
Silk weaving is a manufacturing industry in Varanasi. Varanasi is known throughout India for its production of very fine silk and Banarasi saris.

Silk weaving is a manufacturing industry in Varanasi. Varanasi is known throughout India for its production of very fine silk and Banarasi saris.
Weaving is typically done within the household, and most weavers in Varanasi are Momin Ansari Muslims. [1] Many of Varanasi's Muslims belong to a weaver community that is known by the name of Ansari, which means "helper" in Arabic. For generations they have passed on their craft from father to son, hand-weaving silk on room-sized foot-powered looms. They are fashioned into Sarees worn only for special occasions; many Indian girls dream of wearing Varanasi silk Saree for their wedding day. [2] [ page needed ]
Varanasi saris are adorned with intricate designs and zari embellishments making it popular during traditional functions and weddings. Earlier, the embroidery on sarees were often done with threads of pure gold. In 2009, weaver associations and cooperatives together secured Geographical Indication (GI) rights for ‘Banaras Brocades and Sarees’. [3] This silk is used in large part for the production of Banarasi saris, which are a regional type of sari made from silk.
As of 2015, [update] there are roughly 40,000 weavers in Varanasi, down from 300,000. [4] Some attribute the decline to lower demand of Saris or higher number of imported Saris. [5] Others suggest that power looms played a role. [4]
Varanasi has a high rate of Child labour given the unorganised nature of small scale industries. [6] According to Human Rights Watch, it is common for children as young as 5 or 6 to begin working in industry because it is believed to be more efficient to teach them from a very young age rather than teaching an older child of 12 the trade. [7]
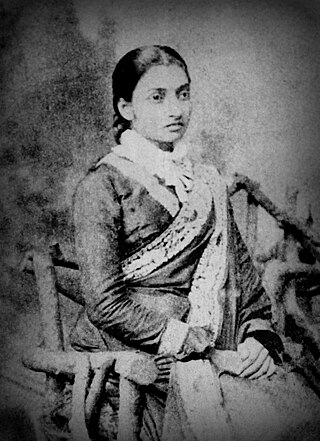
A sari is a women's garment from the Indian subcontinent. It consists of an un-stitched stretch of woven fabric arranged over the body as a robe, with one end attached to the waist, while the other end rests over one shoulder as a stole, sometimes baring a part of the midriff. It may vary from 4.1 to 8.2 metres in length, and 60 to 120 centimetres in breadth, and is a form of ethnic wear in India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Pakistan. There are various names and styles of sari manufacture and draping, the most common being the Nivi style. The sari is worn with a fitted bodice also called a choli and a petticoat called ghagra, parkar, or ul-pavadai. It remains fashionable in the Indian subcontinent today.
Ikat is a dyeing technique from Southeast Asia used to pattern textiles that employs resist dyeing on the yarns prior to dyeing and weaving the fabric. In Southeast Asia, where it is the most widespread, ikat weaving traditions can be divided into two general groups of related traditions. The first is found among Daic-speaking peoples. The second, larger group is found among the Austronesian peoples and spread via the Austronesian expansion to as far as Madagascar. It is most prominently associated with the textile traditions of Indonesia in modern times, from where the term ikat originates. Similar unrelated dyeing and weaving techniques that developed independently are also present in other regions of the world, including India, Central Asia, Japan, Africa, and the Americas.
Clothing in India varies with the different ethnicities, geography, climate, and cultural traditions of the people of each region of India. Historically, clothing has evolved from simple garments like kaupina, langota, achkan, lungi, sari, to perform rituals and dances. In urban areas, western clothing is common and uniformly worn by people of all social levels. India also has a great diversity in terms of weaves, fibers, colors, and the material of clothing. Sometimes, color codes are followed in clothing based on the religion and ritual concerned. The clothing in India also encompasses a wide variety of Indian embroidery, prints, handwork, embellishments, and styles of wearing clothes. A wide mix of Indian traditional clothing and western styles can be seen in India.

Jamdani is a fine muslin textile produced for centuries in South Rupshi of Narayanganj district in Bangladesh on the bank of Shitalakhwa river.

A Banarasi sari is a sari made in Varanasi, an ancient city which is also called Benares (Banaras). The saris are among the finest saris in India and are known for their gold and silver brocade or zari, fine silk and opulent embroidery. The saris are made of finely woven silk and are decorated with intricate designs, and, because of these engravings, are relatively heavy.

A Shalu is a regional variant of the sari from Banaras (Varanasi), India. It is one of many types of saris and differs in the fact that it is the end result of combining Paithani fabric and Banarasi fabric. Paithani, named after the Paithan town in Aurangabad Maharashtra, is made from very fine silk and is characterized by borders of an oblique square design, and a pallu with a Peacock design. Banarasi, also known as Banarasi Silk, is a fine variant of Silk that originates from the city of Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh, India. One of the biggest differences with the Shalu Sari, in comparison to others, is that it is completely embellished at the base with what is called "jari" motifs.

