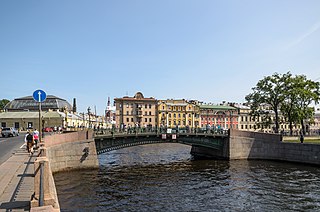The Neva is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of 74 kilometres (46 mi), it is the fourth-largest river in Europe in terms of average discharge.

Bridge of Four Lions is a 28-metre-long pedestrian bridge over the Griboedov Canal in St Petersburg, connecting L'vinyi Drive to Malaya Podyacheskaya Street. The Lion Bridge is in the Admiralteysky District of St. Petersburg, connecting the Kazansky and Spassky Islands. Its abutments are crowned with four cast-iron sculptures of lions, which give the bridge its name. The structure, suspended by cables emerging from the mouths of lions, was constructed in 1825 according to the design of two well-established bridge builders, Tratter and Kristianovich. It is an outstanding monument of bridge-building architecture of the first quarter of the 19th century [5]. It is also one of the three surviving pedestrian chain bridges in St. Petersburg.

The Griboyedov Canal or Kanal Griboyedova is a canal in Saint Petersburg, constructed in 1739 along the existing Krivusha river. In 1764–90, the canal was deepened and the banks were reinforced and covered with granite.

Trinity Bridge is a bascule bridge across the Neva in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It connects Kamennoostrovsky Prospect with Suvorov Square. It was the third permanent bridge across the Neva, built between 1897 and 1903 by the French firm Société de Construction des Batignolles. It is 582 meters (1,909 ft) long and 23.6 meters (77 ft) wide.

The New Michael Palace was the third Saint Petersburg palace designed by Andrei Stackenschneider for Nicholas I's children. It was built between 1857 and 1862 on the Palace Embankment, between the Hermitage Museum buildings and the Marble Palace.

The Volodarsky Bridge is a moveable bridge across the Neva River in Saint Petersburg, Russia. The bridge connects Narodnaya and Ivanovskaya streets. It is named after V. Volodarsky, a revolutionary, who was killed near the future bridge in 1918. It is the only bridge in the city with an overpass for trams. The bridge is part of the Central Arc Thoroughfare. In 1932-1936, according to engineer G.P. Peredery's project, a three-span reinforced concrete arch bridge with a metal double-winged drawbridge was built. In 1986-1993, the old bridge was dismantled and replaced with a metal girder. The bridge length is 332 meters, the width is 24–27 meters. Upstream is the Bolshoy Obukhovsky Bridge, and below is the Finland Railway Bridge.
The Liteyny Bridge is the second permanent bridge across the Neva river in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It connects Liteyny Prospekt with Vyborgsky district. The bridge's length is 396 meters, the width is 34 meters. At the vicinity of the Liteyny Bridge, the Neva river reaches the maximum depth of 24 meters.
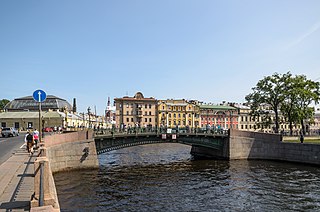
The First Engineer Bridge is one of several bridges that span the Moika River in Saint Petersburg, Russia. The bridge is one of a group of four bridges located near the Mars Field, and opposite the main entrance to the Summer Garden, spanning the Moika River, the Fontanka River, and the Swan Canal in the historic center of the city. The First Engineer Bridge is one of the most decorative of Saint Petersburg's more than 500 bridges.

The Potseluev Bridge is a bridge across the Moyka River in Saint Petersburg, Russia. The name of the bridge spurred numerous urban legends. The panoramic view of Saint Isaac's Cathedral that opens from the bridge makes it a popular subject of artists paintings.

The Hermitage Bridge is a bridge across the Winter Canal along Palace Embankment in Saint Petersburg, Russia. The bridge constitutes part of the Hermitage and Winter Palace ensemble.

The Swan Canal is a waterway located in Saint Petersburg. Dating from the early years of the foundation of the city, it connects the Moyka and Neva Rivers.

Upper Swan Bridge is a single-span stone bridge in Saint Petersburg. It is one of the oldest stone bridges in the city and carries Palace Embankment across the Swan Canal.

Lower Swan Bridge is a single-span stone bridge in Saint Petersburg crossing the Swan Canal at its junction with the Moyka River.

Red Canal was an eighteenth-century waterway in Saint Petersburg. Built between 1711 and 1719, it was part of a series of canals dug to improve the drainage of the marshy areas of the city. The canal was one of two connecting the Moyka River and the Neva River in the area of what is now the Field of Mars. Opened in the presence of Peter the Great and Tsarina Catherine in 1719, the canal became a popular site for the nobility to construct large townhouses. By the 1770s the canal was no longer required for its original purpose, and with the expansion of buildings across the Neva embankment, the canal was filled in. A stone bridge built over the canal in 1768 was transferred to the Winter Canal, and survives today as the First Winter Bridge.

The First Winter Bridge is a single-span stone bridge in Saint Petersburg, carrying Millionnaya Street across the Winter Canal. The current bridge was originally built in 1768 to cross a different watercourse, and was rebuilt and opened in its present location in 1784.

Mogilyovsky Bridge is a bridge across the Griboyedov Canal to Admiralteysky District of Saint Petersburg that connects Kolomensky and Pokrovsky Islands. This bridge is located along the Lermontovsky Avenue axis. It is near the Estonian Orthodox Brotherhood St. Isidor's Church which was built in 1903—1907 by architect Alexander Poleshchuk. Upstream from Mogilyovsky Bridge is Pikalov Bridge; below is Alarchin Bridge. The closest metro station is 1.6 км away and is called Sadovaya.

Smezhny Bridge is a bridge across the Kryukov Canal in the Admiralteysky District of Saint Petersburg that connects the Spassky and Pokrovsky Islands.

Kryukov Canal is one of the Canals in central Saint Petersburg, Russia.

The Kashin Bridge is a hingeless vault bridge across the Kryukov Canal in the Admiralteysky District of Saint Petersburg, Russia. The bridge connects Kolomensky and Kazansky Islands.

Matveevsky Bridge — is a steel girder bridge over the Kryukov Canal in the Admiralteysky District of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It connects the Kolomensky and Kazansky Islands. The bridge has retained the architectural appearance characteristic of the bridges of the Kryukov Canal during the 1780s. It is a monument of history and culture.