
The Open Systems Interconnection model is a conceptual model that characterises and standardises the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard communication protocols.
The Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards is a nonprofit consortium that works on the development, convergence, and adoption of open standards for cybersecurity, blockchain, Internet of things (IoT), emergency management, cloud computing, legal data exchange, energy, content technologies, and other areas.
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that supports service orientation. By consequence, it is as well applied in the field of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online. SOA is also intended to be independent of vendors, products and technologies.
Enterprise architecture (EA) is an analytical discipline that provides methods to comprehensively define, organize, standardize, and document an organization’s structure and interrelationships in terms of certain critical business domains characterizing the entity under analysis. The goal of EA is to create an effective representation of the business enterprise that may be used at all levels of stewardship to guide, optimize, and transform the business as it responds to real-world conditions. EA serves to capture the relationships and interactions between domain elements as described by their processes, functions, applications, events, data, and employed technologies.
Quality management ensures that an organization, product or service is consistent. It has four main components: quality planning, quality assurance, quality control and quality improvement. Quality management is focused not only on product and service quality, but also on the means to achieve it. Quality management, therefore, uses quality assurance and control of processes as well as products to achieve more consistent quality. Quality control is also part of Quality Management. What a customer wants and is willing to pay for it, determines quality. It is a written or unwritten commitment to a known or unknown consumer in the market. Thus, quality can be defined as fitness for intended use or, in other words, how well the product performs its intended function.
The ISO/IEC 11179 Metadata Registry (MDR) standard is an international ISO standard for representing metadata for an organization in a metadata registry. It documents the standardization and registration of metadata to make data understandable and shareable.
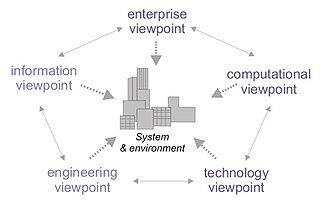
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.
SOA Governance is a set of processes used for activities related to exercising control over services in a service-oriented architecture (SOA). One viewpoint, from IBM and others, is that SOA governance is an extension (subset) of IT governance which itself is an extension of corporate governance. The implicit assumption in this view is that services created using SOA are just one more type of IT asset in need of governance, with the corollary that SOA governance does not apply to IT assets that are "not SOA". A contrasting viewpoint, expressed by blogger Dave Oliver and others, is that service orientation provides a broad organising principle for all aspects of IT in an organisation — including IT governance. Hence SOA governance is nothing but IT governance informed by SOA principles.
International standards in the ISO/IEC 19770 family of standards for IT asset management address both the processes and technology for managing software assets and related IT assets. Broadly speaking, the standard family belongs to the set of Software Asset Management standards and is integrated with other Management System Standards.

ISO/TC 37 is a technical committee within the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that prepares standards and other documents concerning methodology and principles for terminology and language resources.
The ISO/IEC 27000-series comprises information security standards published jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
ISO/IEC JTC 1, entitled "Information technology", is a joint technical committee (JTC) of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its purpose is to develop, maintain and promote standards in the fields of information and communications technology (ICT).
ISO/IEC 29110: Systems and Software Life Cycle Profiles and Guidelines for Very Small Entities (VSEs) International Standards (IS) and Technical Reports (TR) are targeted at Very Small Entities (VSEs). A Very Small Entity (VSE) is an enterprise, an organization, a department or a project having up to 25 people. The ISO/IEC 29110 is a series of international standards and guides entitled "Systems and Software Engineering — Lifecycle Profiles for Very Small Entities (VSEs)". The standards and technical reports were developed by working group 24 (WG24) of sub-committee 7 (SC7) of Joint Technical Committee 1 (JTC1) of the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electrotechnical Commission.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 38 Cloud Computing and Distributed Platforms is a standardization subcommittee, which is part of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7 Software and systems engineering is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops and facilitates standards within the field of engineering of software products and systems. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7 is the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) located in India.
The Banking Industry Architecture Network e.V. (BIAN) is an independent, member owned, not-for-profit association to establish and promote a common architectural framework for enabling banking interoperability. It was established in 2008.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 17 Cards and personal identification is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which develops and facilitates standards within the field of identification cards and personal identification. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 17 is the British Standards Institution (BSI) located in the United Kingdom.
COSMIC functional size measurement is a method to measure a standard functional size of a piece of software. COSMIC is an acronym of COmmon Software Measurement International Consortium, a voluntary organization that has developed the method and is still expanding its use to more software domains.

