
The Potomac River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States that flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to the Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is 405 miles (652 km) long, with a drainage area of 14,700 square miles (38,000 km2), and is the fourth-largest river along the East Coast of the United States and the 21st-largest in the United States. More than 5 million people live within its watershed.

The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, abbreviated as the C&O Canal and occasionally called the Grand Old Ditch, operated from 1831 until 1924 along the Potomac River between Washington, D.C. and Cumberland, Maryland. It replaced the Potomac Canal, which shut down completely in 1828, and could operate during months in which the water level was too low for the former canal. The canal's principal cargo was coal from the Allegheny Mountains.

The Potomac Company was created in 1785 to make improvements to the Potomac River and improve its navigability for commerce. The project is perhaps the first conceptual seed planted in the minds of the new American capitalists in what became a flurry of transportation infrastructure projects, most privately funded, that drove wagon road turnpikes, navigations, and canals, and then as the technology developed, investment funds for railroads across the rough country of the Appalachian Mountains.

The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park is located in the District of Columbia and the state of Maryland. The park was established in 1961 as a National Monument by President Dwight D. Eisenhower to preserve the neglected remains of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal and many of its original structures.

The Monocacy River is a free-flowing left tributary to the Potomac River, which empties into the Atlantic Ocean via the Chesapeake Bay. The river is 58.5 miles (94.1 km) long, with a drainage area of about 970 square miles (2,500 km2). It is the largest Maryland tributary to the Potomac.

The Patowmack Canal, sometimes called the Potomac Canal, is a series of five inoperative canals located in Maryland and Virginia, United States, that was designed to bypass rapids in the Potomac River upstream of the present Washington, D.C., area. The most well known of them is the Great Falls skirting canal, whose remains are managed by the National Park Service since it is within Great Falls Park, an integral part of the George Washington Memorial Parkway.

Great Falls Park is a small National Park Service (NPS) site in Virginia, United States. Situated on 800 acres (3.2 km2) along the banks of the Potomac River in northern Fairfax County, the park is a disconnected but integral part of the George Washington Memorial Parkway. The Great Falls of the Potomac River are near the northern boundary of the park, as are the remains of the Patowmack Canal, the first canal in the United States that used locks to raise and lower boats.

Seneca Creek is a 5.8-mile-long (9.3 km) stream in Montgomery County, Maryland, USA, roughly 16 miles (26 km) northwest of Washington, D.C. It drains into the Potomac River.
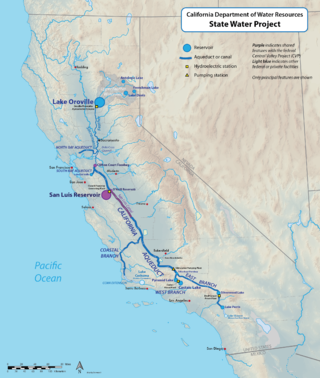
The California State Water Project, commonly known as the SWP, is a state water management project in the U.S. state of California under the supervision of the California Department of Water Resources. The SWP is one of the largest public water and power utilities in the world, providing drinking water for more than 27 million people and generating an average of 6,500 GWh of hydroelectricity annually. However, as it is the largest single consumer of power in the state itself, it has a net usage of 5,100 GWh.

Auburn Dam was a proposed concrete arch dam on the North Fork of the American River east of the town of Auburn, California, in the United States, on the border of Placer and El Dorado Counties. Slated to be completed in the 1970s by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, it would have been the tallest concrete dam in California and one of the tallest in the United States, at a height of 680 feet (210 m) and storing 2,300,000 acre-feet (2.8 km3) of water. Straddling a gorge downstream of the confluence of the North and Middle Forks of the American River and upstream of Folsom Lake, it would have regulated water flow and provided flood control in the American River basin as part of Reclamation's immense Central Valley Project.

The Bear River is a tributary of the Feather River in the Sierra Nevada, winding through four California counties: Yuba, Sutter, Placer, and Nevada. About 73 miles (117 km) long, the river flows generally southwest through the Sierra then west through the Central Valley, draining a narrow, rugged watershed of 295 square miles (760 km2).

Little Falls Branch, a 3.8-mile-long (6.1 km) tributary stream of the Potomac River, is located in Montgomery County, Maryland. In the 19th century, the stream was also called Powder Mill Branch. It drains portions of Bethesda, Somerset, Friendship Heights, and Washington, D.C., flows under the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal (C&O), and empties into the Potomac at Little Falls rapids, which marks the upper end of the tidal Potomac.

A series of projects in the 18th and 19th centuries attempted to make the Potomac River navigable and connect the Ohio River valley and the East Coast. The first project was started by the Potomac Company, but it was the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal Company (C&O) that finished the project in the 1830s and 1840s.

Glacier View Dam was proposed in 1943 on the North Fork of the Flathead River, on the western border of Glacier National Park in Montana. The 416-foot (127 m) tall dam, to be designed and constructed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers in the canyon between Huckleberry Mountain and Glacier View Mountain, would have flooded in excess of 10,000 acres (4,000 ha) of the park. In the face of determined opposition from the National Park Service and conservation groups, the dam was never built.

Paradise Dam was a proposed dam on the Clark Fork River in Montana. It was proposed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers as an alternative to the construction of Glacier View Dam on the western boundary of Glacier National Park, to capture the flow of the Flathead River. The earth embankment dam was planned to be about 250 feet (76 m) high, impounding a reservoir of 4,080,000 acre-feet (5.03 km3). While it was viewed as a desirable power generation and water storage project by the Corps of Engineers, it was opposed by those it would displace from towns and productive agricultural lands, and was never built.

Brocks Gap Dam was a never-built proposal for a water storage dam on the North Fork of the Shenandoah River at Brocks Gap in northwest Virginia. The proposal by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers encountered opposition from local residents and was withdrawn in 1967.
The Potomac River basin reservoir projects were U.S. Army Corps of Engineers programs that sought to regulate the flow of the Potomac River to control flooding, to assure a reliable water supply for Washington, D.C., and to provide recreational opportunities. Beginning in 1921 the Corps studied a variety of proposals for an ambitious program of dam construction on the Potomac and its tributaries, which proposed as many as sixteen major dam and reservoir projects. The most ambitious proposals would have created a nearly continuous chain of reservoirs from tidewater to Cumberland, Maryland. The 1938 program was focused on flood control, on the heels of a major flood in 1936. The reformulated 1963 program focused on water supply and quality, mitigating upstream pollution from sewage and coal mine waste.

Riley's Lock (Lock 24) and lock house are part of the 184.5-mile (296.9 km) Chesapeake and Ohio Canal that operated in the United States along the Potomac River from the 1830s through 1923. They are located at towpath mile-marker 22.7 adjacent to Seneca Creek, in Montgomery County, Maryland. The lock is sometimes identified as Seneca because of the Seneca Aqueduct that carried the canal over the creek to the lift lock. The name Riley comes from John C. Riley, who was lock keeper from 1892 until the canal closed permanently in 1924.

Violette's Lock is part of the 184.5-mile (296.9 km) Chesapeake and Ohio Canal that operated in the United States along the Potomac River from the 1830s through 1923. It is located at towpath mile-marker 22.1, in Montgomery County, Maryland. The name Violette comes from Alfred L. "Ap" Violette and his wife Kate, who were lock keepers from the beginning of the 20th century through the permanent closure of the canal in 1924.



















