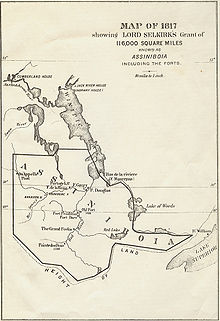

The Selkirk Concession was a land grant issued by the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) to Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, in 1812. The Hudson's Bay Company held a commercial monopoly in Rupert's Land, consisting of the entire Hudson Bay drainage basin. The Selkirk Concession, also known as Selkirk's Grant, included a large section of the southwest area of Rupert's Land, bounded: on the north by the line of 52° N latitude roughly from the Assiniboine River east to Lake Winnipegosis, then by the line of 52° 30′ N latitude from Lake Winnipegosis to Lake Winnipeg; on the east by the Winnipeg River, Lake of the Woods and Rainy River; on the west roughly by the current boundary between modern Saskatchewan and Manitoba; and on the south by the (mostly very slight) rise of land marking the extent of the Hudson Bay watershed. This covered portions of present-day southern Manitoba, northern Minnesota and eastern North Dakota, in addition to small parts of eastern Saskatchewan, northwestern Ontario and northeastern South Dakota. [1] [2]
Lord Selkirk referred to the area as the District of Assiniboia and planned to create an agricultural colony there. To do so he populated the territory with impoverished people from Scotland and Ireland. Lord Selkirk had been profoundly upset by the poverty his people faced and believed that emigration to Western Canada would be their salvation. [3] In return he was to provide The Hudson's Bay Company with 200 employees per year, allow the company to set up trading posts in the colony and give land for company employees when they retired. In 1812 the first settlers arrived when Miles MacDonell brought a small group of Scots to the colony.
While The Hudson's Bay Company held the commercial monopoly in Rupert's Land, numerous aboriginal groups lived in the same territory and disputed the sovereignty of the area. Furthermore, The Hudson's Bay Company was facing competition from the North West Company (NWC), which flagrantly violated the Hudson's Bay Company's commercial monopoly and disputed its territory. In 1814, The Hudson's Bay Company invoked its royal charter and ordered The North West Company to leave. Selkirk's settlement, commonly known as The Red River Colony, was embroiled in these issues, meeting resistance from fur traders of The North West Company, commercial interests from the United States as well as from some local Métis population. In November 1815 the newly appointed governor of Red River Colony, Robert Semple, arrived with around 160 new settlers. Tensions continued to rise, culminating in the Battle of Seven Oaks in June 1816. This confrontation involved a group of North West Company employees led by Cuthbert Grant and some local Métis against a group of Red River settlers and Hudson's Bay Company employees led by Governor Semple, with the battle claiming the lives of 1 North West Company-related and 21 Hudson's Bay Company-related men, including Semple. (see Pemmican War)
Lord Selkirk signed a treaty with Chief Peguis that eventually became St. Peter’s Reserve in 1817, but Chief Peguis’s people would eventually lose the land and forced to move to the current Peguis First Nation by 1930s [4] when Selkirk’s colony became the province of Manitoba in 1870, the area then became St. Peter’s Settlement and eventually merge into Selkirk, Manitoba.
By the 1830s agricultural production of flour was over 50,000 pounds, with over 1,000 settlers residing at the colony. [5] The promise of free land ensured there was no shortage of settlers arriving at the area. By the 1850s the Hudson's Bay Company lost interest in providing financial aid to the colony. In 1867, the United Kingdom had passed the British North America Act, creating the Dominion of Canada from British holdings in the eastern portion of British North America. In 1869 the HBC "sold" Rupert's Land (received compensation for surrendering its trading monopoly back to the British Crown) to the expanding Canada. A lack of attention to concerns of the existing Red River settlers, Métis, and aboriginal groups caused Métis leader Louis Riel to establish a local provisional government to negotiate the political treatment of the local population in the handover to Canada, resulting in the Red River Rebellion of 1869-70 and Canada agreeing to create the province of Manitoba – on land that had been part of the Selkirk Concession – in 1870.

Rupert's Land, or Prince Rupert's Land, was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin. The right to "sole trade and commerce" over Rupert's Land was granted to Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), based at York Factory, effectively giving that company a commercial monopoly over the area. The territory operated for 200 years from 1670 to 1870. Its namesake was Prince Rupert of the Rhine, who was a nephew of King Charles I and the first governor of HBC. In December 1821, the HBC monopoly was extended from Rupert's Land to the Pacific coast.

The Red River Colony, also known as Assiniboia, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, on 300,000 square kilometres (120,000 sq mi) of land in British North America. This land was granted to Douglas by the Hudson's Bay Company in the Selkirk Concession. It included portions of Rupert's Land, or the watershed of Hudson Bay, bounded on the north by the line of 52° N latitude roughly from the Assiniboine River east to Lake Winnipegosis. It then formed a line of 52° 30′ N latitude from Lake Winnipegosis to Lake Winnipeg, and by the Winnipeg River, Lake of the Woods and Rainy River.

The Battle of Seven Oaks—also known as the Seven Oaks Massacre and the Seven Oaks Incident—was a violent confrontation of the Pemmican War between the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and the North West Company (NWC) which occurred on 19 June 1816 near modern-day Winnipeg, Manitoba.

Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk FRS FRSE was a Scottish peer. He was noteworthy as a Scottish philanthropist who sponsored immigrant settlements in Canada at the Red River Colony.