In India, about 97% of the raw mulberry silk is produced in the Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal. Mysore and North Bangalore, the upcoming site of a US$20 million "Silk City", contribute to a majority of silk production. Another emerging silk producer is Tamil Nadu in the place in where mulberry cultivation is concentrated in Salem, Erode and Dharmapuri districts. Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh and Gobichettipalayam, Tamil Nadu were the first locations to have automated silk reeling units.

Kota Doria or Kota Doriya is the name of a light woven fabric made of tiny woven squares (khat) which is still handwoven on traditional pit looms in Kaithoon near Kota in Rajasthan and in some of the surrounding villages. Kota Doriya Sarees are made of pure cotton and silk and have square like patterns known as khats on them. The chequered weave of a Kota sari is very popular for their lightweight and comfortable wear. They are very fine weaves and weigh very little.

Kerala sari (Set-sari) is a clothing of women in the Indian state of Kerala.

Dupioni is a plain weave silk fabric, produced using fine yarn in the warp and uneven yarn reeled from two or more entangled cocoons in the weft. This creates tightly woven yardage with a highly-lustrous surface and a crisp hand. It is similar to shantung, but slightly thicker, heavier, and with a greater slub count. In Japan a cocoon containing more than one silkworm is called tamamayu.

Baluchari Sari is a type of sari, a garment worn by women in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam and the country of Bangladesh. This particular type of sari originated in West Bengal and is known for depictions of mythological scenes on the anchal of the sari. It used to be produced in Murshidabad but presently Bishnupur and its surrounding areas of West Bengal are the only place where authentic Baluchari saris are produced. It takes approximately one week to produce one such sari. In 2011, the Baluchari Sari was granted the status of Geographical Indication for West Bengal in India.

Tant sari is a traditional Bengali sari, originating from the Bengal region in the eastern part and usually used by Bengali women. Tant sari are woven from cotton threads and distinguished by its lightness and transparency. It is considered to be the most comfortable sari for the hot and humid climate in the Indian subcontinent.
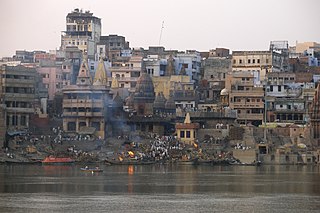
Varanasi is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world. The city has a syncretic tradition of Islamic artisanship that underpins its religious tourism. Located in the middle-Ganges valley in the southeastern part of the state of Uttar Pradesh, Varanasi lies on the left bank of the river. It is 692 kilometres (430 mi) to the southeast of India's capital New Delhi and 320 kilometres (200 mi) to the southeast of the state capital, Lucknow. It lies 121 kilometres (75 mi) downstream of Prayagraj, where the confluence with the Yamuna river is another major Hindu pilgrimage site.

The Chanderi sari is a traditional Koli sari made in Chanderi, Madhya Pradesh, India.
Uppada Jamdani saree is a silk sari style woven in Uppada of East Godavari district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It was registered as one of the geographical indication from Andhra Pradesh by Geographical Indications of Goods Act, 1999. Uppada Jamdani saris are known for their light weight.

Pochampally sari or Pochampalli ikat is a saree made in Bhoodan Pochampally, Yadadri Bhuvanagiri district, Telangana State, India. They have traditional geometric patterns in "Paagadu Bandhu" (Ikat) style of dyeing. The intricate geometric designs find their way into sarees and dress materials. The Indian government's official airplane company, Air India, has its cabin crew wear specially designed Pochampally silk sarees.

Handloom saris are a traditional textile art of Bangladesh and India. The production of handloom saris is important for economic development in rural India.

Habaspuri is a cotton-based traditional handloom textiles of Odisha, India. Habaspuri sari is a major product of this textile. The Bhulia weavers of Chicheguda, Kalahandi district, Odisha are originally attributed for weaving of the Habaspuri fabric. For its uniqueness in weaving, design and production, it has been identified as one of the 14 Geographical Indications of Odisha.

Smriti Morarka is an Indian social activist reviving handwoven cloth and improving mental health. In 2019 she was awarded the "Woman Power Award" Nari Shakti Puraskar by the President of India on International Women's Day in recognition of the example she has made.

Shantipur Handloom Industry, also known Shantipur Handloom Cluster, is a handloom weaving industry in Nadia district of West Bengal. It is one of the foremost handloom centers of India. This handloom industry is world famous for the production of cotton Sari (saree). The two main centers of this industrial zone are Shantipur and Phulia. Shantipur has an old reputation for cotton sarees, known as Shantipuri sarees, and Phulia is well known for Tangail-Jamdani sarees.