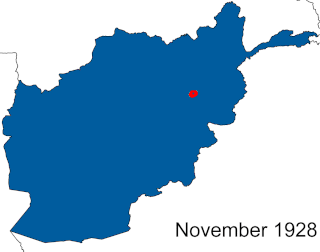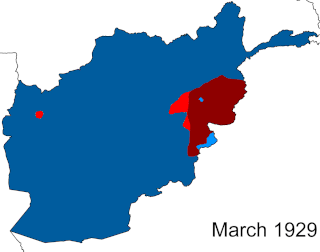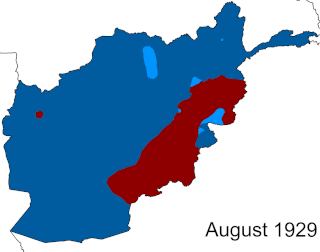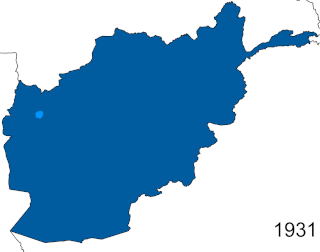
The Afghan Civil War was fought from 14 November 1928 to 13 October 1929. Rebelling, and subsequently governing Saqqawist (Saqāwīhā) forces under Habibullāh Kalakāni fought against various opposing tribes and rival monarchs in the Kingdom of Afghanistan, among whom Mohammed Nādir Khān eventually achieved a preponderant role. Despite early successes, such as the capture of Kabul and defeat of Amanullah Khan on 17 January 1929 or the capture of Kandahar on 3 June, the Saqqawists were eventually deposed by anti-Saqqawist forces led by Nadir on 13 October 1929, leading to Nadir's ascension as King of Afghanistan, who ruled until his assassination on 3 November 1933.

Dost Mohammad Khan Barakzai, nicknamed the Amir-i Kabir, was the founder of the Barakzai dynasty and one of the prominent rulers of Afghanistan during the First Anglo-Afghan War. With the decline of the Durrani dynasty, he became the Emir of Afghanistan in 1826. An ethnic Pashtun, he belonged to the Barakzai tribe. He was the 11th son of Payinda Khan, chief of the Barakzai Pashtuns, who was killed in 1799 by King Zaman Shah Durrani.
Sultan Ahmad Khan b. Sardar 'Azim Muhammadzai, also known as Sultan Jan was the ruler of the Principality of Herat from September 1857 to April 1863. He was a nephew of Dost Mohammad Khan. In 1855-56, Sultan Ahmad Khan sent a petition to the Shah, Nasir al-Din. If the Iranians would support Sultan Ahmad Khan with an army, he would overthrow the Amir-i Kabir and incorporate Afghanistan into the Guarded Domains. However, Sultan Ahmad Khan was intercepted by Dost Mohammad Khan, who exiled Sultan Ahmad Khan to Iran.

Mohammad Yaqub Khan was Emir of Afghanistan from February 21 to October 12, 1879. He was a Pashtun and the son of the previous ruler, Sher Ali Khan.
The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians is a book comprising translations of medieval Persian chronicles based on the work of Henry Miers Elliot. It was originally published as a set of eight volumes between 1867–1877 in London. The translations were in part overseen by Elliot, whose efforts were then extended and edited posthumously by John Dowson.

Faiz Muhammad Kāteb also known as Kāteb (کاتب) was a writer and historian. He was Afghan court chronicler, a skilled calligrapher and secretary to Habibullah Khan from 1901 to 1919.

Mohammad Afzal Khan was the governor of Afghan Turkestan from 1849 to 1863 and Emir of Afghanistan from May 1866 to October 1867. The oldest son of Dost Mohammad Khan, Afzal Khan was born in Kabul in 1815. His father died on 9 June 1863 followed by a civil war between Dost Mohammad Khan's sons. In May 1866 he seized power from his brother Sher Ali Khan and captured Kabul. A year later he contracted cholera and died on 7 October 1867. Following Afzal Khan's death, Mohammad Azam Khan was proclaimed Amir of Afghanistan. He was an ethnic Pashtun and belonged to the Barakzai tribe.
Robert Duncan McChesney is a scholar of the social and cultural history of Central Asia, Iran, and Afghanistan.
Takhteh Pol, also known as Takhtapul, is a village in Balkh Province in northern Afghanistan. It was created in by Afzal Khan as a cantonment after the Afghan conquest of the Balkh Wilayat in 1849-1850. Balkh was in ruins, so with materials from the ruined town of Balkh, he established the city of Takhtapul. Gardens and courts were created as well. Within three years the city was established.