The Red River Rebellion, also known as the Red River Resistance, Red River uprising, or First Riel Rebellion, was the sequence of events that led up to the 1869 establishment of a provisional government by Métis leader Louis Riel and his followers at the Red River Colony, in the early stages of establishing today's Canadian province of Manitoba. It had earlier been a territory called Rupert's Land and been under control of the Hudson's Bay Company before it was sold.

In January 1814, Governor Miles MacDonell, appointed by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk issued to the inhabitants of the Red River area a proclamation which became known as the Pemmican Proclamation. The proclamation was issued in attempt to stop the Métis people from exporting pemmican out of the Red River district. Cuthbert Grant, leader of the Métis, disregarded MacDonell's proclamation and continued the exportation of pemmican to the North West Company. The proclamation overall, became one of many areas of conflict between the Métis and the Red River settlers. Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk had sought interest in the Red River District, with the help of the Hudson's Bay Company as early as 1807. However, it was not until 1810 that the Hudson's Bay Company asked Lord Selkirk for his plans on settling in the interior of Canada.
Assiniboia District refers to two historical districts of Canada's Northwest Territories. The name is taken from the Assiniboine First Nation.

The Manitoba Act, 1870 is an act of the Parliament of Canada, and part of the Constitution of Canada, that provided for the admission of Manitoba as the fifth province of Canada.

Robert Semple was an American-born fur trader and merchant who served as governor of the territories controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company in the Canadas from 1815 until his death in 1816.
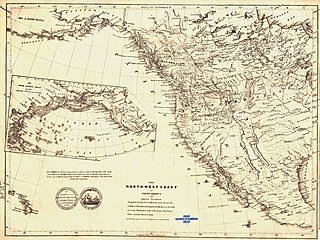
New Caledonia was a fur-trading district of the Hudson's Bay Company that comprised the territory of the north-central portions of present-day British Columbia, Canada. Though not a British colony, New Caledonia was part of the British claim to North America. Its administrative centre was Fort St. James. The rest of what is now mainland British Columbia was called the Columbia Department by the British, and the Oregon Country by the Americans. Even before the partition of the Columbia Department by the Oregon Treaty in 1846, New Caledonia was often used to describe anywhere on the mainland not in the Columbia Department, such as Fort Langley in the Fraser Valley.
Pierre Guillaume Sayer was a Métis fur trader who challenged the monopoly of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) of the fur trade in the Red River region. Ultimately this led to its end.

Fort Douglas was the Selkirk Settlement fort and the first fort associated with the Hudson's Bay Company near the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers in today's city of Winnipeg.
The Pembina Region, also referred to as the Pembina District and Pembina Department, is the historic name of an unorganized territory of land that was ceded to the United States in 1818. The area included the portions of what became the States of Minnesota, North Dakota, and South Dakota lying within the Hudson Bay drainage basin. The area included settlements in the Pembina River area. The region was formerly part of British Rupert's Land, granted by British royal charter to the Hudson's Bay Company. After the Selkirk Concession and establishment of the agricultural Red River Colony in 1812, the area was governed as the District of Assiniboia. The Treaty of 1818 de jure transferred the region south of the 49th parallel to the United States from the British. Settlements south of the boundary continued to be de facto administered as part of Assiniboia until at least 1823.

Fort Gibraltar was founded in 1809 by Alexander Macdonell of Greenfield of the North West Company in present-day Manitoba, Canada. It was located at the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers in or near the area now known as The Forks in the city of Winnipeg. Fort Gibraltar was renamed Fort Garry after the merger of North West Company and the Hudson's Bay Company in 1821, and became Upper Fort Garry in 1835.

Colin Robertson was an early Canadian fur trader and political figure. Born in Scotland, for much of his adult life he was engaged in the North American fur trade, working at different times for the North West Company and the Hudson's Bay Company. He led the Hudson's Bay Company expedition to Lake Athabasca.

The history of Manitoba covers the period from the arrival of Paleo-Indians thousands of years ago to the present day. When European fur traders first travelled to the area present-day Manitoba, they developed trade networks with several First Nations. European fur traders in the area during the late-17th century, with the French under Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye set up several trading post forts. In 1670, Britain declared sovereignty over the watershed of Hudson's Bay, known as Rupert's Land; with the Hudson's Bay Company granted a commercial monopoly over the territory.

The Red River Trails were a network of ox cart routes connecting the Red River Colony and Fort Garry in British North America with the head of navigation on the Mississippi River in the United States. These trade routes ran from the location of present-day Winnipeg in the Canadian province of Manitoba across the Canada–United States border, and thence by a variety of routes through what is now the eastern part of the Dakotas and across western and central Minnesota to Mendota and Saint Paul, Minnesota on the Mississippi.

Peguis was a Saulteaux chief, who moved from the Great Lakes area to Red Lake, then arriving in what is now southern Manitoba in the 1790s.

The Pemmican War was a series of violent confrontations between the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and the North West Company (NWC) in the Canadas from 1812 to 1821. It started after the establishment of the Red River Colony by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk in 1812, and ended in 1821 when the NWC was merged into the HBC. The conflict was sparked by the Pemmican Proclamation issued by Governor Miles Macdonell, which disallowed any person from exporting pemmican, a key foodstuff for those involved in the North American fur trade, out of the Red River Colony. This was fiercely opposed by the Métis, who were mostly affiliated with the NWC and opposed to both the colony and the HBC's dominance in the region.
Most of the following timelines for Manitoba's history is taken from either the Manitoba Historical Society, or from the Heritage Manitoba and the Gimli Municipal Heritage Advisory Committee, as adapted from a three-volume history of Manitoba published in 1993 titled Manitoba: 125.