Related Research Articles

Anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Sedentariness began in South Asia around 7000 BCE; by 4500 BCE, settled life had spread, and gradually evolved into the Indus Valley Civilisation, one of three early cradles of civilisation in the Old World, flourished between 2500 BCE and 1900 BCE in present-day Pakistan and north-western India. Early in the second millennium BCE, persistent drought caused the population of the Indus Valley to scatter from large urban centres to villages. Indo-Aryan tribes moved into the Punjab from Central Asia in several waves of migration. The Vedic Period of the Vedic people in northern India was marked by the composition of their extensive collections of hymns (Vedas). The social structure was loosely stratified via the varna system, incorporated into the highly evolved present-day Jāti system. The pastoral and nomadic Indo-Aryans spread from the Punjab into the Gangetic plain. Around 600 BCE, a new, interregional culture arose; then, small chieftaincies (janapadas) were consolidated into larger states (mahajanapadas). Second urbanization took place, which came with the rise of new ascetic movements and religious concepts, including the rise of Jainism and Buddhism. The latter was synthesized with the preexisting religious cultures of the subcontinent, giving rise to Hinduism.
Jāti is the term traditionally used to describe a cohesive group of people in the Indian subcontinent, like a tribe, community, clan, sub-clan, or a religious sect. Each Jāti typically has an association with an occupation, geography or tribe. Different intrareligious beliefs or linguistic groupings may also define some Jātis. The term is often translated approximately in English as caste.

Hindūstān was a historical region, polity, and a name for India, historically used to refer to the northern Indian subcontinent later expanded to the entire subcontinent, used in the modern day to refer to the Republic of India. Being the Iranic cognate of the Indic word Sindhu, it originally referred to the land of lower Indus basin during the ancient era, but was later extended to refer to northern Indian subcontinent. It finally referred to the entire subcontinent since the early modern period. Since the Partition of India in 1947, Hindustan continues to be used to the present day as a historic name for the Republic of India.

In the field of comparative religion, many scholars, academics, and religious figures have looked at the relationships between Hinduism and other religions.
The Indian numbering system is used in the Indian subcontinent to express large numbers. The terms lakh or 1,00,000 and crore or 1,00,00,000 are the most commonly used terms in Indian English to express large numbers in the system.

Muzaffarabad is a city in Pakistani-administered Azad Kashmir in the disputed Kashmir region. It is the largest city and the capital of Azad Kashmir, which is a Pakistani-administered administrative territory.

Charas is a cannabis concentrate made from the resin of a live cannabis plant and is handmade in the Indian subcontinent. The plant grows wild throughout Northern India along the stretch of the Himalayas and is an important cash crop for the local people. The difference between charas and hashish is that hashish is made from a dead cannabis plant and charas is made from a live one.
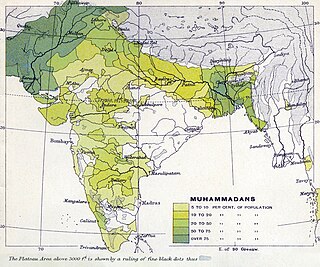
The two-nation theory was an ideology of religious nationalism that advocated Muslim Indian nationhood, with separate homelands for Indian Muslims and Indian Hindus within a decolonised British India, which ultimately led to the Partition of India in 1947. Its various descriptions of religious differences were the main factor in Muslim separatist thought in the Indian subcontinent, asserting that Indian Muslims and Indian Hindus are two separate nations, each with their own customs, traditions, art, architecture, literature, interests, and ways of life.
India's Most Wanted (IMW) was a crime busting fugitive hunter television show initially on Zee TV and later on DD1, India's national broadcaster Doordarshan. The show was made famous by its Anchor-Director and Producer, Suhaib Ilyasi with his unique presentation style and criminals actually being caught with the help of television.

Indica is the name of a short military history about interior Asia, particularly India, written by Arrian in the 2nd century CE. The subject of the book is the expedition of Alexander the Great that occurred between 336 and 323 BCE, about 450 years before Arrian. The book mainly tells the story of Alexander's officer Nearchus' voyage from India to the Persian Gulf after Alexander the Great's conquest of the Indus Valley. However, much of the importance of the work comes from Arrian's in-depth asides describing the history, geography, and culture of Ancient India. Arrian wrote his Indica in the Ionic dialect, taking Herodotus for his literary mode.

India is one of the most biodiverse regions and is home to a large variety of wildlife. It is one of the 17 megadiverse countries and includes three of the world's 36 biodiversity hotspots – the Western Ghats, the Eastern Himalayas, and the Indo-Burma hotspot.
Indian Filipinos are Filipinos of Indian descent who have historical connections with and have established themselves in what is now the Philippines. The term refers to Filipino citizens of either pure or mixed Indian descent currently residing in the country, the latter a result of intermarriages between the Indians and local populations.
The history of Indian cuisine consists of cuisine of the Indian subcontinent, which is rich and diverse. The diverse climate in the region, ranging from deep tropical to alpine, has also helped considerably broaden the set of ingredients readily available to the many schools of cookery in India. In many cases, food has become a marker of religious and social identity, with varying taboos and preferences which has also driven these groups to innovate extensively with the food sources that are deemed acceptable.

The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia, mostly situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geographically, it spans the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, the British Indian Ocean Territory, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Although the terms "Indian subcontinent" and "South Asia" are often used interchangeably to denote the region, the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanistan, which is not considered a part of the subcontinent, while excluding the British Indian Ocean Territory which is geologically associated with the subcontinent.

The history of cave paintings in India or rock art range from drawings and paintings from prehistoric times, beginning in the caves of Central India, typified by those at the Bhimbetka rock shelters from around 10,000 BP, to elaborate frescoes at sites such as the rock-cut artificial caves at Ajanta and Ellora, extending as late as 6th–10th century CE.
The Muslim Dhobi are a South Asian Muslim caste whose traditional occupation is washing clothes. They are considered to be Muslim converts from Hinduism, where the Dhobi castes are launderers. Muslim Dhobis are found throughout the Indian subcontinent.
Suhaib Ilyasi is an Indian television producer and director. He was the host of the notable TV crime show India's Most Wanted. He was the editor of the news magazine Bureaucracy Today. After his wife died in 2000, Ilyasi was charged under Section 304B of the Indian Penal Code for dowry death. He also got involved in a legal battle with his in-laws for the custody of his daughter. Ilyasi was acquitted in the case, while the charges 498A and 304B were also not proven and Ilyasi was discharged for the aforesaid charges in the trial court. Later, he was charged with murdering his wife after 14 years of the incident. On December 20, 2017, he was convicted for the murder and sentenced to life imprisonment. On 5 October 2018, Delhi High Court acquitted him, stating that there was no evidence against him on record to sustain the conviction.
Mansoori (Mansuri) is the community of an Indian Muslim, and this community belongs to Pathans and Rajputs. They are regionally known as Mansoori, Naddaf and Pinjara. They are found in the states of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and North India.
Indo-Haitians are Haitians of Indian ancestry who immigrated to or were born in Haiti. As of 2011, there were about 10,000 people of East Indian ancestry or ancestry from the Indian subcontinent living in Haiti, with the overwhelming majority of them being mixed with people of African and European ancestry. Their descendants are known as Marabous.

Indian reunification refers to the potential reunification of India with Pakistan and Bangladesh, which were partitioned from British India in 1947.