Sodium laureth sulfate (SLES), an accepted contraction of sodium lauryl ether sulfate, also called sodium alkylethersulfate, is an anionic detergent and surfactant found in many personal care products and for industrial uses. SLES is an inexpensive and very effective foaming agent. SLES, sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), ammonium lauryl sulfate (ALS), and sodium pareth sulfate are surfactants that are used in many cosmetic products for their cleaning and emulsifying properties. It is derived from palm kernel oil or coconut oil. In herbicides, it is used as a surfactant to improve absorption of the herbicidal chemicals and reduces time the product takes to be rainfast, when enough of the herbicidal agent will be absorbed.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) or sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), sometimes written sodium laurilsulfate, is an organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)11OSO3Na and structure H3C−(CH2)11−O−S(=O)2−O−Na+. It is an anionic surfactant used in many cleaning and hygiene products. This compound is the sodium salt of the 12-carbon organosulfate. Its hydrocarbon tail combined with a polar "headgroup" give the compound amphiphilic properties that make it useful as a detergent. SDS is also component of mixtures produced from inexpensive coconut and palm oils. SDS is a common component of many domestic cleaning, personal hygiene and cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food products, as well as of industrial and commercial cleaning and product formulations.

Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word "surfactant" is a blend of surface-active agent, coined in 1950. As they consist of a water-repellent and a water-attracting part, they enable water and oil to mix; they can form foam and facilitate the detachment of dirt.

Windex is an American brand of glass and hard-surface cleaners—originally in glass containers, later in plastic ones.
Ammonium lauryl sulfate (ALS) is the INCI name and common name for ammonium dodecyl sulfate (CH3(CH2)10CH2OSO3NH4). The anion consists of a nonpolar hydrocarbon chain and a polar sulfate end group. The combination of nonpolar and polar groups confers surfactant properties to the anion: it facilitates dissolution of both polar and non-polar materials. This salt is classified as a sulfate ester. It is made from coconut or palm kernel oil for use primarily in shampoos and body-wash as a foaming agent. Lauryl sulfates are very high-foam surfactants that disrupt the surface tension of water in part by forming micelles at the surface-air interface.
Ivory is an American flagship personal care brand created by the Procter & Gamble Company (P&G), including varieties of white and mildly scented bar soap that became famous for its claim of purity and for floating on water. Over the years, the brand has been extended to other varieties and products.
The International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) are the unique identifiers for cosmetic ingredients such as waxes, oils, pigments, and other chemicals that are assigned in accordance with rules established by the Personal Care Products Council (PCPC), previously the Cosmetic, Toiletry, and Fragrance Association (CTFA). INCI names often differ greatly from systematic chemical nomenclature or from more common trivial names and is a mixture of conventional scientific names, Latin and English words. INCI nomenclature conventions "are continually reviewed and modified when necessary to reflect changes in the industry, technology, and new ingredient developments".

1,4-Dioxane is a heterocyclic organic compound, classified as an ether. It is a colorless liquid with a faint sweet odor similar to that of diethyl ether. The compound is often called simply dioxane because the other dioxane isomers are rarely encountered.
A foaming agent is a material such as a surfactant or a blowing agent that facilitates the formation of foam. A surfactant, when present in small amounts, reduces surface tension of a liquid or increases its colloidal stability by inhibiting coalescence of bubbles. A blowing agent is a gas that forms the gaseous part of the foam.
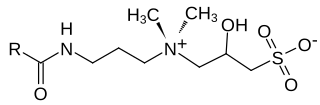
Hydroxysultaines are chemical compounds used in high-foaming shampoos, bath products and shower gels especially in conjunction with ether sulfates and alkyl sulfates. They are also used in industrial applications where high, stable foam is required. Chemically, hydroxysultaines are zwitterionic, typically containing covalently linked positive and negative ions.
Sodium myreth sulfate is a mixture of organic compounds with both detergent and surfactant properties. It is found in many personal care products such as soaps, shampoos, and toothpaste. It is an inexpensive and effective foaming agent. Typical of many detergents, sodium myreth sulfate consists of several closely related compounds. Sometimes the number of ethylene glycol ether units (n) is specified in the name as myreth-n sulfate, for example myreth-2 sulfate.
Glycol ethers are a class of chemical compounds consisting of alkyl ethers that are based on glycols such as ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. They are commonly used as solvents in paints and cleaners. They have good solvent properties while having higher boiling points than the lower-molecular-weight ethers and alcohols.
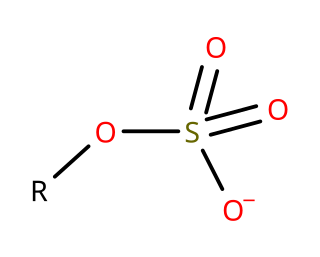
In organosulfur chemistry, organosulfates are a class of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the structure R−O−SO−3. The SO4 core is a sulfate group and the R group is any organic residue. All organosulfates are formally esters derived from alcohols and sulfuric acid although many are not prepared in this way. Many sulfate esters are used in detergents, and some are useful reagents. Alkyl sulfates consist of a hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain, a polar sulfate group and either a cation or amine to neutralize the sulfate group. Examples include: sodium lauryl sulfate and related potassium and ammonium salts.
Oleochemistry is the study of vegetable oils and animal oils and fats, and oleochemicals derived from these fats and oils. The resulting product can be called oleochemicals (from Latin: oleum "olive oil"). The major product of this industry is soap, approximately 8.9×106 tons of which were produced in 1990. Other major oleochemicals include fatty acids, fatty acid methyl esters, fatty alcohols and fatty amines. Glycerol is a side product of all of these processes. Intermediate chemical substances produced from these basic oleochemical substances include alcohol ethoxylates, alcohol sulfates, alcohol ether sulfates, quaternary ammonium salts, monoacylglycerols (MAG), diacylglycerols (DAG), structured triacylglycerols (TAG), sugar esters, and other oleochemical products.

Shampoo is a hair care product, typically in the form of a viscous liquid, that is formulated to be used for cleaning (scalp) hair. Less commonly, it is available in solid bar format. Shampoo is used by applying it to wet hair, massaging the product in the hair, roots and scalp, and then rinsing it out. Some users may follow a shampooing with the use of hair conditioner.

Woolite is an American brand of laundry detergent and cleaning products owned by the English-Dutch company Reckitt Benckiser. The company acquired the Woolite brand when it bought Boyle-Midway from American Home Products / Wyeth in 1990. The company manufactures laundry accessories, among other consumer goods.
C12-15 pareth-12 (INCI name) is an emulsifier and surfactant commonly used in cosmetics formulations. It is a polyethylene glycol ether formed by combining synthetic C12–C15 fatty alcohols with 12 moles of ethylene oxide.
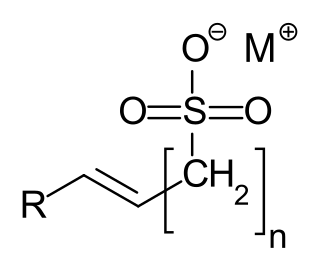
α-Olefin sulfonates are a group of anionic surfactants, which are used as detergents. The compounds contain a - mostly linear, primary - alkyl R and a monovalent cation M, preferably sodium. The most frequently used example of this group of substances is sodium α-olefin sulfonate.

Scymnol, more specifically 5β-scymnol, is a synthetic INCI-listed skin conditioning ingredient. The molecule is a steroid derivative that behaves as a hydroxyl radical scavenger and is used for the treatment of skin blemishes such as blocked pores and acne.








