Related Research Articles

Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic disorder in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Most people have two sex chromosomes. It only affects females. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hairline at the back of the neck, short stature, and swollen hands and feet are seen at birth. Typically, those affected do not develop menstrual periods or breasts without hormone treatment and are unable to have children without reproductive technology. Heart defects, diabetes, and hypothyroidism occur in the disorder more frequently than average. Most people with Turner syndrome have normal intelligence; however, many have problems with spatial visualization that may be needed in order to learn mathematics. Vision and hearing problems also occur more often than average.
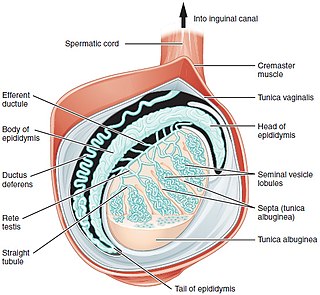
A testicle or testis is the male gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testicles are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone.

Doggy style is a sex position in which one participant bends over, crouches on all fours, or lies on their abdomen, for sexual intercourse, other forms of sexual penetration or other sexual activity. Doggy style is a form of a rear-entry position, others being with the receiving partner lying on the side in the spoons sex position or the reverse cowgirl sex position. Non-penetrative sex in this position may also be regarded as doggy style.

Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become discolored or the testicle may disappear from its usual place.
Gender-affirming surgery for male-to-female transgender women or transfeminine non-binary people describes a variety of surgical procedures that alter the body to provide physical traits more comfortable and affirming to an individual's gender identity and overall functioning.
Organization studies is the academic field interested in a collective activity, and how it relates to organization, organizing, and management. It is "the examination of how individuals construct organizational structures, processes, and practices and how these, in turn, shape social relations and create institutions that ultimately influence people".

Scrotoplasty, also known as oscheoplasty, is a type of surgery to create or repair the scrotum. The history of male genital plastic surgery is rooted in many cultures and dates back to ancient times. However, scientific research for male genital plastic surgery such as scrotoplasty began to develop in the early 1900s. The development of testicular implants began in 1940 made from materials outside of what is used today. Today, testicular implants are created from saline or gel filled silicone rubber. There are a variety of reasons why scrotoplasty is done. Some transgender men and intersex or non-binary people who were assigned female at birth may choose to have this surgery to create a scrotum, as part of their transition. Other reasons for this procedure include addressing issues with the scrotum due to birth defects, aging, or medical conditions such as infection. For newborn males with penoscrotal defects such as webbed penis, a condition in which the penile shaft is attached to the scrotum, scrotoplasty can be performed to restore normal appearance and function. For older male adults, the scrotum may extend with age. Scrotoplasty or scrotal lift can be performed to remove the loose, excess skin. Scrotoplasty can also be performed for males who undergo infection, necrosis, traumatic injury of the scrotum.

Santorio Santorio whose real name was Santorio Santori better known in English as Sanctorius of Padua was an Italian physiologist, physician, and professor, who introduced the quantitative approach into the life sciences and is considered the father of modern quantitative experimentation in medicine. He is also known as the inventor of several medical devices. His work De Statica Medicina, written in 1614, saw many publications and influenced generations of physicians.

The Lameta Formation, also known as the Infratrappean Beds, is a sedimentary geological formation found in Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh, India, associated with the Deccan Traps. It is of the Maastrichtian age, and is notable for its dinosaur fossils

In human male anatomy, the radix or root of the penis is the internal and most proximal portion of the human penis that lies in the perineum. Unlike the pendulous body of the penis, which is suspended from the pubic symphysis, the root is attached to the pubic arch of the pelvis and is not visible externally. It is triradiate in form, consisting of three masses of erectile tissue; the two diverging crura, one on either side, and the median bulb of the penis or urethral bulb. Approximately one third to one half of the penis is embedded in the pelvis and can be felt through the scrotum and in the perineum.

