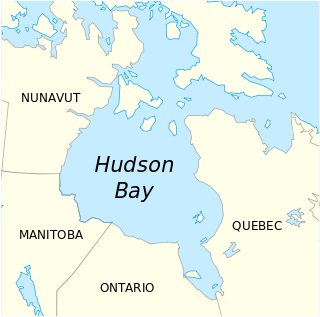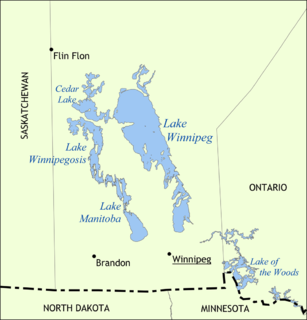
Lake Winnipeg is a very large, but relatively shallow 24,514-square-kilometre (9,465 sq mi) lake in North America, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Its southern end is about 55 kilometres (34 mi) north of the city of Winnipeg. It is the largest lake within southern Canada's borders, and is part of the most undeveloped large watershed of southern Canada.

Lake Winnipegosis is a large (5,370 km²) lake in central North America, in Manitoba, Canada, some 300 km northwest of Winnipeg. It is Canada's eleventh-largest lake. An alternate spelling, once common but now rare, is Lake Winipigoos or simply 'Lake Winipigis'.

The Nelson River is a river of north-central North America, in the Canadian province of Manitoba. The river drains Lake Winnipeg and runs 644 kilometres (400 mi) before it ends in Hudson Bay. Its full length is 2,575 kilometres (1,600 mi), it has mean discharge of 2,370 cubic metres per second (84,000 cu ft/s), and has a drainage basin of 1,072,300 square kilometres (414,000 sq mi), of which 180,000 square kilometres (69,000 sq mi) is in the United States.

The Souris River or Mouse River is a river in central North America. It is about 700 km (435 mi) in length and drains about 23,600 square miles (61,100 km2). It rises in the Yellow Grass Marshes north of Weyburn, Saskatchewan. It wanders south through North Dakota beyond Minot to its most southern point at the city of Velva, and then back north into Manitoba. The river passes through the communities of Melita, Hartney, Souris and Wawanesa and on to its confluence with the Assiniboine River at Treesbank, about 25 miles (40 km) south east of Brandon. The main tributaries which flow into the Souris in Manitoba are the Antler River, the Gainsborough and Plum Creeks. Much of its drainage basin is fertile silt and clay deposited by former glacial Lake Souris.

The Pembina River is a tributary of the Red River of the North, approximately 319 miles (513 km) long, in southern Manitoba in Canada and northeastern North Dakota in the United States. It drains an area of the prairie country along the Canada–US border, threading the Manitoba-North Dakota border eastward to the Red River. Via the Red River, Lake Winnipeg and the Nelson River, it is part of the watershed of Hudson Bay.
The Winnipeg River is a Canadian river which flows roughly northwest from Lake of the Woods in the province of Ontario to Lake Winnipeg in Manitoba. This river is 235 kilometres (146 mi) long from the Norman Dam in Kenora to its mouth at Lake Winnipeg. Its watershed is 106,500 square kilometres (41,100 sq mi) in area, mainly in Canada. About 29,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi) of the watershed is in northern Minnesota, United States.

The Qu'Appelle River is a Canadian river that flows 430 kilometres (270 mi) east from Lake Diefenbaker in southwestern Saskatchewan to join the Assiniboine River in Manitoba, just south of Lake of the Prairies, near the village of St. Lazare.

The Hayes River is a river in Northern Region, Manitoba, Canada that flows from Molson Lake to Hudson Bay at York Factory. It was an historically important river in the development of Canada, and is today a Canadian Heritage River and the longest naturally flowing river in Manitoba.
McCreary is an unincorporated urban community in the Municipality of McCreary within the Canadian province of Manitoba that held village status prior to January 1, 2015. McCreary covers an area of 1.70 km2, and has a population of 472. Though settled as early as the 19th century, it was incorporated as a village in 1964, and amalgamated with the Municipality of McCreary in 2015. As the self-proclaimed Ski Capital of Manitoba, the former village previously held significance as the closest settlement to the former Mount Agassiz Ski Area.

East St. Paul is a rural municipality in Manitoba, Canada. It is located north-east of and adjacent to the city of Winnipeg, and is part of the Winnipeg Metropolitan Area. The municipality was formed on 3 November 1915 when the municipality of St. Paul (1888-1914) was subdivided into West St. Paul and East St. Paul, with the Red River acting as the dividing line. It encompasses 41 square kilometres (16 sq mi).

Pilot Mound is an unincorporated community recognized as a local urban district that also once held town status in the Canadian province of Manitoba. It is located within the Municipality of Louise approximately 60 km west of the City of Morden.

Division No. 19, also informally known as North East Manitoba, is a census division in the Canadian province of Manitoba. Division No. 19 actually extends all the way across the province from west to east at near its middle, although the overwhelming majority of its territory is located in its eastern and southeastern portions. It includes most of Lake Winnipeg, most of Lake Winnipegosis, and some of the north basin of Lake Manitoba.The Northern Region of Manitoba begins at the 53rd Parallel is known as Norman region denoting the start of Northern Manitoba.

Spruce Woods Provincial Park is located in south-central Manitoba, Canada where the Assiniboine River passes through the delta of sediment left by the last glaciation. An area of open and stabilized sand dunes within the park provides habitat to species of plants and animals not found elsewhere in Manitoba. In descending order of land area contained, the park lies within the Rural Municipalities of South Cypress, Victoria, and North Cypress.
Provincial Highway 13 by the Manitoba Infrastructure and Transportation is a Regional Transportation Advisory Committee RTAC Route of Manitoba. The RTAC route is capable of handling RTAC vehicles such as a truck, a truck and pony trailer, a truck and full trailer, a truck tractor and semi-trailer, an A-train, a B-train, or a C-train. The route extends south to north from its junction with PTH 3 and PR 245 in Carman to its junction with PTH 1 and PR 430 north of Oakville. The northern terminus of PTH 13 is located between Portage la Prairie and Manitoba's capital city Winnipeg. The Central Manitoba Railway (CEMR) shortline rail intersects PTH 13 north of Carman, the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) intersects at Elm Creek, and the Canadian National Railway (CNR) at Oakville.

CFB Rivers was a Royal Canadian Air Force base located 5 km (3.1 mi) southwest of Rivers, Manitoba, Canada at the junction of Manitoba Highway 25 and Manitoba Provincial Road 259.

The Echoing River is a river in the Hudson Bay drainage basin in Manitoba and Ontario, Canada. Its flows from its source at Echoing Lake in Unorganized part of Kenora District, Northwestern Ontario to its mouth at the Gods River in Northern Manitoba. The Gods River flows via the Hayes River to Hudson Bay.

Lobsticks are traditional markers found in the Boreal Forests of Canada created by removing the middle branches of a coniferous (pine) tree.
Northway Aviation Ltd is a Canadian bush airline providing scheduled and charter passenger and freight service from St. Andrews Airport, St Andrews Manitoba, Canada utilizing both wheel and float equipped aircraft. The 22-minute Canadian documentary film, Bush Pilot: Reflections on a Canadian Myth, made in 1980 by the National Film Board of Canada (NFB) and directed by Norma Bailey and Robert Lower, is about the early days of Northway Aviation and Canadian bush flying.