Related Research Articles

Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include conserving energy and replacing fossil fuels with clean energy sources. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Current climate change mitigation policies are insufficient as they would still result in global warming of about 2.7 °C by 2100,significantly above the 2015 Paris Agreement's goal of limiting global warming to below 2 °C.
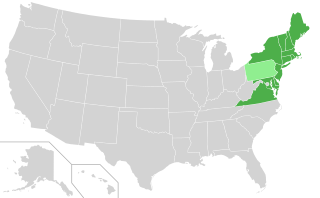
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI,pronounced "Reggie") is the first mandatory market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States. RGGI is a cooperative effort among the states of Connecticut,Delaware,Maine,Maryland,Massachusetts,New Hampshire,New Jersey,New York,Rhode Island,Vermont,and Virginia to cap and reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the power sector. RGGI compliance obligations apply to fossil-fueled power plants 25 megawatts (MW) and larger within the 11-state region. Pennsylvania's participation in the RGGI cooperative was ruled unconstitutional on November 1,2023,although that decision has been appealed. North Carolina's entrance into RGGI has been blocked by the enactment of the state's fiscal year 2023–25 budget.

Front Range Passenger Rail is a proposed inter-city passenger train service along the Front Range and broader I-25 corridors in Colorado and Wyoming. Most proposals envision a route from Pueblo north to Colorado Springs,Denver,Boulder,and Fort Collins. Extensions north to Cheyenne and south to Trinidad,Albuquerque,and even El Paso have been discussed.

Jacob Joseph Lew is an American attorney and diplomat serving as the United States ambassador to Israel. He was the seventy-sixth United States secretary of the treasury from 2013 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party,he also served as the twenty-fifth White House chief of staff from 2012 to 2013 and as director of the Office of Management and Budget in both the Clinton administration and Obama administration.

A low-carbon economy (LCE) is an economy which absorbs as much greenhouse gas as it emits. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions due to human activity are the dominant cause of observed climate change since the mid-20th century. There are many proven approaches for moving to a low-carbon economy,such as encouraging renewable energy transition,energy conservation,and electrification of transportation. An example are zero-carbon cities.
The social cost of carbon (SCC) is the marginal cost of the impacts caused by emitting one extra tonne of carbon emissions at any point in time. The purpose of putting a price on a tonne of emitted CO2 is to aid policymakers or other legislators in evaluating whether a policy designed to curb climate change is justified. The social cost of carbon is a calculation focused on taking corrective measures on climate change which can be deemed a form of market failure. The only governments which use the SCC are in North America. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change suggested that a carbon price of $100 per tonne of CO2 could reduce global GHG emissions by at least half the 2019 level by 2030.

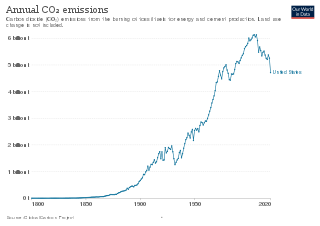
The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020,the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG,followed by the United States with 11%,then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG,more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and,amongst the top eight emitters,is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.

The Colorado Department of Transportation is the principal department of the Colorado state government that administers state government transportation responsibilities in the state of Colorado. CDOT is responsible for maintaining 9,144 mile highway system,including 3,429 bridges with over 28 billion vehicle miles of travel per year. CDOT's Mission is "To provide the best multi-modal transportation system for Colorado that most effectively moves people,goods,and information." It is governed by the Transportation Commission of Colorado.
The environmental policy of the United States is a federal governmental action to regulate activities that have an environmental impact in the United States. The goal of environmental policy is to protect the environment for future generations while interfering as little as possible with the efficiency of commerce or the liberty of the people and to limit inequity in who is burdened with environmental costs. As his first official act bringing in the 1970s,President Richard Nixon signed the U.S. National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) into law on New Year's Day,1970. Also in the same year,America began celebrating Earth Day,which has been called "the big bang of U.S. environmental politics,launching the country on a sweeping social learning curve about ecological management never before experienced or attempted in any other nation." NEPA established a comprehensive US national environmental policy and created the requirement to prepare an environmental impact statement for "major federal actions significantly affecting the quality of the environment." Author and consultant Charles H. Eccleston has called NEPA the world's "environmental Magna Carta".
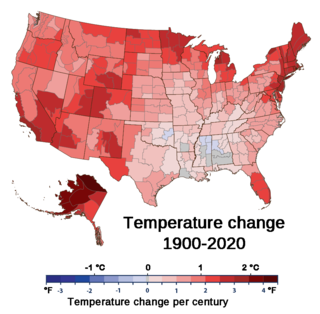
Climate change has led to the United States warming by 2.6 °F since 1970. The climate of the United States is shifting in ways that are widespread and varied between regions. From 2010 to 2019,the United States experienced its hottest decade on record. Extreme weather events,invasive species,floods and droughts are increasing. Climate change's impacts on tropical cyclones and sea level rise also affect regions of the country.
New Energy for America was a plan led by President Barack Obama and Vice President Joe Biden beginning in 2008 to invest in renewable energy sources,reduce reliance on foreign oil,address global warming issues,and create jobs for Americans. The main objective of the New Energy for America plan was to implement clean energy sources in the United States to switch from nonrenewable resources to renewable resources. The plan led by the Obama Administration aimed to implement short-term solutions to provide immediate relief from pain at the pump,and mid- to- long-term solutions to provide a New Energy for America plan. The goals of the clean energy plan hoped to:invest in renewable technologies that will boost domestic manufacturing and increase homegrown energy,invest in training for workers of clean technologies,strengthen the middle class,and help the economy.
The White House Office of Energy and Climate Change Policy was a government entity in the United States created in 2008 by President Barack Obama by Executive Order. It existed for over two years and was combined with another presidential office in April 2011. The office was created to coordinate administration policy on energy and global warming. Under the Biden administration,it has been succeeded by both the Office of Domestic Climate Policy and the Office on Clean Energy Innovation and Implementation.

