
Chaldea was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BC, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was located in the marshy land of the far southeastern corner of Mesopotamia and briefly came to rule Babylon. The Hebrew Bible uses the term כשדים (Kaśdim) and this is translated as Chaldaeans in the Greek Old Testament, although there is some dispute as to whether Kasdim in fact means Chaldean or refers to the south Mesopotamian Kaldu.

Hammurabi, also spelled Hammurapi, was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from c. 1792 to c. 1750 BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered the city-states of Larsa, Eshnunna, and Mari. He ousted Ishme-Dagan I, the king of Assyria, and forced his son Mut-Ashkur to pay tribute, bringing almost all of Mesopotamia under Babylonian rule.

Babylonia was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia. It emerged as an Akkadian populated but Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BC. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was retrospectively called "the country of Akkad", a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older ethno-linguistically related state of Assyria in the north of Mesopotamia and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom centered around the city of Babylon.

The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to c. 1894–1595 BC, and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty of Babylonia is debated; there is a Babylonian King List A and also a Babylonian King List B, with generally longer regnal lengths. In this chronology, the regnal years of List A are used due to their wide usage.

Nabopolassar was the founder and first king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from his coronation as king of Babylon in 626 BC to his death in 605 BC. Though initially only aimed at restoring and securing the independence of Babylonia, Nabopolassar's uprising against the Neo-Assyrian Empire, which had ruled Babylonia for more than a century, eventually led to the complete destruction of the Assyrian Empire and the rise of the Neo-Babylonian Empire in its place.

Nabonidus was the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 556 BC to the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenian Empire under Cyrus the Great in 539 BC. Nabonidus was the last native ruler of ancient Mesopotamia, the end of his reign marking the end of thousands of years of Sumero-Akkadian states, kingdoms and empires. He was also the last independent king of Babylon. Regarded as one of the most vibrant and individualistic rulers of his time, Nabonidus is characterised by some scholars as an unorthodox religious reformer and as the first archaeologist.

Sîn-šar-iškun was the penultimate king of Assyria, reigning from the death of his brother and predecessor Aššur-etil-ilāni in 627 BC to his own death at the Fall of Nineveh in 612 BC.

The 1790s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1799 BC to December 31, 1790 BC. During this decade, the Near East was in the midst of the Middle Bronze Age.

Samsu-iluna was the seventh king of the founding Amorite dynasty of Babylon, ruling from 1749 BC to 1712 BC, or from 1686 to 1648 BC. He was the son and successor of Hammurabi by an unknown mother. His reign was marked by the violent uprisings of areas conquered by his father and the abandonment of several important cities.

The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and being firmly established through the fall of the Assyrian Empire in 612 BC, the Neo-Babylonian Empire was conquered by the Achaemenid Persian Empire in 539 BC, marking the collapse of the Chaldean dynasty less than a century after its founding.
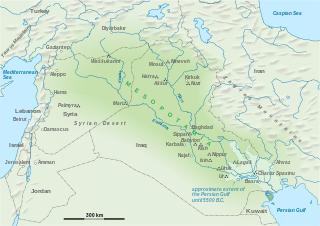
The history of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often called a cradle of civilization.
The Dynasty of Isin refers to the final ruling dynasty listed on the Sumerian King List (SKL). The list of the Kings Isin with the length of their reigns, also appears on a cuneiform document listing the kings of Ur and Isin, the List of Reigns of Kings of Ur and Isin.
Apil-Sin was an Amorite King of the First Dynasty of Babylon. He possibly reigned between c. 1767 to 1749 BC.

The First Sealand dynasty (URU.KÙKI), or the 2nd Dynasty of Babylon, very speculatively c. 1732–1460 BC, is an enigmatic series of kings attested to primarily in laconic references in the king lists A and B, and as contemporaries recorded on the Assyrian Synchronistic king list A.117. Initially it was named the "Dynasty of the Country of the Sea" with Sealand later becoming customary.
'Damiq-ilīšu, was the 15th and final king of Isin. He succeeded his father Sîn-māgir and reigned for 23 years. Some variant king lists provide a shorter reign, but it is thought that these were under preparation during his rule. He was defeated first by Sîn-muballiṭ of Babylon and then later by Rīm-Sîn I of Larsa.
Aššur-uballiṭ II, also spelled Assur-uballit II and Ashuruballit II, was the final ruler of Assyria, ruling from his predecessor Sîn-šar-iškun's death at the Fall of Nineveh in 612 BC to his own defeat at Harran in 609 BC. He was possibly the son of Sîn-šar-iškun and likely the same person as a crown prince mentioned in inscriptions at the Assyrian capital of Nineveh in 626 and 623 BC.

The timeline of ancient Assyria can be broken down into three main eras: the Old Assyrian period, Middle Assyrian Empire, and Neo-Assyrian Empire. Modern scholars typically also recognize an Early period preceding the Old Assyrian period and a post-imperial period succeeding the Neo-Assyrian period.

The Sargonid dynasty was the final ruling dynasty of Assyria, ruling as kings of Assyria during the Neo-Assyrian Empire for just over a century from the ascent of Sargon II in 722 BC to the fall of Assyria in 609 BC. Although Assyria would ultimately fall during their rule, the Sargonid dynasty ruled the country during the apex of its power and Sargon II's three immediate successors Sennacherib, Esarhaddon and Ashurbanipal are generally regarded as three of the greatest Assyrian monarchs. Though the dynasty encompasses seven Assyrian kings, two vassal kings in Babylonia and numerous princes and princesses, the term Sargonids is sometimes used solely for Sennacherib, Esarhaddon and Ashurbanipal.
The Isin-Larsa period is a phase in the history of ancient Mesopotamia, which extends between the end of the Third Dynasty of Ur and the conquest of Mesopotamia by King Hammurabi of Babylon leading to the creation of the First Babylonian dynasty. According to the approximate conventional dating, this period begins in 2025 BCE and ended in 1763 BCE. It constitutes the first part of the Old Babylonian period, the second part being the period of domination of the first dynasty of Babylon, which ends with the Sack of Babylon in 1595 BCE and the rise of the Kassites.













