VMware, Inc. is an American cloud computing and virtualization technology company with headquarters in California. VMware was the first commercially successful company to virtualize the x86 architecture.

Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon providing on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs to individuals, companies, and governments, on a metered pay-as-you-go basis. These cloud computing web services provide a variety of basic abstract technical infrastructure and distributed computing building blocks and tools. One of these services is Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), which allows users to have at their disposal a virtual cluster of computers, available all the time, through the Internet. AWS's virtual computers emulate most of the attributes of a real computer, including hardware central processing units (CPUs) and graphics processing units (GPUs) for processing; local/RAM memory; hard-disk/SSD storage; a choice of operating systems; networking; and pre-loaded application software such as web servers, databases, and customer relationship management (CRM).
Bertrand Serlet is a French software engineer; he worked first at the Institut national de recherche en informatique et en automatique (INRIA) before leaving France for the United States in 1985. He was the Senior Vice President of Software Engineering at Apple Inc.

Salesforce is an American cloud-based software company headquartered in San Francisco, California. It provides customer relationship management (CRM) service and also provides enterprise applications focused on customer service, marketing automation, analytics, and application development.
Techstars is an American seed accelerator founded in 2006 in Boulder, Colorado. As of 2019, the company had accepted over 1,600 companies into its programs with a combined market capitalization of $18.2bn USD. Fewer than 1% of the over 17,000 applicants are accepted.
SOASTA, Inc. is an American subsidiary of Akamai Technologies that provides services to test websites and web applications.
CloudShare is a cloud computing provider founded in 2007 in Israel. It is now headquartered in San Francisco, California.
Joyent Inc. was a software and services company based in San Francisco, California. Specializing in cloud computing, it marketed infrastructure-as-a-service. On June 15, 2016, the company was acquired by Samsung Electronics.
Nimbula was a computer software company that existed from 2008 to 2017. It developed software for the implementation of public and private cloud computing environments.

ServiceNow is an American software company based in Santa Clara, California that develops a cloud computing platform to help companies manage digital workflows for enterprise operations. Founded in 2003 by Fred Luddy, ServiceNow is listed on the New York Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the Russell 1000 Index and S&P 500 Index. In 2018, Forbes magazine named it number one on its list of the world's most innovative companies.
Silk is a technology company headquartered in Needham, Massachusetts, United States. Silk offers a cloud platform for enterprise customers with mission-critical applications. The company has offices in Boston and Israel.

Nebula, Inc. was a hardware and software company with offices in Mountain View, California, and Seattle, Washington, USA. Nebula developed Nebula One, a cloud computing hardware appliance that turned racks of standard servers into a private cloud. The Nebula One private cloud system was built on the OpenStack open source cloud framework, as well as many other open source software projects.
CloudBees is a continuous delivery software company. Sacha Labourey and Francois Dechery co-founded the company in early 2010, and investors include Matrix Partners, Lightspeed Venture Partners, HSBC, and Verizon Ventures. CloudBees is headquartered in San Jose, CA with additional offices in Raleigh, NC, Lewes, DE, Brussels, Belgium, Seville, Spain and Neuchâtel, Switzerland. CloudBees' software originally included a Platform as a Service offering, which let developers use Jenkins in the cloud, along with an on-premise version of Jenkins with additional functions for enterprise companies. In 2020, CloudBees also introduced a Software Delivery Management platform.
Numecent is an Irvine, California-based software technology company that develops software used to deliver native software applications from on premises, a server farm or the cloud. The patented technology, called Cloudpaging, is based on virtualization which allows the delivery of pre-virtualized software instructions to a user's machine on-demand, where the instructions are executed as soon as they are received.

Indix was a company based in Seattle, Washington in the United States that was offering a cloud-based product information platform. It did also built a broad and deep product catalog to enable mobile and desktop apps and websites to become product-aware. Indix provided access to APIs that enable developers to build product-aware applications. The big data startup was headquartered in Seattle with a product development office in Chennai and was founded in 2010 by former Microsoft executive Sanjay Parthasarathy.
OrionVM Wholesale Pty Limited is an Australian infrastructure as a service provider and white-label cloud platform. Resellers present customers with a rebranded interface for deploying virtual machine instances, which are only billed for what their customers use. Cloud Harmony benchmarked the OrionVM Cloud Platform's InfiniBand-backed network storage as the world's fastest in 2011.

Turbonomic is an enterprise software company headquartered in Boston, MA. The company's product simulates supply and demand forces in order to efficiently allocate resources such as computing, database, memory and storage. It was updated in 2017 for use with cloud computing platforms.
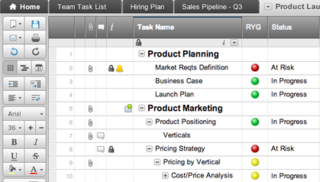
Smartsheet is a software as a service (SaaS) offering for collaboration and work management, developed and marketed by Smartsheet Inc. It is used to assign tasks, track project progress, manage calendars, share documents, and manage other work, using a tabular user interface.
Yottaa is a web and mobile optimization services company based in Waltham, Massachusetts. Its main product is a platform that helps with website conversions, as well as performance and security.
AnswerDash is a B2B software company that facilitates customer service for e-commerce businesses. AnswerDash was founded in Seattle, Washington in 2012 as a spin-off from the Information school of the University of Washington. Its software-as-a-service utilizes machine learning to create databases of context-sensitive support answers for end-users of webpages and mobile applications, thus reducing the need for human customer service. AnswerDash claims to be the first, and as of 2015, the world's leading provider of contextual point-and-click answer technology. In June 2020, AnswerDash was acquired by CloudEngage.