A low-carbon fuel standard (LCFS) is an emissions trading rule designed to reduce the average carbon intensity of transportation fuels in a given jurisdiction,as compared to conventional petroleum fuels,such as gasoline and diesel. The most common methods for reducing transportation carbon emissions are supplying electricity to electric vehicles,supplying hydrogen fuel to fuel cell vehicles and blending biofuels,such as ethanol,biodiesel,renewable diesel,and renewable natural gas into fossil fuels. The main purpose of a low-carbon fuel standard is to decrease carbon dioxide emissions associated with vehicles powered by various types of internal combustion engines while also considering the entire life cycle,in order to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation.
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China,and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. Cumulatively,the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gases,more than any country in the world.

The energy policy of the Obama administration was defined by an "all-of-the-above" approach which offered federal support for renewable energy deployment,increased domestic oil and gas extraction,and export of crude oil and natural gas. His presidency's first term was shaped by the failure of his signature climate legislation,the American Clean Energy and Security Act,to pass,and then climate and energy disasters including the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 and then Hurricane Sandy,which took place during the 2012 election. In his second term,Obama lifted the ban on crude oil exports and approved liquified natural gas exports;his planned regulatory approach to reducing greenhouse pollution in the electricity sector,the Clean Power Plan,was blocked by the U.S. Supreme Court.

The Clean Power Plan was an Obama administration policy aimed at combating climate change that was first proposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in June 2014. The final version of the plan was unveiled by President Barack Obama on August 3,2015. Each state was assigned an individual goal for reducing carbon emissions,which could be accomplished how they saw fit,but with the possibility of the EPA stepping in if the state refused to submit a plan. If every state met its target,the plan was projected to reduce carbon emissions from electricity generation 32% by 2030,relative to 2005 levels,as well as achieving various health benefits due to reduced air pollution.

The Marine Policy of the Barack Obama administration comprises several significant environmental policy decisions for the oceans made during his two terms in office from 2009 to 2017. By executive action,US President Barack Obama increased fourfold the amount of protected marine space in waters under United States control,setting a major precedent for global ocean conservation. Using the U.S. president's authority under the Antiquities Act of 1906,he expanded to 200 nautical miles the seaward limits of Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in Hawaiʻi and the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument around the U.S. island possessions in the Central Pacific. In the Atlantic,Obama created the Northeast Canyons and Seamounts Marine National Monument,the first marine monument in the U.S. exclusive economic zone (EEZ) in the Atlantic.

As the most populous state in the United States,California's climate policies influence both global climate change and federal climate policy. In line with the views of climate scientists,the state of California has progressively passed emission-reduction legislation.

The White House Office of Domestic Climate Policy is an office within the White House Office that is part of the Executive Office of the President of the United States. It is headed by the Assistant to the President and National Climate Advisor,which is president's chief advisor on domestic climate change policy. In addition,the National Climate Advisor serves as vice-chair of the National Climate Task Force.
The environmental policy of the Joe Biden administration includes a series of laws,regulations,and programs introduced by United States President Joe Biden since he took office in January 2021. Many of the actions taken by the Biden administration reversed the policies of his predecessor,Donald Trump. Biden's climate change policy focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions,similar to the efforts taken by the Obama administration. Biden promised to end and reverse deforestation and land degradation by 2030. The main climate target of the Biden administration is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States to net zero by 2050. A climate team was created to lead the effort.
References
- ↑ "Shoshana Lew confirmed as CDOT Executive Director". February 5, 2019. Retrieved April 23, 2020.
- ↑ Anderson, Patrick (December 27, 2018). "R.I. transporation [sic] official heads west". Providence Journal. Retrieved April 24, 2020.
- ↑ "Shoshana Lew, Nonresident Senior Fellow, Metropolitan Policy Program". The Brookings Institution. Retrieved April 24, 2020.
- ↑ "About CDOT Executive Director & Staff" . Retrieved December 2, 2020.
- ↑ "President Obama announces more key administration posts". The White House, President Barack Obama. September 18, 2015. Retrieved April 24, 2020.
- 1 2 3 "Colorado Proposes Climate-Conscious Transportation Rules". Governing. October 13, 2021. Retrieved December 20, 2021.
- 1 2 Woodruff, Chase (December 16, 2021). "Transportation Commission approves planning rule aimed at greenhouse gas cuts". Colorado Newsline. Retrieved December 20, 2021.
- ↑ Minor, Nathaniel. "A Climate-Friendly Shift In Transportation Planning Would Bring Economic Benefits Too, A New Report Says". Colorado Public Radio. Retrieved December 20, 2021.
- ↑ "StackPath". www.masstransitmag.com. Retrieved December 20, 2021.
- ↑ Walker, Alissa (December 17, 2021). "One State Is Showing Us How to End America's Addiction to Highway Expansion". Curbed. Retrieved December 20, 2021.
- ↑ "Shoshana Lew | RAQC". raqc.org. Retrieved December 20, 2021.