
A pole weapon or pole arm is a close combat weapon in which the main fighting part of the weapon is fitted to the end of a long shaft, typically of wood, thereby extending the user's effective range and striking power. Pole weapons are predominantly melee weapons, with a subclass of spear-like designs fit for both thrusting and throwing. Because many pole weapons were adapted from agricultural implements or other tools in fairly large amount of abundance, and contain relatively little metal, they were cheap to make and readily available. When warfare breaks out and the belligerents have a poorer class who cannot pay for dedicated weapons made for war, military leaders often resort to the appropriation of tools as cheap weapons. The cost of training was minimal, since these conscripted farmers had spent most of their lives in the familiar use of these "weapons" in the fields. This made polearms the favored weapon of peasant levies and peasant rebellions the world over.
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, iron, steel, or bronze. The most common design for hunting or combat spears since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, lozenge, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature barbs or serrated edges.

A halberd is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word halberd is most likely equivalent to the German word Hellebarde, deriving from Middle High German halm (handle) and barte (battleaxe) joined to form helmbarte. Troops that used the weapon were called halberdiers.

Yari (槍) is the term for a traditionally-made Japanese blade in the form of a spear, or more specifically, the straight-headed spear. The martial art of wielding the yari is called sōjutsu.

A bill is a class of agricultural implement used for trimming tree limbs, which was often repurposed for use as an infantry polearm. In English, the term 'Italian Bill' is applied to the similarly functioning ronche/runka/roncone. In contrast to the English bill, the Italian 'bill', tended toward long thrusting points. The English distinguished between several varieties of bill, including the black, brown and forest bills, but the differences between them are currently not fully understood. Bills were adapted to military use through addition of various projecting blades. Other variants include bill hook and bill-guisarme

A glaive is a European polearm, consisting of a single-edged blade on the end of a pole. It is similar to the Japanese naginata, the Chinese guandao, the Korean woldo, and the Russian sovnya.
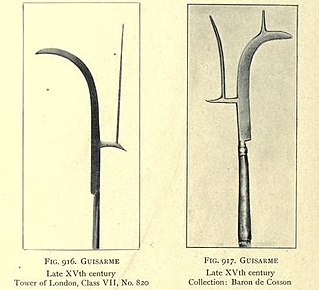
A guisarme is a pole weapon used in Europe primarily between 1000 and 1400. Its origin is likely Germanic, from the Old High German getīsarn, literally "weeding iron". Like many medieval polearms, the exact early form of the weapon is hard to define from literary references, and the identification of surviving weapons can be speculative.

A bardiche, berdiche, bardische, bardeche, or berdish is a type of polearm used from the 14th to 17th centuries in Europe. Ultimately a descendant of the medieval sparth or Danish axe, the bardiche proper appears around 1400, but there are numerous medieval manuscripts that depict very similar weapons beginning c. 1250. The bardiche differs from the halberd in having neither a hook at the back nor a spear point at the top.

The Lochaber axe is a type of poleaxe that was used almost exclusively in Scotland. It was usually mounted on a staff about five feet long.

The Dane axe is an early type of battle axe, primarily used during the transition between the European Viking Age and early Middle Ages. Other names for the weapon include English long axe, Danish axe, and hafted axe.

The poleaxe is a European polearm that was widely used by medieval infantry.
A brandistock was a short type of pole weapon which was used by both infantry and civilians alike, primarily police officers in Italy between the 16th and 19th centuries. Measuring some 1.5 meters (5 ft) long, the brandistock construction was unique for polearms in that it had a retractable blade. The head consisted of either a single or a trio of long thin points, which were kept in a hollow aperture inside the rest of the shaft. A sharp thrust of the weapon forward propelled the heads out, where they could be readily locked in place. This weapon is essentially a spear with a sliding blade, or alternatively, a long handled out-the-front gravity knife.

A battle axe is an axe specifically designed for combat. Battle axes were specialized versions of utility axes. Many were suitable for use in one hand, while others were larger and were deployed two-handed.

The dagger-axe is a type of pole weapon that was in use from the Erlitou culture until the Han dynasty in China. It consists of a dagger-shaped blade, mounted by its tang to a perpendicular wooden shaft. The earliest dagger-axe blades were made of stone. Later versions used bronze. Jade versions were also made for ceremonial use. There is a variant type with a divided two-part head, consisting of the usual straight blade and a scythe-like blade.

The ji was a Chinese polearm, sometimes translated into English as spear or halberd, though they are fundamentally different weapons. They were used in one form or another for over 3000 years, from at least as early as the Zhou dynasty, until the end of the Qing dynasty. They are still used for training purposes in many Chinese martial arts.

An axe is an implement that has been used for millennia to shape, split and cut wood, to harvest timber, as a weapon, and as a ceremonial or heraldic symbol. The axe has many forms and specialised uses but generally consists of an axe head with a handle, or helve.
The term "halberd" has been used to translate several Old Norse words relating to polearms in the context of Viking Age arms and armour, and in scientific literature about the Viking Age. In referring to the Viking Age weapon, the term "halberd" is not to be taken as referring to the classical Swiss halberd of the 15th century, but rather in its literal sense of "axe-on-a-pole", describing a weapon of the more general glaive type.
The Jedwart stave was a polearm weapon commonly found in the Scottish Borders in the 16th century. It consisted of a large, thin, double-edged axe-like blade attached to a roughly four-foot long studded stave with a hand guard, similar in appearance to a bardiche. The upheaval of the sixteenth century in the borders proved the weapon to be too light to be effective against the heavy cavalry of the Border Reivers and attacks from the English, and it fell out of favour in combat. It remained however a common household weapon for purpose of self-defence.
The saintie is an Indo-Persian parrying spear. It is a staff weapon that can be used both for offensive and defensive purposes. They have been produced since the 16th century and were used up to the 19th century. The use of saintie is extremely scarce today.

The three most common types of Chinese polearms are the ge (戈), qiang (槍), and ji (戟). They are translated into English as dagger-axe, spear, and halberd. Dagger-axes were originally a short slashing weapon with a 0.9 to 1.8 m long shaft, but around the 4th century BC a spearhead was added to the blade, and it became a halberd. The spear is also sometimes called a mao (矛), which is sometimes used to designate polearms with a wavy snake-like spearhead. There was another polearm weapon known as the pi (鈹), translated into English as either sword-staff or long lance, that was used from ancient times until the Han dynasty. It was essentially a short sword attached to a stick. From the Warring States period onward, the length of Chinese polearms varied from around 2.8 m to 5.5 m, however there is no specific designation for a pike in the traditional Chinese lexicon. A very long spear is just called a long spear.
















