
The Atlantic jackknife clam, Ensis leei, also known as the bamboo clam, American jackknife clam or razor clam, is a large edible marine bivalve mollusc found on the North American Atlantic coast, from Canada to South Carolina. The species has also been introduced to Europe. The name "razor clam" is also used to refer to different species such as the Pacific razor clam or Razor shell.
Jackknife clam is a common name which is used for several species in the genera Ensis and Solen within the family Solenidae, species which are found on Atlantic and Pacific beaches of temperate North America. Species in these families are also found elsewhere in the world, but in other English-speaking countries they usually have other common names. All the species in these genera have thin, highly elongate shells. Many of these bivalves are collected for food.

Chitoria is a genus of butterflies in the family Nymphalidae found in Southeast Asia.

Nacaduba is a genus of gossamer-winged butterflies (Lycaenidae). It contains many of the species commonly called "lineblues". As they are the genus initially erected to contain all lineblues, they might be considered the "typical" lineblues, as opposed to the species relatives now separated in Catapyrops, Prosotas and Petrelea.
Homidia is a genus of springtails belonging to the family Entomobryidae. Species include:

Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms.
Sessiluncus is a genus of mites in the family Ologamasidae.
Sessiluncus abalaae is a species of mite in the family Ologamasidae.
Sessiluncus aegypticus is a species of mite in the family Ologamasidae.
Sessiluncus calcuttaensis is a species of mite in the family Ologamasidae.
Sessiluncus reticulatus is a species of mite in the family Ologamasidae.
Sessiluncus indicus is a species of mite in the family Ologamasidae.

Escobaria sneedii is a rare species of cactus known by the common names Sneed's pincushion cactus and carpet foxtail cactus. It is native to the Chihuahuan Desert, where it occurs in scattered locations in New Mexico, Texas, and Chihuahua. Some plants occurring in Arizona may be included within this species. Botanical authors do not necessarily agree on the circumscription of this species. Most will agree at this point in the research, however, that there are two varieties of Escobaria sneedii, and that both are rare and endangered. The plant is popular with cactus enthusiasts and dealers because of its often petite size and tolerance for moderately cold climates. They have been overharvested from their natural habitat, the main reason why the two varieties, var. sneedii and var. leei, have been federally listed as endangered and threatened, respectively.
Kaneis de leei s' agapo is a Greek popular television series written by Markella Grigoriou and Antigoni Pappa and directed by Stefanos Kontomaris, which aired on Mega Channel in 2004 and ran for 32 episodes.
Blackman Bay is located on the south-east coast of Tasmania. It extends from the bay's inlet at the southern peninsula of Marion Bay to the village of Dunalley. Historically this bay was referred to as "Frederick Henry Bay".
Ambicodamus is a genus of spiders in the family Nicodamidae. It was first described in 1995 by Mark Harvey. As of 2017, it contains 11 species, all from Australia.
Phyllodactylus leei, also known as the San Cristóbal Island leaf-toed gecko or Chatham leaf-toed gecko, is a species of gecko. It is endemic to San Cristóbal Island in the Galapagos Islands.
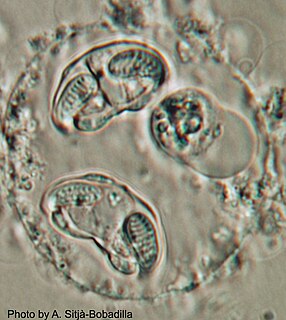
Enteromyxum leei is a species of myxozoan, histozoic parasite that infects the intestinal tract and sometimes associated organs, like gall bladder and liver, of several teleostean fish species. Myxozoans are microscopic metazoans, with an obligate parasitic life-style. The parasite stages of this species live in the paracelullar space between fish enterocytes. It is the causative agent of enteromyxosis, or emaciative disease, also known as “razor blade syndrome” in sparid fish. E. leei has a wide host and geographical range within marine fish, and even freshwater fish have been infected experimentally. E. leei initially emerged in the Mediterranean in the late 1980s and it is believed to have been unintentionally introduced into the Red Sea. Its pathogenicity and economic impact depend on the host species. In the gilt-head seabream, it is manifested as a chronic disease that provokes anorexia, delayed growth with weight loss, cachexia, reduced marketability and increased mortality. In other species, it has no clinical signs. In sharpsnout seabream, infection results in very high mortality rates, which have pushed fish farmers to abandon the culture of this fish species.
Enteromyxum scophthalmi is a species of parasitic myxozoan, a pathogen of fish. It is an intestinal parasite of the turbot and can cause outbreaks of disease in farmed fish. It causes a cachectic syndrome characterised by loss of weight, muscle atrophy, weakness and fatigue.
Cherwellia is an extinct genus of mammaliaforms, possibly belonging to Morganucodonta, that lived in what is now England during the Middle Jurassic. The type and only known species is Cherwellia leei. It was first described in 2016 by Percy M. Butler and Denise Sigogneau-Russell from a single lower molar found at the Kirtlington Quarry of the Forest Marble Formation.





