
The ancient Egyptian Hill-country or "Foreign land" hieroglyph (𓈉) is a member of the sky, earth, and water hieroglyphs. A form of the hieroglyph in color, has a green line-(banding) at the base of the hieroglyph. The hieroglyph refers to the hills, and mountains, on both sides of the Nile River, and thus the green references the verdant black farming land adjacent to the river proper. It is coded N25 in Gardiner's sign list, and U+13209 in Unicode. It is a determinative hieroglyph, simply conveying a meaning, and has no phonetic value.
The Egyptian hieroglyph representing gold, phonetic value nb, is important due to its use in the Horus-of-Gold name, one of the Fivefold Titulary names of the Egyptian pharaoh.
The ancient Egyptian Branch hieroglyph, also called a Stick, is a member of the trees and plants hieroglyphs.
The ancient Egyptian child hieroglyph is part of the Egyptian Gardiner's Sign List hieroglyphs for the beginning core subgroup of Man and his Occupations. It relates to the child, and childhood, and has a version for the Pharaoh, as a child.

The Egyptian hieroglyph Townsite-city-region is Gardiner sign listed no. O49 for the intersection of a town's streets. In some Egyptian hieroglyph books it is called a city plan.
The ancient Egyptian Brazier hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. Q7 for the cooking brazier. It is shown from the Old Kingdom in the style of a vertical burning flame upon four feet, but the hieroglyph has the flame hiding the fourth foot. Another Gardiner unlisted form has the four feet, with no flame, and in a plan view.

The use of the Spine with fluid hieroglyph is for words showing "length", as opposed to 'breadth',. Some example words for 'length' are: to be long, length, to extend, extended; and for to expand, to dilate, words like: joy, gladness, pleasure, delight.
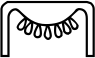
The Ancient Egyptian Swallow hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. G36 for swallow birds. The Sparrow hieroglyph appears similar in size and shape, but it is used to represent small, or bad items.
The ancient Egyptian Grape arbor hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. M43 in Gardiner's subcategory for trees and plants. The hieroglyph shows a horizontal vine with stylized bunches suspended below; each end is supported by the hieroglyph for a "prop", Gardiner no. O30,
The ancient Egyptian Face hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. D2 is a portrayal of the human face, frontal view.

The ancient Egyptian Pick hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed nos. U17, U18 is a portrayal of a 'pick upon the side view of a block'; it is in the Gardiner subset for agriculture, crafts, and professions.

The ancient Egyptian Night hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed nos. N3 is a portrayal of the sky with the 'was' scepter hanging from it; it is in the Gardiner subset for "sky, earth, and water".

The ancient Egyptian Two Whips with Shen ring hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. S23 is a portrayal of the Shen ring with two Egyptian flails-(Crook and flail); it is a member of the Gardiner subset for "crowns, dress, staves, etc".

In the Egyptian language, the single stair hieroglyph is used as a determinative.

The ancient Egyptian Water-jugs-in-stand hieroglyph, is Gardiner sign listed no. W17, W18, within the Gardiner signs for vessels of stone and earthenware.

The ancient Egyptian Scribe equipment hieroglyph 𓏞, or its reversed form 𓏟, portrays the equipment of the scribe. Numerous scribes used the hieroglyph in stating their name, either on papyrus documents, but especially on statuary or tomb reliefs.

The Egyptian hieroglyph representing a honey bee. It is used as an ideogram for "bee" (bjt), but most frequently as part of the title of the King of Upper and Lower Egypt, rendered nswt-bjtj.

The Land, irrigated hieroglyph represents "district, nome". It is a determinative in the name of provinces and regions in the noun ḥsp, for "garden", "vegetable garden", and "orchard".

In Egyptian hieroglyphs, the hieroglyph is used for the phonetic value of sma, with meanings of to join together, to unite with.

The Hippopotamus hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. E25, in the category of mammals. It is used in Egyptian hieroglyphs as a determinative in words designating the animal, in Egyptian as db, and kh3b.

















