
Sheboygan County is a county in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. It is named after the Sheboygan River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 118,034. Its county seat is Sheboygan. The county was created in 1836 and organized in 1846. At the time, it was located in the Wisconsin Territory. Sheboygan County comprises the Sheboygan, WI Metropolitan Statistical Area. Part of the Holyland region is located in northwestern Sheboygan County.

Plymouth is a city in Sheboygan County, Wisconsin, along the Mullet River. It is included in the Sheboygan, Wisconsin Metropolitan Statistical Area. The city is located in the Town of Plymouth, but is politically independent. Plymouth is known as "Hub City" for its former role as a center of wooden wheelwrighting. The population was 8,932 at the 2020 census. Mayor Don Pohlman was last re-elected in April 2018.

Sheboygan Falls is a city in Sheboygan County, Wisconsin, United States, along the Sheboygan River. The population was 8,210 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Sheboygan metropolitan area.

The Wisconsin and Southern Railroad is a Class II regional railroad in Southern Wisconsin and Northeastern Illinois currently operated by Watco. It operates former Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad and Chicago and North Western Railway (C&NW) trackage, mostly acquired by the state of Wisconsin in the 1980s.

The Arkansas, Louisiana and Mississippi Railroad is a 52.9-mile (85.1 km) short-line railroad in northern Louisiana and southern Arkansas. Opened in 1908, it has undergone several corporate reorganizations, but has remained independent of larger carriers. In 2004, paper producer Georgia-Pacific sold the company to shortline operator Genesee & Wyoming Inc. Traffic generally consists of lumber, paper, forest products, and chemicals.

The Mullet River is a tributary of the Sheboygan River, 40 miles (64 km) long, in eastern Wisconsin in the United States. Via the Sheboygan, it is part of the watershed of Lake Michigan, draining an area of 88 square miles (228 km²) in a primarily agricultural area of the Eastern Ridges and Lowlands region of Wisconsin.
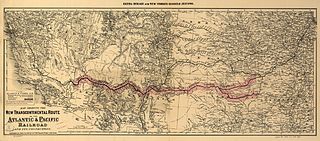
The Atlantic and Pacific Railroad was a U.S. railroad that owned or operated two disjointed segments, one connecting St. Louis, Missouri with Tulsa, Oklahoma, and the other connecting Albuquerque, New Mexico with Needles in Southern California. It was incorporated by the U.S. Congress in 1866 as a transcontinental railroad connecting Springfield, Missouri and Van Buren, Arkansas with California. The central portion was never constructed, and the two halves later became parts of the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway systems, now both merged into the BNSF Railway.

The Sylvanus Wade House is a former stagecoach inn located in Greenbush, Wisconsin, United States. The house provided lodging and meals to travelers in the mid-1800s, before the construction of a nearby railroad made the stagecoach route obsolete. Today, it is part of the Wade House Historic Site.

State Trunk Highway 23 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The route is signed as a north–south route from Shullsburg to Wisconsin Dells and as an east–west route from Wisconsin Dells to Sheboygan. With the exception of freeway segments between Sheboygan Falls and Sheboygan, an expressway segment between Sheboygan Falls past Greenbush to Fond du Lac, a freeway concurrency with Interstate 39 (I-39), and an expressway segment concurrent with U.S. Highway 151 (US 151), the highway is generally either two-lane surface road or urban multilane arterial. WIS 23 provides access to several important Wisconsin destinations, such as the House on the Rock, the Wisconsin Dells area and various state parks.
Wisconsin's 6th congressional district is a congressional district of the United States House of Representatives in eastern Wisconsin. It is based in the rural, suburban and exurban communities between Madison, Milwaukee, and Green Bay. It also includes the village of River Hills in far northern Milwaukee County. The district is currently represented by Glenn Grothman (R-Glenbeaulah) who took office in January 2015.
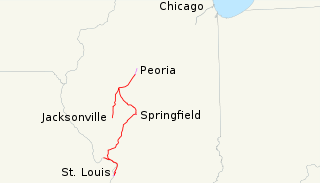
The Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad (CP&StL) was a railroad in the U.S. state of Illinois that operated a main line between Pekin and Madison via Springfield. Its property was sold at foreclosure to several new companies in the 1920s; the portion north of Springfield has since become the Illinois and Midland Railroad, while the remainder has been abandoned, except for a portion near St. Louis that is now owned by the Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Sheboygan and Fond du Lac Railroad and its predecessor the Sheboygan and Mississippi Railroad operated the line from Sheboygan, Wisconsin through Fond du Lac, Wisconsin and terminating in Princeton, Wisconsin for one hundred years and provided service to the communities along the way. Trains carried cattle, freight, lumber, coal, mail, sugar beets, produce, supplies, passengers, and the latest news. Stops along the way included Sheboygan, Sheboygan Falls, Plymouth, Glenbeulah, St Cloud, Calvary, Malone, Silica, Peebles, Taycheedah, Fond du Lac, Eldorado, Rosendale, Ripon, Green Lake, and Princeton.
John Albert Eastman was an American lawyer from Fond du Lac, Wisconsin who spent two years (1850–1851) as a Democratic member of the Wisconsin State Senate.
John A. Bentley was an American lawyer and politician. He was United States Commissioner of Pensions under the last year of Ulysses S. Grant's presidency and through the presidency of Rutherford B. Hayes. He also served as a member of the Wisconsin State Senate in 1865 and 1866.

David R. Giddings was an American surveyor, civil engineer, and Wisconsin pioneer. He served in the 2nd Wisconsin Territorial Assembly, representing the northeast quadrant of the Wisconsin Territory, and was a delegate to the first Wisconsin constitutional convention. He was responsible for the initial surveys of dozens of Wisconsin towns in Brown, Dodge, Fond du Lac, Kenosha, Racine, Sheboygan, and Winnebago counties.

The Waukesha Subdivision or Waukesha Sub is a railway line owned and operated by the Canadian National Railway. It meets the Neenah Subdivision to the north in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin and runs south to Chicago, Illinois.
Elihu Lyman Phillips was an American businessman, politician, and Wisconsin pioneer. He was a member of the Wisconsin Senate, representing Fond du Lac County during the 1860 and 1861 sessions, and earlier represented Onondaga County, New York, in the New York State Assembly during the 1846 session. His name was often abbreviated as E. L. Phillips.
The Beloit and Madison Railroad was a railroad company in the United States. It was incorporated in 1852 and opened its first line in 1854. It was leased by the Galena and Chicago Union Railroad on its completion, and merged into the Chicago and North Western Railway in 1871.
The Mineral Point Railroad was a railroad company in the United States. It was established in 1852 to connect Mineral Point, Wisconsin, with the Illinois Central Railroad in Warren, Illinois. Partial service began in December 1856; the full line to Mineral Point opened in June 1857. The Milwaukee Road acquired the company in 1880; the last remnant of the company's lines was abandoned in the 1980s.
The Sheboygan Falls Subdivision is a railway line in the state of Wisconsin. It runs 14 miles (23 km) between Sheboygan, Wisconsin, and Plymouth, Wisconsin. Ownership is split between Wisconsin and Southern Railroad and the Union Pacific Railroad. The line was originally built in 1859–1860 by the Sheboygan and Mississippi Railroad.













