
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance, as opposed to cell signaling by endocrine factors, hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system; juxtacrine interactions; and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.

Cluster of differentiation 40, CD40 is a type I transmembrane protein found on antigen-presenting cells and is required for their activation. The binding of CD154 (CD40L) on TH cells to CD40 activates antigen presenting cells and induces a variety of downstream effects.
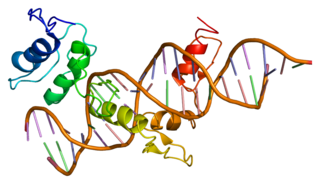
Zinc finger protein GLI1 also known as glioma-associated oncogene is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI1 gene. It was originally isolated from human glioblastoma cells.
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a signaling pathway that transmits information to embryonic cells required for proper cell differentiation. Different parts of the embryo have different concentrations of hedgehog signaling proteins. The pathway also has roles in the adult. Diseases associated with the malfunction of this pathway include cancer.

Smoothened is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMO gene. Smoothened is a Class Frizzled G protein-coupled receptor that is a component of the hedgehog signaling pathway and is conserved from flies to humans. It is the molecular target of the natural teratogen cyclopamine. It also is the target of vismodegib, the first hedgehog pathway inhibitor to be approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
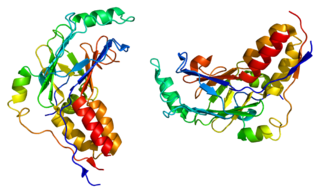
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene.

The sigma-2 receptor (σ2R) is a sigma receptor subtype that has attracted attention due to its involvement in diseases such as neurological diseases, neurodegenerative, neuro-ophthalmic and cancer. It is currently under investigation for its potential diagnostic and therapeutic uses.

Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD274 gene.

Leukotriene B4 receptor 2, also known as BLT2, BLT2 receptor, and BLTR2, is an Integral membrane protein that is encoded by the LTB4R2 gene in humans and the Ltbr2 gene in mice.

G-protein coupled receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family of transmembrane receptors and is involved in signal transduction.

Protein patched homolog 1 is a protein that is the member of the patched family and in humans is encoded by the PTCH1 gene.

CD47 also known as integrin associated protein (IAP) is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the CD47 gene. CD47 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and partners with membrane integrins and also binds the ligands thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) and signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα). CD-47 acts as a don't eat me signal to macrophages of the immune system which has made it a potential therapeutic target in some cancers, and more recently, for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis.

Indian hedgehog homolog (Drosophila), also known as IHH, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the IHH gene. This cell signaling protein is in the hedgehog signaling pathway. The several mammalian variants of the Drosophila hedgehog gene have been named after the various species of hedgehog; the Indian hedgehog is honored by this one. The gene is not specific to Indian hedgehogs.

This gene encodes a member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase subfamily of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and is most highly similar to GRK4 and GRK5. The protein phosphorylates the activated forms of G protein-coupled receptors to regulate their signaling.

Interleukin 17 receptor A, also known as IL17RA and CDw217, is a human gene.

The STAT3-Ser/Hes3 signaling axis is a specific type of intracellular signaling pathway that regulates several fundamental properties of cells.

Purmorphamine was the first small-molecule agonist developed for the protein Smoothened, a key part of the hedgehog signaling pathway, which is involved in bone growth, cardiovascular regeneration and brain development as well as having a number of other functions in the body. Purmorphamine has been shown to induce osteogenesis in bone tissue as well as influencing growth and differentiation of neurons in the brain.
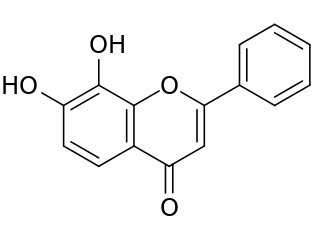
Tropoflavin, also known as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (DHF), is a naturally occurring flavone found in Godmania aesculifolia, Tridax procumbens, and primula tree leaves. It has been found to act as a potent and selective small-molecule agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), the main signaling receptor of the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Tropoflavin is both orally bioavailable and able to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. A prodrug of tropoflavin with greatly improved potency and pharmacokinetics, R13, is under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Hedgehog pathway inhibitors, also sometimes called hedgehog inhibitors, are small molecules that inhibit the activity of a component of the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Due to the role of aberrant Hedgehog signaling in tumor progression and cancer stem cell maintenance across cancer types, inhibition of the Hedgehog signaling pathway can be a useful strategy for restricting tumor growth and for preventing the recurrence of the disease post-surgery, post-radiotherapy, or post-chemotherapy. Thus, Hedgehog pathway inhibitors are an important class of anti-cancer drugs. At least three Hedgehog pathway inhibitors have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for cancer treatment. These include vismodegib and sonidegib, both inhibitors of Smoothened (SMO), which are being used for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Arsenic trioxide, an inhibitor of GLI transcription factors, is being used for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. In addition, multiple other Hedgehog pathway inhibitors are in different phases of clinical trials.
Ted M. Dawson is an American neurologist and neuroscientist. He is the Leonard and Madlyn Abramson Professor in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Director of the Institute for Cell Engineering at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. He has joint appointments in the Department of Neurology, Neuroscience and Department of Pharmacology and Molecular Sciences.

















