Related Research Articles

The Gulf of Aden is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, Socotra and Somalia to the south. In the northwest, it connects with the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, and it connects with the Arabian Sea to the east. To the west, it narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura in Djibouti. The Aden Ridge lies along the middle of the Gulf and is causing it to widen about 15mm per year.
Agatharchides or Agatharchus of Cnidus was a Greek historian and geographer.

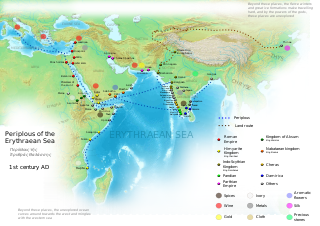
The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, also known by its Latin name as the Periplus Maris Erythraei, is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports like Berenice Troglodytica along the coast of the Red Sea, and others along Horn of Africa, the Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean, including the modern-day Sindh region of Pakistan and southwestern regions of India.

A periplus, or periplous, is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense, the periplus was a type of log and served the same purpose as the later Roman itinerarium of road stops. However, the Greek navigators added various notes, which, if they were professional geographers, as many were, became part of their own additions to Greek geography.

Azania is a name that has been applied to various parts of southeastern tropical Africa. In the Roman period and perhaps earlier, the toponym has been hypothesised to have referred to a portion of the Southeast Africa coast extending from southern Somalia to the border between Mozambique and South Africa. If this is correct, then during classical antiquity Azania was mostly inhabited by Southern Cushitic peoples, whose groups would rule the area until the great Bantu Migration.
Rhapta was an emporion said to be on the coast of Southeast Africa, first described in the 1st century CE. Its location has not been firmly identified, although there are a number of plausible candidate sites. The ancient Periplus of the Erythraean Sea described Rhapta as "the last emporion of Azania", two days' travel south of the Menouthias islands. The Periplus also states that the city and port were ruled by South Arabian vassals of the Himyarite kingdom, particularly a certain “ Mapharitic chieftain.”
Ptolemais Theron was a marketplace on the African side of the Red Sea, whose location is now uncertain.
Simmias was a Macedonian officer, son of Andromenes from Tymphaia and brother of Attalus and Amyntas, the officers of Alexander the Great. He probably served in the division of the phalanx, commanded by his brother Amyntas, as we find him taking the command of it at the battle of Gaugamela during his brother's absence. On this occasion his division was one of those which bore the chief brunt of the battle. In 330 BC, he was accused, together with his brothers, of having been concerned in the conspiracy of Philotas; but the vigorous defence of Amyntas before the Macedonian army procured their joint acquittal.

Zabargad Island is the largest of a group of islands in Foul Bay, Egypt. It covers an area of 4.50 square kilometres. It is not a quaternary volcanic island, but rather is believed to be an upthrusted part of upper mantle material. The nearest island is known as "Rocky Island". The island is slightly north of the Tropic of Cancer, and its highest point is 235 metres.
Simmias of Thebes was an ancient Greek philosopher, disciple of Socrates, and a friend of Cebes. In his Memorabilia, Xenophon includes him in the inner circle of Socrates' followers. He appears in Plato's Phaedo as a main discussion partner of Socrates alongside Cebes, as well as Crito, Phaedrus, and EpistleXIII.
Simmias may refer to:

Ancient Aethiopia, first appears as a geographical term in classical documents in reference to the upper Nile region of Sudan, as well as certain areas south of the Sahara. Its earliest mention is in the works of Homer: twice in the Iliad, and three times in the Odyssey. The Greek historian Herodotus "specifically" uses the appellation to refer to such parts of sub-Saharan Africa as were then known within the inhabitable world.

The Erythraean Sea was a former maritime designation that always included the Gulf of Aden and at times other seas between Arabia Felix and the Horn of Africa. Originally an ancient Greek geographical designation, it was used throughout Europe until the 18–19th centuries. At times the name frequently extended beyond the Gulf of Aden—as in the famous 1st-century Periplus of the Erythraean Sea—to include the present-day Red Sea, Arabian Sea, Persian Gulf, and Indian Ocean as a single maritime area.
The history of Socotra describes the cultures, events, peoples and strategic relevance for sea trade of what is Socotra, an island of the Republic of Yemen, currently under control of the United Arab Emirates (UAE)-backed Southern Transitional Council, a secessionist participant in Yemen's ongoing civil war. Lying between the Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Sea and near major shipping routes, Socotra is the largest of the four islands in the Socotra archipelago.
The Troglodytae, or Troglodyti, were people mentioned in various locations by many ancient Greek and Roman geographers and historians, including Herodotus, Agatharchides, Diodorus Siculus, Strabo, Pliny, Josephus, Tacitus, Claudius Aelianus, Porphyry.
The first documented relations between Ancient India and Ancient Rome occurred during the reign of Caesar Augustus, the first Roman Emperor.
Nelcynda is a place in ancient Kerala. It was described in Pliny's classical work The Natural History as well as in Periplus of the Erythraean Sea. It was believed to be the capital of the Ay kingdom. Nakkada near Niranam in Pathanamthitta district are often identified with Nelcynda.
Lake Monoleus was a coastal feature mentioned by Pliny as being on the Red Sea Coast near Ptolemais Theron. The lake was probably a coastal lagoon.

Avalites was an ancient port city in present-day Somalia. It corresponds with what later became the city of Zeila.
References
- (Diod. iii. 18.)
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Bunbury, Edward Herbert (1870). "Simmias". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology .
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Bunbury, Edward Herbert (1870). "Simmias". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology .