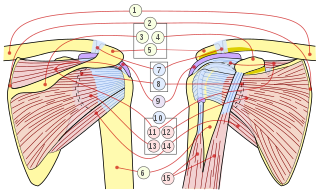
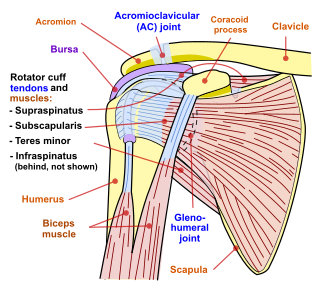
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are:
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are often caused by sudden trauma on the joint like an impact or fall. A joint dislocation can cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any major joint or minor joint. The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation.
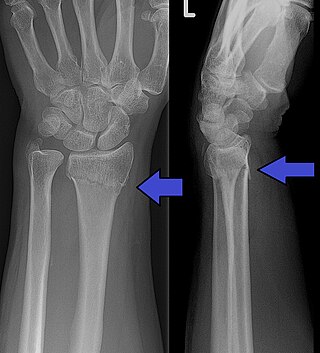
A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken.

The teres minor is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule.
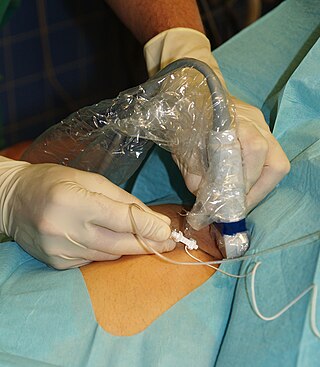
Nerve block or regional nerve blockade is any deliberate interruption of signals traveling along a nerve, often for the purpose of pain relief. Local anesthetic nerve block is a short-term block, usually lasting hours or days, involving the injection of an anesthetic, a corticosteroid, and other agents onto or near a nerve. Neurolytic block, the deliberate temporary degeneration of nerve fibers through the application of chemicals, heat, or freezing, produces a block that may persist for weeks, months, or indefinitely. Neurectomy, the cutting through or removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve, usually produces a permanent block. Because neurectomy of a sensory nerve is often followed, months later, by the emergence of new, more intense pain, sensory nerve neurectomy is rarely performed.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.

A hip dislocation is when the thighbone (femur) separates from the hip bone (pelvis). Specifically it is when the ball–shaped head of the femur separates from its cup–shaped socket in the hip bone, known as the acetabulum. The joint of the femur and pelvis is very stable, secured by both bony and soft-tissue constraints. With that, dislocation would require significant force which typically results from significant trauma such as from a motor vehicle collision or from a fall from elevation. Hip dislocations can also occur following a hip replacement or from a developmental abnormality known as hip dysplasia.

A separated shoulder, also known as acromioclavicular joint injury, is a common injury to the acromioclavicular joint. The AC joint is located at the outer end of the clavicle where it attaches to the acromion of the scapula. Symptoms include non-radiating pain which may make it difficult to move the shoulder. The presence of swelling or bruising and a deformity in the shoulder is also common depending on how severe the dislocation is.

A dislocated shoulder is a condition in which the head of the humerus is detached from the glenoid fossa. Symptoms include shoulder pain and instability. Complications may include a Bankart lesion, Hill-Sachs lesion, rotator cuff tear, or injury to the axillary nerve.

A Bankart lesion is a type of shoulder injury that occurs following a dislocated shoulder. It is an injury of the anterior (inferior) glenoid labrum of the shoulder. When this happens, a pocket at the front of the glenoid forms that allows the humeral head to dislocate into it. It is an indication for surgery and often accompanied by a Hill-Sachs lesion, damage to the posterior humeral head.

A Hill–Sachs lesion, or Hill–Sachs fracture, is a cortical depression in the posterolateral head of the humerus. It results from forceful impaction of the humeral head against the anteroinferior glenoid rim when the shoulder is dislocated anteriorly.

The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa, and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term elbow is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used.
Procedural sedation and analgesia (PSA) is a technique in which a sedating/dissociative medication is given, usually along with an analgesic medication, in order to perform non-surgical procedures on a patient. The overall goal is to induce a decreased level of consciousness while maintaining the patient's ability to breathe on their own. Airway protective reflexes are not compromised by this process and therefore endotracheal intubation is not required. PSA is commonly used in the emergency department, in addition to the operating room.

Dislocations occur when two bones that originally met at the joint detach. Dislocations should not be confused with subluxation. Subluxation is when the joint is still partially attached to the bone.

Cunningham shoulder reduction was originally published in 2003 and is an anatomically based method of shoulder reduction that utilizes positioning, voluntary scapular retraction, and bicipital massage. It is designed for true anterior/subcoracoid glenohumeral dislocations in patients who can fully adduct their humerus. This is distinct from anteroinferior/subglenoid glenohumeral dislocations for which alternative techniques should be used. The method is one of several techniques used for shoulder reduction.

Watsu is a form of aquatic bodywork used for deep relaxation and passive aquatic therapy. Watsu is characterized by one-on-one sessions in which a practitioner or therapist gently cradles, moves, stretches, and massages a receiver in chest-deep warm water.
The Latarjet operation, also known as the Latarjet-Bristow procedure, is a surgical procedure used to treat recurrent shoulder dislocations, typically caused by bone loss or a fracture of the glenoid. The procedure was first described by French surgeon Dr. Michel Latarjet in 1954.

A knee dislocation is an injury in which there is disruption of the knee joint between the tibia and the femur. Symptoms include pain and instability of the knee. Complications may include injury to an artery, most commonly the popliteal artery behind the knee, or compartment syndrome.




