The snow leopard, occasionally called ounce, is a species of large cat in the genus Panthera of the family Felidae. The species is native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because the global population is estimated to number fewer than 10,000 mature individuals and is expected to decline about 10% by 2040. It is mainly threatened by poaching and habitat destruction following infrastructural developments. It inhabits alpine and subalpine zones at elevations of 3,000–4,500 m (9,800–14,800 ft), ranging from eastern Afghanistan, the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau to southern Siberia, Mongolia and western China. In the northern part of its range, it also lives at lower elevations.

Stegotetrabelodon is an extinct genus of primitive elephantid from the Late Miocene to Early Pliocene of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and Italy.
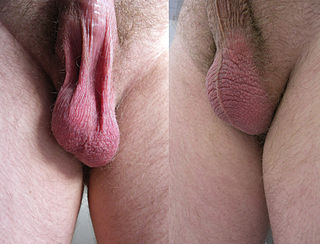
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten when exposed to cold temperatures.
Hippopotamus creutzburgi, the Cretan dwarf hippopotamus, is an extinct species of hippopotamus from the island of Crete. It lived on the island from the Early Pleistocene to early Middle Pleistocene, and probably descended from Hippopotamus antiquus. It was considerably smaller than H. antiquus, weighing approximately 400 kilograms (880 lb). It was one of only two large herbivores on the island during its existence, alongside the dwarf mammoth Mammuthus creticus, with large predators being absent, the only other species of mammal present on the island being the giant rat Kritimys. It is known from abundant remains collected from the Katharo basin in the eastern uplands of Crete, approximately 1,100–1,200 metres (3,600–3,900 ft) above sea level, as well as much rarer remains found in coastal caves. Analysis of its limbs suggests that it was more adapted to terrestrial locomotion than living hippopotamus, primarily walking on its hooves rather than its footpads as in living hippopotamus, and capable of traversing the rugged terrain of Crete. Analysis of its teeth suggests that it had a grazing diet, similar to modern Hippopotamus amphibius. The previous suggestion that the species can be divided into two subspecies is not supported by modern research.
Glomeruloid hemangioma is a distinctive vascular tumor first described in 1990 when found to be associated with POEMS syndrome and Castleman disease. Glomeruloid hemangiomas can manifest as wine-red sessile or pedunculated papules, papulonodules, subcutaneous bluish compressible tumors, or small, firm, reddish-violaceous, dome-shaped papules.
Protein contact dermatitis is a cutaneous condition, and was a term originally used to describe an eczematous reaction to protein-containing material in food handlers. Usually affecting the hands or forearms, it manifests clinically as a subacute or chronic dermatitis that recurs frequently over time. Niels Hjorth and Jytte Roed-Petersen coined the phrase "protein contact dermatitis" in 1976.

In male human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce, is the double-layered fold of skin, mucosal and muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans and the urinary meatus. The foreskin is attached to the glans by an elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum. The outer skin of the foreskin meets with the inner preputial mucosa at the area of the mucocutaneous junction. The foreskin is mobile, fairly stretchable and sustains the glans in a moist environment. Except for humans, a similar structure known as a penile sheath appears in the male sexual organs of all primates and the vast majority of mammals.
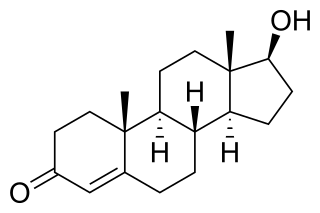
The pharmacology of testosterone, an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.
This article lists Jewish population estimates by scope, by year, by country and by geographical area.

The penile raphe is a visible line or ridge of tissue that runs on the ventral (urethral) side of the human penis beginning from the base of the shaft and ending in the prepuce between the penile frenulum. The line is typically darker than the rest of the shaft skin, even though its shape and pigmentation may vary greatly among males. The penile raphe is part of a broader line in the male reproductive organs, that runs from the anus through the perineum and continues to the scrotum and penis, collectively referred to as median raphe. The penile raphe is homologous to the female labia minora.
References
- ↑ Reardon, William (2008). "Shawl Scrotum and Penoscrotal Transposition". The bedside dysmorphologist. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 170–171. ISBN 978-0-19-530045-1.