Related Research Articles
uniq is a utility command on Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems which, when fed a text file or standard input, outputs the text with adjacent identical lines collapsed to one, unique line of text.

In computing, ls is a command to list computer files and directories in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is specified by POSIX and the Single UNIX Specification.
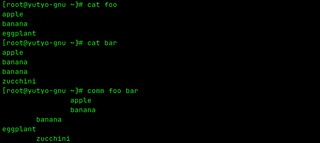
The comm command in the Unix family of computer operating systems is a utility that is used to compare two files for common and distinct lines. comm is specified in the POSIX standard. It has been widely available on Unix-like operating systems since the mid to late 1980s.
xargs is a command on Unix and most Unix-like operating systems used to build and execute commands from standard input. It converts input from standard input into arguments to a command.
dd is a command-line utility for Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems and beyond, the primary purpose of which is to convert and copy files. On Unix, device drivers for hardware and special device files appear in the file system just like normal files; dd can also read and/or write from/to these files, provided that function is implemented in their respective driver. As a result, dd can be used for tasks such as backing up the boot sector of a hard drive, and obtaining a fixed amount of random data. The dd program can also perform conversions on the data as it is copied, including byte order swapping and conversion to and from the ASCII and EBCDIC text encodings.

In computing, time is a command in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is used to determine the duration of execution of a particular command.
join is a command in Unix and Unix-like operating systems that merges the lines of two sorted text files based on the presence of a common field. It is similar to the join operator used in relational databases but operating on text files.

wc is a command in Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems. The program reads either standard input or a list of computer files and generates one or more of the following statistics: newline count, word count, and byte count. If a list of files is provided, both individual file and total statistics follow.
In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, iconv is a command-line program and a standardized application programming interface (API) used to convert between different character encodings. "It can convert from any of these encodings to any other, through Unicode conversion."
split is a utility on Unix, Plan 9, and Unix-like operating systems most commonly used to split a computer file into two or more smaller files.
paste is a Unix command line utility which is used to join files horizontally by outputting lines consisting of the sequentially corresponding lines of each file specified, separated by tabs, to the standard output.
nl is a Unix utility for numbering lines, either from a file or from standard input, reproducing output on standard output.

In Unix-like computer operating systems, a pipeline is a mechanism for inter-process communication using message passing. A pipeline is a set of processes chained together by their standard streams, so that the output text of each process (stdout) is passed directly as input (stdin) to the next one. The second process is started as the first process is still executing, and they are executed concurrently. The concept of pipelines was championed by Douglas McIlroy at Unix's ancestral home of Bell Labs, during the development of Unix, shaping its toolbox philosophy. It is named by analogy to a physical pipeline. A key feature of these pipelines is their "hiding of internals". This in turn allows for more clarity and simplicity in the system.
In computing, tee is a command in command-line interpreters (shells) using standard streams which reads standard input and writes it to both standard output and one or more files, effectively duplicating its input. It is primarily used in conjunction with pipes and filters. The command is named after the T-splitter used in plumbing.
cpio is a general file archiver utility and its associated file format. It is primarily installed on Unix-like computer operating systems. The software utility was originally intended as a tape archiving program as part of the Programmer's Workbench (PWB/UNIX), and has been a component of virtually every Unix operating system released thereafter. Its name is derived from the phrase copy in and out, in close description of the program's use of standard input and standard output in its operation.

In computing, sort is a standard command line program of Unix and Unix-like operating systems, that prints the lines of its input or concatenation of all files listed in its argument list in sorted order. Sorting is done based on one or more sort keys extracted from each line of input. By default, the entire input is taken as sort key. Blank space is the default field separator. The command supports a number of command-line options that can vary by implementation. For instance the "-r" flag will reverse the sort order.
dirname is a standard computer program on Unix and Unix-like operating systems. When dirname is given a pathname, it will delete any suffix beginning with the last slash ('/') character and return the result. dirname is described in the Single UNIX Specification and is primarily used in shell scripts.
XMLStarlet is a set of command line utilities (toolkit) to query, transform, validate, and edit XML documents and files using a simple set of shell commands in a way similar to how it is done with UNIX grep, sed, awk, diff, patch, join, etc commands.
In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, printf is a shell builtin that formats and prints data.

cat is a standard Unix utility that reads files sequentially, writing them to standard output. The name is derived from its function to (con)catenate files. It has been ported to a number of operating systems.