
A polearm or pole weapon is a close combat weapon in which the main fighting part of the weapon is fitted to the end of a long shaft, typically of wood, extending the user's effective range and striking power. Polearms are predominantly melee weapons, with a subclass of spear-like designs fit for thrusting and/or throwing. Because many polearms were adapted from agricultural implements or other fairly abundant tools, and contained relatively little metal, they were cheap to make and readily available. When belligerents in warfare had a poorer class who could not pay for dedicated military weapons, they would often appropriate tools as cheap weapons. The cost of training was comparatively low, since these conscripted farmers had spent most of their lives using these "weapons" in the fields. This made polearms the favoured weapon of peasant levies and peasant rebellions the world over.
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, copper, bronze, iron, or steel. The most common design for hunting and/or warfare, since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, diamond, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature multiple sharp points, with or without barbs.

A halberd is a two-handed polearm that came to prominent use from the 13th to 16th centuries. The halberd consists of an axe blade topped with a spike mounted on a long shaft. It can have a hook or thorn on the back side of the axe blade for grappling mounted combatants. The halberd was usually 1.5 to 1.8 metres long.

A longsword is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use, a straight double-edged blade of around 80 to 110 cm, and weighing approximately 1 to 1.5 kg.

Yari (槍) is the term for a traditionally-made Japanese blade in the form of a spear, or more specifically, the straight-headed spear. The martial art of wielding the yari is called sōjutsu.

A glaive, sometimes spelled as glave, is a type of pole weapon with historical origins in Europe, known for its distinctive design and versatile combat applications. It is similar to other polearms such as the war scythe, the Japanese naginata, the Chinese guandao, the Korean woldo, and the Russian sovnya.
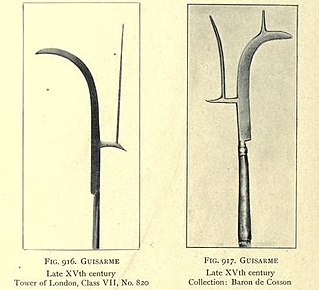
A guisarme is a polearm used in Europe primarily between 1000 and 1400. Its origin is likely Germanic, from the Old High German getīsarn, literally "weeding iron". Like many medieval polearms, the exact early form of the weapon is hard to define from literary references, and the identification of surviving weapons can be speculative.

A bardiche, berdiche, bardische, bardeche, or berdish is a type of polearm used from the 14th to 17th centuries in Europe. Ultimately a descendant of the medieval sparth axe or Dane axe, the bardiche proper appears around 1400, but there are numerous medieval manuscripts that depict very similar weapons beginning c. 1250. The bardiche differs from the halberd in having neither a hook at the back nor a spear point at the top. The use of bardiches started in early 14th-century Austria.

A voulge is a type of polearm that existed in medieval Europe, primarily in 15th century France.

A partisan is a type of polearm that was used in Europe during the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries. It consisted of a spearhead mounted on a long wooden shaft, with protrusions on the sides which aided in parrying sword thrusts. The partisan was often used by infantry soldiers, who would use the weapon to fend off cavalry charges. The protrusions on the sides of the spearhead were also useful for catching and trapping an opponent's sword, allowing the user to disarm them. In profile, the head of a partisan may look similar to other types of polearm, such as the halberd, pike, ranseur, spontoon, ox tongue, or spetum.

The Lochaber axe is a type of poleaxe that was used almost exclusively in Scotland. It was usually mounted on a staff about five feet long.

The Dane axe or long axe is a type of European early medieval period two-handed battle axe with a very long shaft, around 0.9–1.2 metres at the low end to 1.5–1.7 metres or more at the long end. Sometimes called a broadaxe, the blade was broad and thin, intended to give a long powerful cut when swung, effective against cavalry, shields and unarmored opponents.

The poleaxe is a European polearm that was used by medieval infantry.

A bisentō is a polearm used in feudal Japan. The bisentō has various descriptions, "a double-edged long sword with a thick truncated blade", "a spear-like weapon with a blade at the end that resembles a scimitar", "a polearm resembling a glaive, with a long, heavy haft and a heavy, curved blade". The bisentō is said to have been used by ninja and peasants.

A battle axe is an axe specifically designed for combat. Battle axes were specialized versions of utility axes. Many were suitable for use in one hand, while others were larger and were deployed two-handed.

A war scythe or military scythe is a form of polearm with a curving single-edged blade with the cutting edge on the concave side of the blade. Its blade bears a superficial resemblance to that of an agricultural scythe from which it is likely to have evolved, but the war scythe is otherwise unrelated to agricultural tools and is a purpose-built infantry melee weapon. The blade of a war scythe has regularly proportioned flats, a thickness comparable to that of a spear or sword blade, and slightly curves along its edge as it tapers to its point. This is different from farming scythes, which have very thin and irregularly curved blades, specialised for mowing grass and wheat only, unsuitable as blades for improvised spears or polearms.
The Bohemian earspoon is a polearm featuring a long, broad, socketed spearhead with two out-turned lugs at the base of the head, forming a guard similar to that of a boar spear.

The woldo, was a Korean polearm that closely resembled the Chinese guandao, though proportionally smaller. It was so named because of its curved blade. Its use and its methods were described in the Muyedobotongji, which was published in 1795.
A sovnya is a traditional polearm used in Russia. Similar to the glaive, the sovnya had a curved, single-edged blade mounted on the end of a long pole. This was a weapon used by late-medieval Muscovite cavalry and it retained use until the mid-17th century.

The three most common types of Chinese polearms are the ge (戈), qiang (槍), and ji (戟). They are translated into English as dagger-axe, spear, and halberd. Dagger-axes were originally a short slashing weapon with a 0.9–1.8 m long shaft, but around the 4th century BC a spearhead was added to the blade, and it became a halberd. The spear is also sometimes called a mao (矛), which is sometimes used to designate polearms with a wavy snake-like spearhead. There was another polearm weapon known as the pi (鈹), translated into English as either sword-staff or long lance, that was used from ancient times until the Han dynasty. It was essentially a short sword attached to a stick. From the Warring States period onward, the length of Chinese polearms varied from around 2.8 to 5.5 m ; however, there is no specific designation for a pike in the traditional Chinese lexicon. A very long spear is just called a long spear.

















