
Iceland is an island country at the confluence of the North Atlantic and Arctic oceans, east of Greenland and immediately south of the Arctic Circle, atop the constructive boundary of the northern Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The island country is the world's 18th largest in area and one of the most sparsely populated. It is the westernmost European country when not including Greenland and has more land covered by glaciers than continental Europe. Its total size is 103,125 km2 (39,817 sq mi) and possesses an exclusive economic zone of 751,345 km2 (290,096 sq mi).

A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma or by circulation through faults to hot rock deep in the Earth's crust. In either case, the ultimate source of the heat is the radioactive decay of naturally occurring radioactive elements in the Earth's mantle, the layer beneath the crust.

Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the Earth's crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for millennia.

A mudpot, or mud pool, is a type of acidic hot spring, or fumarole, with limited water. It usually takes the form of a pool of bubbling mud, as a result of the acid and microorganisms decomposing surrounding rock into clay and mud.

Landmannalaugar is a location in Iceland's Fjallabak Nature Reserve in the Highlands. It is on the edge of the Laugahraun lava field. This lava field was formed by an eruption in approximately 1477. It is largely known for its natural geothermal hot springs and surrounding landscape.

Thermae Bath Spa is a combination of the historic spa and a contemporary building in the city of Bath, England, and reopened in 2006. Bath and North East Somerset council own the buildings, and, as decreed in a Royal Charter of 1590, are the guardians of the spring waters, which are the only naturally hot, mineral-rich waters in the UK. The Spa is operated by YTL Hotels.
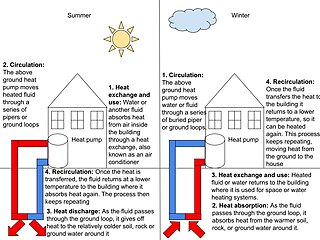
Geothermal heating is the direct use of geothermal energy for some heating applications. Humans have taken advantage of geothermal heat this way since the Paleolithic era. Approximately seventy countries made direct use of a total of 270 PJ of geothermal heating in 2004. As of 2007, 28 GW of geothermal heating capacity is installed around the world, satisfying 0.07% of global primary energy consumption. Thermal efficiency is high since no energy conversion is needed, but capacity factors tend to be low since the heat is mostly needed in the winter.

Public baths originated when most people in population centers did not have access to private bathing facilities. Though termed "public", they have often been restricted according to gender, religious affiliation, personal membership, and other criteria.

A spa is a location where mineral-rich spring water is used to give medicinal baths. Spa towns or spa resorts typically offer various health treatments, which are also known as balneotherapy. The belief in the curative powers of mineral waters goes back to prehistoric times. Such practices have been popular worldwide, but are especially widespread in Europe and Japan. Day spas and medspas are also quite popular, and offer various personal care treatments.

Larderello is a frazione of the comune of Pomarance, in Tuscany in central Italy, renowned for its geothermal productivity.

A hot tub is a large tub full of water used for hydrotherapy, relaxation or pleasure. Some have powerful jets for massage purposes. Hot tubs are sometimes also known as "spas" or by the trade name Jacuzzi. Hot tubs may be located outdoors or indoors.

The Blue Lagoon is a geothermal spa in southwestern Iceland. The spa is located in a lava field 5 km (3.1 mi) from Grindavík and in front of Mount Þorbjörn on the Reykjanes Peninsula, in a location favourable for geothermal power, and is supplied by water used in the nearby Svartsengi geothermal power station. The Blue Lagoon is approximately 20 km (12 mi) from Keflavík International Airport, and is one of the most visited tourist attractions in Iceland.

A mud bath is a therapeutic spa treatment that involves soaking in a bath of warm mud, often in a natural hot spring or geothermal pool. Mud baths have been used for centuries as a way to promote health and relaxation, and are still popular today in many parts of the world.

Southern Peninsula is an administrative unit and part of Reykjanesskagi, or Reykjanes Peninsula, a region in southwest Iceland. It was named after Reykjanes, the southwestern tip of Reykjanesskagi.

Waiwera Hot Pools is a hot springs system located in the small coastal village of Waiwera, just north of Auckland, New Zealand. They were known to the Māori people for centuries before being developed. In the 1960s and 70s overproduction and overpumping of the geothermal aquifer led to significant loss of pressure and desiccation of the springs in the late 1970. A decade later the thermal springs began to recover, although the system has not returned to the former artesian conditions.

Tikitere, also known as "Hell's Gate", is a suburb in Rotorua's most active geothermal area on State Highway 30, between Lake Rotorua and Lake Rotoiti in the Bay of Plenty, New Zealand. It includes many geothermal features such as steaming lakes, mudpools, fumaroles, a mud volcano and the Kakahi Falls, the largest hot waterfall in the southern hemisphere.

Halcyon Hot Springs, also known simply as Halcyon, is a hot springs resort and spa on the east side of Upper Arrow Lake, between Galena Bay and Nakusp, in the West Kootenay region of British Columbia. Nearby to the northeast, Halcyon Mountain derives its name from the springs.

Vaðlaheiðargöng is a toll tunnel in the north of Iceland along Route 1, just east of Akureyri. It passes between Eyjafjörður and Fnjóskadalur. It is 7.4 km (4.6 mi) long and replaces a 21 km section of Route 1 including the Víkurskarð pass, often closed during winter. The tunnel shortens the travel between Akureyri and Husavik by 16 km. As of 2022, it is the only toll road in Iceland.
Fairmont Hot Springs Resort is a resort in Silver Bow County, Montana, United States.





















