
Humulus, hop, is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The hop is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Hops are the female flowers of the hop species H. lupulus; as a main flavor ingredient in beer, H. lupulus is widely cultivated for use by the brewing industry.

Solanum is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants, which include three food crops of high economic importance, the potato, the tomato and the eggplant. It also contains the nightshades and horse nettles, as well as numerous plants cultivated for their ornamental flowers and fruit.

Fennel is a flowering plant species in the carrot family. It is a hardy, perennial herb with yellow flowers and feathery leaves. It is indigenous to the shores of the Mediterranean but has become widely naturalized in many parts of the world, especially on dry soils near the sea-coast and on riverbanks.

The tamarillo is a small tree or shrub in the flowering plant family Solanaceae. It is best known as the species that bears the tamarillo, an egg-shaped edible fruit. It is also known as the tree tomato, tomate de árbol, tomate andino, tomate serrano, blood fruit, tomate de yuca, tomate de españa, sachatomate, berenjena and tamamoro in South America, and terong Belanda in Indonesia. They are popular globally, especially in New Zealand, Ecuador, Rwanda, Australia, and the United States.

Prunus serrulata or Japanese cherry, also called hill cherry, oriental cherry, East Asian cherry, Tai-haku, or Taihaku, is a species of cherry native to China, Japan, Korea, and India, and is used for its spring cherry blossom displays and festivals. Current sources consider it to be part of a species complex with P. jamasakura and P. leveilleana, which have been reduced to synonyms.

Solanum aviculare, commonly called poroporo, kangaroo apple, pam plum (Australia), or New Zealand nightshade, is a soft-wooded shrub native to New Zealand and the east coast of Australia.

Solanum centrale, the kutjera, or Australian desert raisin, is a plant native to the more arid parts of Australia. Like other "bush tomatoes", it has been used as a food source by Central Australia and Aboriginal groups for millennia.

Solanum lycocarpum, or wolf apple, is common in the Brazilian savanna, the Cerrado ecoregion. The plant is called lobeira or fruta-do-lobo in Portuguese.

Solanum aethiopicum, the bitter tomato, Ethiopian eggplant (ባሚያ), or nakati, is a fruiting plant of the genus Solanum mainly found in Asia and Tropical Africa. It is also known as Ethiopian nightshade, garden eggs, and mock tomato. It is a popular vegetable in north-east India, and is known as khamen akhaba in Manipuri and samtawk in Mizo. They are called Titay bii or simply bii in Darjeeling, Sikkim and Nepal and are relished with meat, particularly pork. These names are a result of its varied morphology, with ripe fruit often looking like a cross between an eggplant and a tomato, which are also from Solanum. In fact, the Ethiopian eggplant was so much confused with the ordinary eggplant that this was considered by some a variety violaceum of S. aethiopicum.

Solanum torvum is a bushy, erect and spiny perennial plant used horticulturally as a rootstock for eggplant. Grafted plants are very vigorous and tolerate diseases affecting the root system, thus allowing the crop to continue for a second year.

Ixora coccinea is a species of flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is a common flowering shrub native to Southern India, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. It has become one of the most popular flowering shrubs in South Florida gardens and landscapes. It is the national flower of Suriname.

Goodyera pubescens, the downy rattlesnake plantain, is one of the most common orchids native to eastern North America. It is found from Florida to Nova Scotia, west to eastern Oklahoma, Minnesota and Ontario.

Solanum erianthum is a species of nightshade that is native to southern North America and northern South America. It has been introduced to other parts of the world and has a nearly pantropical distribution. Common names include potatotree, mullein nightshade, velvet nightshade, and salvadora. The potatoes are not the fruits of the trees, they are the leaves.

Manipuri cuisine is usually represented by the traditional cuisine of the Meiteis, an ethnic majority of Manipur, a state of North Eastern India. Daily meals are based on rice, with a few side dishes of vegetables and fish. A meal would usually have a vegetable stew called ensaang or athongba, flavored with dried or fried fish; stir-fried vegetables called kanghou; and a spicy item, which could be morok metpa, iromba, or singju. All piquant side dishes are accompanied by a choice of fresh herbs, collectively called maroi. The base and essence of Meitei cuisine is the fermented fish called ngari.

Flourensia cernua is a species of flowering plant in the aster family known by the English common names American tarwort and tarbush and the Spanish common names hojasé, hojasén, and hoja ancha. It is native to the Chihuahuan Desert of North America, where it occurs in the US states of Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas, and the Mexican states of Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Durango, San Luis Potosí, and Zacatecas. Most of the species in the genus are found in Latin America; this and F. pringlei are the only two species whose ranges extend into the United States.
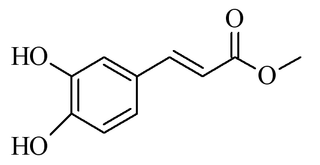
Methyl caffeate is an ester of a hydroxycinnamic acid, a naturally occurring phenolic compound. It is an α-Glucosidase inhibitor.

Solanum macrocarpon otherwise known as the African eggplant or Vietnamese eggplant is a plant of the family Solanaceae. S. macrocarpon is a tropical perennial plant that is closely related to the eggplant. S. macrocarpon originated from West Africa, but is now widely distributed in Central and East Africa. Through an introduction from West Africa, the plant also grows in the Caribbean, South America, and some parts of Southeast Asia. S. macrocarpon is widely cultivated for its use as a food, its medicinal purposes, and as an ornamental plant.

Pilu oil is an extract from seeds of the pilu tree, the meswak tree, and the mustard tree.

African nightshades are several species of plants in the section Solanum of the genus Solanum, that are commonly consumed as leafy vegetables and herbs. African nightshades are grown in both high and lowland areas in West and East Africa, particularly in Nigeria and Cameroon. There is a large variation in diversity of the African nightshades, which have many nutritional and medicinal benefits, even though the family of nightshade is commonly known as comprising dangerous weeds or poisonous plants. Species known as African nightshade include Solanum scabrum, Solanum villosum, Solanum nigrum, and Solanum americanum. Other common names for African nightshade are Black nightshade and Narrow-leaved nightshade. Local names of African nightshade include mnavu (Swahili), managu (Kisii), namasaka (Luhya), osuga (Luo), isoiyot (Kipsigis), kitulu (Kamba), ormomoi (Maa), ndunda (Taita), and nsugga (Luganda).

Solanum conocarpum, commonly known as marron bacoba, is a vascular plant species in the family Solanaceae found in the US Virgin Islands.




