Mohammad Nadir Shah was King of Afghanistan from 15 October 1929 until his assassination in November 1933. He became the king after his victory in the Afghan Civil War of 1928–29. Previously, he served as Minister of War, Afghan Ambassador to France, and as a general in the Royal Afghan Army. He and his son Mohammad Zahir Shah, who succeeded him, are part of the Musahiban.

Arshad Sami Khan was a Pakistani diplomat, civil servant and fighter pilot who at peak of his career attained the highest rank of Federal Secretary. He started his career as a Pakistan Air Force fighter pilot and later served three presidents of Pakistan as their aide-de-camp (ADC) and later went on to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs where he served three presidents and four prime ministers as chief of protocol. He was later appointed as a diplomatic ambassador of Pakistan to 14 countries. This was followed by his appointment as the first commissioner general of Pakistan. He was also Federal Secretary of Culture and retired as a top BPS-22 grade bureaucratic officer. He was also the father of singer and music composer Adnan Sami.

Mohammad Azam Khan was the Emir of Afghanistan from October 7, 1867, to August 21, 1868. He was born in 1820 and was the fifth son of Dost Mohammed Khan. He was an ethnic Pashtun and belonged to the Barakzai tribe. Azam Khan succeeded his brother Mohammad Afzal Khan after the latter's death on October 7, 1867. Sher Ali Khan was reinstated as Amir of Afghanistan and his forces captured Kabul on August 21, 1868. Sher Ali himself entered Kabul on September 8, 1868. Mohammad Azam Khan fled to Sistan and then to Iran, where he died in 1870.

The First Herat War was an attack on the Principality of Herat by Qajar Iran during the Great Game. Herat was held by Kamran Shah and his vizier Yar Mohammad Khan Alakozai. The Shah of Persia was Mohammed Shah Qajar. Four Europeans were involved: the British, Sir John McNeill and Eldred Pottinger as well as the Russians, Count Simonich and Jan Prosper Witkiewicz. Sher Mohammad Khan Hazara, an ally of Kamran and chieftain of the Qala-e Naw Hazaras, helped form a Sunni confederacy of Aimaq, Turkmen, and Uzbek tribes and played a crucial role in defending Herat when the city was besieged. The siege ended when neither side gained a clear advantage, the British threatened to take military action and the Russians withdrew their support.

Timur Shah Durrani, also known as Timur Shah Abdali or Taimur Shah Abdali was the second ruler of the Afghan Durrani Empire, from November 1772 until his death in 1793. An ethnic Pashtun, he was the second eldest son of Ahmad Shah Durrani.

Slavery in Afghanistan was present in the post-Classical history of Afghanistan, continued during the Middle Ages, and persisted into the 1920s.
The Afghan Civil War was fought from 9 June 1863 to January 1869. It began as a result of Dost Mohammad Khan's death on 9 June 1863 and the subsequent power struggles among his sons. Dost Mohammad consolidated his power in the second half of his reign within his inner family. His sons were appointed governors of provinces and effectively acted autonomous from the central government. This would inevitably lead to his sons fighting for control after his death.
The Hazarajat Campaign of 1843 began as a result of the post First Anglo-Afghan War situation in Afghanistan. Behsud and Bamiyan had broken away from Afghan rule as a result of the war, and Dost Mohammad sought to reconquer it following his resumption of power in Kabul.

The Shaghasi are, alongside the Seraj and Telai, a prominent and powerful cadet-branch of the Afghan royal family. They belong to the Zirak branch of the Durrani confederacy, and are primarily centered around Kandahar. They can also be found in other provinces throughout central Afghanistan.












