Related Research Articles

Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses pipes, valves, plumbing fixtures, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. Heating and cooling (HVAC), waste removal, and potable water delivery are among the most common uses for plumbing, but it is not limited to these applications. The word derives from the Latin for lead, plumbum, as the first effective pipes used in the Roman era were lead pipes.

A sanitary sewer is an underground pipe or tunnel system for transporting sewage from houses and commercial buildings to a sewage treatment plant or disposal.

Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid.
Trenchless technology is a type of subsurface construction work that requires few trenches or no continuous trenches. It is a rapidly growing sector of the construction and civil engineering industry. It can be defined as "a family of methods, materials, and equipment capable of being used for the installation of new or replacement or rehabilitation of existing underground infrastructure with minimal disruption to surface traffic, business, and other activities."

High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or "polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density ratio, HDPE is used in the production of plastic bottles, corrosion-resistant piping, geomembranes and plastic lumber. HDPE is commonly recycled, and has the number "2" as its resin identification code.
Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly abbreviated PEX, XPE or XLPE, is a form of polyethylene with cross-links. It is used predominantly in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, insulation for high tension electrical cables, and baby play mats. It is also used for natural gas and offshore oil applications, chemical transportation, and transportation of sewage and slurries. PEX is an alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) or copper tubing for use as residential water pipes.

A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) is a North American set of standard sizes for pipes used for high or low pressures and temperatures. "Nominal" refers to pipe in non-specific terms and identifies the diameter of the hole with a non-dimensional number. Specific pipe is identified by pipe diameter and another non-dimensional number for wall thickness referred to as the Schedule. NPS is often incorrectly called National Pipe Size, due to confusion with the American standard for pipe threads, "national pipe straight", which also abbreviates as "NPS". The European and international designation equivalent to NPS is DN, in which sizes are measured in millimetres, see ISO 6708. The term NB is also frequently used interchangeably with DN.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of fluids such as water for potatory, irrigational, sanitary, and refrigerative purposes, gas, petroleum, liquid waste, or any other liquid or gaseous substances required in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes, connected by various methods, as dictated by the material of which these are made, the material being conveyed, and the particular environmental context in which they will be used, such as soldering, mortaring, caulking, Plastic welding, welding, friction fittings, threaded fittings, and compression fittings.
Directional boring, also referred to as horizontal directional drilling (HDD), is a minimal impact trenchless method of installing underground utilities such as pipe, conduit, or cables in a relatively shallow arc or radius along a prescribed underground path using a surface-launched drilling rig. Directional boring offers significant environmental advantages over traditional cut and cover pipeline/utility installations. The technique is routinely used when conventional trenching or excavating is not practical or when minimal surface disturbance is required.

A cured-in-place pipe (CIPP) is a trenchless rehabilitation method used to repair existing pipelines. It is a jointless, seamless pipe lining within an existing pipe. As one of the most widely used rehabilitation methods, CIPP has applications in sewer, water, gas, chemical and district heating pipelines ranging in diameter from 0.1 to 2.8 meters.
Pipe ramming is a trenchless method for installation of steel pipes and casings. Distances of 30 m or more and over 500 mm in diameter are common, although the method can be used for much longer and larger installations. The method is useful for pipe and casing installations under railway lines and roads, where other trenchless methods could cause subsidence or heaving. The majority of installations are horizontal, although the method can be used for vertical installations.

Plastic pipe is a tubular section, or hollow cylinder, made of plastic. It is usually, but not necessarily, of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow—liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipes are far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.
Line stopping or line plugging is a means of isolating a piping system to provide a shut off where none exists. This process serves as a control, or temporary valve, that can be removed after permanent alterations or valve replacements/additions have been made. With a hot tap previously made on a line, a line stopper is attached to a temporary valve, and the valve is opened. The line stopper is hydraulically or mechanically pushed into the line to seal the pipe. The main is supported by the line stop sleeve. After performing the necessary service, the stop is removed, and a blind flange is installed on the sleeve.

Ductile iron pipe is pipe made of ductile cast iron commonly used for potable water transmission and distribution. This type of pipe is a direct development of earlier cast iron pipe, which it has superseded.
Hot plate welding, also called heated tool welding, is a thermal welding technique for joining thermoplastics. A heated tool is placed against or near the two surfaces to be joined in order to melt them. Then, the heat source is removed, and the surfaces are brought together under pressure. Hot plate welding has relatively long cycle times, ranging from 10 seconds to minutes, compared to vibration or ultrasonic welding. However, its simplicity and ability to produce strong joints in almost all thermoplastics make it widely used in mass production and for large structures, like large-diameter plastic pipes. Different inspection techniques are implemented in order to identify various discontinuities or cracks.
Michels Corporation is a family-owned and operated energy and infrastructure construction company headquartered in Brownsville, WI. Established in 1959, Michels Corporation ranks #27th out of 400 top contractors in North America, performing work throughout the world.
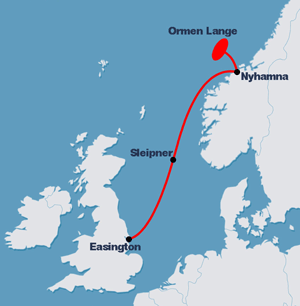
A submarine pipeline is a pipeline that is laid on the seabed or below it inside a trench. In some cases, the pipeline is mostly on-land but in places it crosses water expanses, such as small seas, straits and rivers. Submarine pipelines are used primarily to carry oil or gas, but transportation of water is also important. A distinction is sometimes made between a flowline and a pipeline. The former is an intrafield pipeline, in the sense that it is used to connect subsea wellheads, manifolds and the platform within a particular development field. The latter, sometimes referred to as an export pipeline, is used to bring the resource to shore. Sizeable pipeline construction projects need to take into account many factors, such as the offshore ecology, geohazards and environmental loading – they are often undertaken by multidisciplinary, international teams.
HDPE pipe is a type of flexible plastic pipe used to transfer fluids and gases. It is often employed for replacing aging concrete or steel main pipelines. Constructed from the thermoplastic HDPE, it has low permeability and robust molecular bonding, making it suitable for high-pressure pipelines. HDPE pipe is often used for water mains, gas mains, sewer mains, slurry transfer lines, rural irrigation, fire-suppression system supply lines, electrical and communication conduits, and stormwater and drainage pipes.
A variety of non-destructive examination (NDE) techniques are available for inspecting plastic welds. Many of these techniques are similar to the ones used for inspecting metal welds. Traditional techniques include visual testing, radiography, and various ultrasonic techniques. Advanced ultrasonic techniques such as time of flight diffraction (TOFD) and phased-array ultrasonics (PAUT) are being increasingly studied and used for inspecting plastic pipeline welds. Research in the use of optical coherence tomography (OCT) and microwave reflectrometry has also been conducted.
References
- 1 2 Mohammed Najafi, PhD, PE and Sanjov Gokhale, PhD, PE, Trenchless Technology (New York: McGraw Hill, 2004), p. 295-311. Available from Water Environment Federation at http://www.e-wef.org/timssnet/static/OM/WPM404.htm
- Center for Underground Infrastructure Research and Education CUIRE
- Mohammed Najafi, PhD, PE and Sanjov Gokhale, PhD, PE, Trenchless Technology (New York: McGraw Hill, 2004), p. 295-311. Available from Water Environment Federation at http://www.e-wef.org/timssnet/static/OM/WPM404.htm