberg regulars numbering 40,000, under the command of Maximilian Anton Karl, Count Baillet de Latour, besieged and captured the French-controlled fortifications at the village of Kehl in the German state of Baden-Durlach. The fortifications at Kehl represented important bridgehead crossing the Rhine to Strasbourg, an Alsatian city, a French Revolutionary stronghold. This battle was part of the Rhine Campaign of 1796, in the French Revolutionary War of the First Coalition.

The siege of Leuven was an important siege in the Thirty Years' War in which a Franco-Dutch army under Frederick Henry of Orange and the French Marshals Urbain de Maillé-Brezé and Gaspard III de Coligny, who had invaded the Spanish Netherlands from two sides, laid siege to the city of Leuven, defended by a force of 4,000 comprising local citizen and student militias with Walloons, Germans, Spanish and Irish of the Army of Flanders under Anthonie Schetz, Baron of Grobbendonck. Poor organization and logistics and the spread of sickness among the French, along with the appearance of an Imperial-Spanish relief army of 11,000 under Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand and Ottavio Piccolomini, forced the invading army to lift the siege. This failure allowed the Spanish forces to take the initiative and soon the invaders were forced into a headlong retreat.

The siege of Jülich was a major operation in the second phase of the Eighty Years' War that took place from 5 September 1621 to 3 February 1622. A few months after the Twelve Years' Truce between the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Monarchy expired, the Spanish Army of Flanders, led by the Genoese nobleman Ambrogio Spinola, went on the offensive against the Republic and approached the Rhine river to mask its true intentions: laying siege to the town of Jülich, which the Dutch States Army had occupied in 1610 during the War of the Jülich Succession. Although the capture of the town would not allow for a Spanish invasion of the Republic, its location between the Rhine and Meuse rivers rendered it strategically significant for both sides, given that the United Provinces greatly benefited from the river trade with the neighboring neutral states and Spain was pursuing a strategy of blockading the waterways which flowed across the Republic to ruin its economy.

The siege of Rees of 1599, also known as the relief of Rees, was an unsuccessful attempt by Protestant-German forces led by Count Simon VI of Lippe, and Anglo-Dutch forces sent by Prince Maurice of Nassau, commanded by Philip of Hohenlohe-Neuenstein and the Count Ernst of Solms, to capture the strategic stronghold of Rees, Lower Rhine, Duchy of Cleves from the Spanish forces of Don Francisco de Mendoza, Admiral of Aragon, second-in-command of the Army of Flanders, and Governor Don Ramiro de Guzmán, between 10–12 September 1599, during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). This Spanish victory was part of the campaign of Francisco de Mendoza and Cardinal Andrew of Austria of 1598-1599, also called the Spanish Winter of 1598-99.

Orsoy, till 1974 an independent town in the district of Moers, is today a municipal district of the Lower Rhine town of Rheinberg on the Rhine. The word Orsoy, pronounced Oschau means "horse pasture" (Rossaue). Orsoy itself was in the Middle Ages a powerful fortified town with high walls and four gates. Although much of the fortifications were destroyed in the Second World War, a tower, circa 50 percent of the walls and part of the moat remain today giving some indication of the scale of the fortifications.

The siege of Schenkenschans was a siege that took place from 28 April to 2 May 1599 as part of the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War. Schenkenschans was garrisoned largely by English troops and was besieged by a Spanish force led by Francisco de Mendoza. The siege failed with losses and the Spanish were forced to retreat when a relief force arrived.

The siege of Zaltbommel was a campaign that took place during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War from 15 May to 22 July 1599. The Spanish led by Francisco López de Mendoza y Mendoza launched an offensive campaign around Bommelerwaard, which was defended by an Anglo-Dutch force under the command of Maurice of Orange. A siege on the town of Zaltbommel by Spanish troops was attempted but they had to lift the siege and were defeated in subsequent attempts to regain the initiative. Mendoza retreated and the Spanish army then found itself in chaos: mutinies took effect and as a result further operations were suspended for a number of years. As a result, the Dutch and English followed with a counter-offensive in the Spanish Netherlands.