
Sedoreoviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses have a wide host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi. They lack lipid envelopes and package their segmented genome within multi-layered capsids. Lack of a lipid envelope has allowed three-dimensional structures of these large complex viruses to be obtained, revealing a structural and likely evolutionary relationship to the cystovirus family of bacteriophage. There are currently 97 species in this family, divided among 15 genera in two subfamilies. Reoviruses can affect the gastrointestinal system and respiratory tract. The name "reo-" is an acronym for "respiratory enteric orphan" viruses. The term "orphan virus" refers to the fact that some of these viruses have been observed not associated with any known disease. Even though viruses in the family Reoviridae have more recently been identified with various diseases, the original name is still used.

Barnaviridae is a family of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses. Cultivated mushrooms serve as natural hosts. The family has one genus, Barnavirus, which contains one species: Mushroom bacilliform virus. Diseases associated with this family includes La France disease.

Comovirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae; its genera were formerly classified in the family Comoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 62 species in this subfamily, assigned to 3 genera.
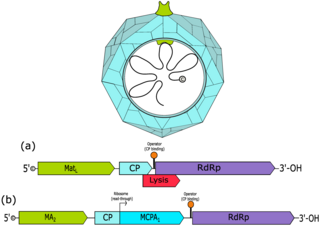
Fiersviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes. Bacteria serve as the natural host. They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells. The family has 185 genera, most discovered by metagenomics. In 2020, the family was renamed from Leviviridae to its current name.

Tombusviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA plant viruses. There are three subfamilies, 17 genera, and 95 species in this family. The name is derived from Tomato bushy stunt virus (TBSV).

Tymoviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 42 species in this family, assigned to three genera, with two species unassigned to a genus.

Arteriviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect vertebrates. Host organisms include equids, pigs, Possums, nonhuman primates, and rodents. The family includes, for example, equine arteritis virus in horses which causes mild-to-severe respiratory disease and reproductive failure, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus type 1 and type 2 in pigs which causes a similar disease, simian hemorrhagic fever virus which causes a highly lethal fever, lactate dehydrogenase–elevating virus which affects mice, and wobbly possum disease virus.

Avulavirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the family Paramyxoviridae. Members of the subfamily are collectively known as avulaviruses. All members of the subfamily primarily infect birds. Avulavirinae was previously recognized as the genus Avulavirus before being elevated to a subfamily. The term avula comes from "avian rubula", distinguishing it from rubulaviruses of the subfamily Rubulavirinae due to avulaviruses only infecting birds and translating protein V from an edited RNA transcript. The most notable avulavirus is the Newcastle disease virus, a strain of Avian orthoavulavirus 1.
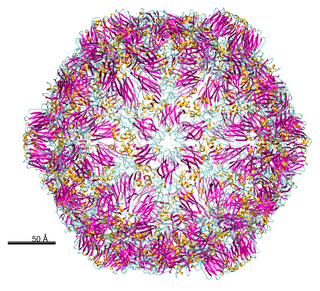
Nepovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae, in the subfamily Comovirinae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 40 species in this genus. Nepoviruses, unlike the other two genera in the subfamily Comovirinae, are transmitted by nematodes.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Betaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 108 species in this family, assigned to 13 genera in two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.

Gammacoronavirus (Gamma-CoV) is one of the four genera of coronaviruses. It is in the subfamily Orthocoronavirinae of the family Coronaviridae. They are enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses of zoonotic origin. Coronaviruses infect both animals and humans.
Alphatetraviridae is a family of viruses. Moths and butterflies serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in the family. Infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.

Alvernaviridae is a family of non-enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Dinoflagellates serve as natural hosts. There is one genus in this family, Dinornavirus, which contains one species: Heterocapsa circularisquama RNA virus 01. Diseases associated with this family include host population control, possibly through lysis of the host cell.
Alphamononivirus is a genus of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect planarian flatworms. Member virus planarian secretory cell nidovirus (PSCNV) has the largest known nonsegmented RNA genome of 41.1kb of any RNA virus. The genus is monotypic. It contains the subgenus Dumedivirus, which contains only one species, Planidovirus 1. Alphamononivirus is also the only member of the subfamily Mononivirinae, which in turn is the only member of family Mononiviridae, which likewise is the only member of the Monidovirineae suborder.

Tobaniviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect vertebrates. Host organisms include mammals, fish, and snakes. The genome size of tobaniviruses ranges from 20 to 32 kilobases. The family is the only member of the suborder Tornidovirineae.

Solemoviridae is a family of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Solemoviridae is a member of the order Sobelivirales.

Betaarterivirus is a genus of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect vertebrates. The genus is in the family Arteriviridae and order Nidovirales. The genus contains four subgenera and six species.

Variarterivirinae is a subfamily of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect vertebrates. The subfamily is in the family Arteriviridae and order Nidovirales. The subfamily contains three genera.















