Related Research Articles

Jamaica lies 140 km (87 mi) south of Cuba and 190 km (118 mi) west of Haiti. At its greatest extent, Jamaica is 235 km (146 mi) long, and its width varies between 34 and 84 km. Jamaica has a small area of 10,992 km2 (4,244 sq mi). However, Jamaica is the largest island of the Commonwealth Caribbean and the third largest of the Greater Antilles, after Cuba and Hispaniola. Many small islands are located along the south coast of Jamaica, such as the Port Royal Cays. Southwest of mainland Jamaica lies Pedro Bank, an area of shallow seas, with a number of cays, extending generally east to west for over 160 km (99 mi). To the southeast lies Morant Bank, with the Morant Cays, 51 km (32 mi) from Morant Point, the easternmost point of mainland Jamaica. Alice Shoal, 260 km (160 mi) southwest of the main island of Jamaica, falls within the Jamaica–Colombia Joint Regime. It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 258,137 km2 (99,667 sq mi).

Ukraine is the second-largest European country, after Russia. Its various regions have diverse geographic features ranging from highlands to lowlands, as well as climatic range and a wide variety in hydrography. Most of the country lies within the East European Plain.

Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity. When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow.

A monsoon is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains.

A capping inversion is an elevated inversion layer that caps a convective planetary boundary layer.

A microwave radiometer (MWR) is a radiometer that measures energy emitted at one millimeter-to-metre wavelengths (frequencies of 0.3–300 GHz) known as microwaves. Microwave radiometers are very sensitive receivers designed to measure thermally-emitted electromagnetic radiation. They are usually equipped with multiple receiving channels to derive the characteristic emission spectrum of planetary atmospheres, surfaces or extraterrestrial objects. Microwave radiometers are utilized in a variety of environmental and engineering applications, including remote sensing, weather forecasting, climate monitoring, radio astronomy and radio propagation studies.

A katabatic wind is a downslope wind caused by the flow of an elevated, high-density air mass into a lower-density air mass below under the force of gravity. The spelling catabatic is also used. Since air density is strongly dependent on temperature, the high-density air mass is usually cooler, and the katabatic winds are relatively cool or cold.

A sea breeze or onshore breeze is any wind that blows from a large body of water toward or onto a landmass. By contrast, a land breeze or offshore breeze is any wind that blows from a landmass toward or onto a large body of water. Sea breezes and land breezes are both important factors in coastal regions' prevailing winds.

In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. It is the opposite of a high-pressure area. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather, while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places:
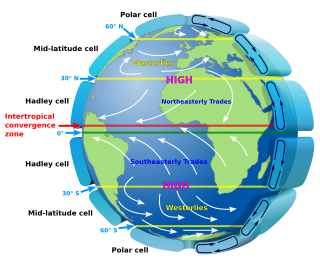
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface at any given time. A region's prevailing and dominant winds are the result of global patterns of movement in the Earth's atmosphere. In general, winds are predominantly easterly at low latitudes globally. In the mid-latitudes, westerly winds are dominant, and their strength is largely determined by the polar cyclone. In areas where winds tend to be light, the sea breeze-land breeze cycle is the most important cause of the prevailing wind. In areas which have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes dominate the wind pattern. Highly elevated surfaces can induce a thermal low, which then augments the environmental wind flow. Wind direction at any given time is influenced by synoptic-scale and mesoscale weather like pressure systems and fronts. Local wind direction can also be influenced by microscale features like buildings.

A funnel cloud is a funnel-shaped cloud of condensed water droplets, associated with a rotating column of wind and extending from the base of a cloud but not reaching the ground or a water surface. A funnel cloud is usually visible as a cone-shaped or needle like protuberance from the main cloud base. Funnel clouds form most frequently in association with supercell thunderstorms, and are often, but not always, a visual precursor to tornadoes. Funnel clouds are visual phenomena, but these are not the vortex of wind itself.
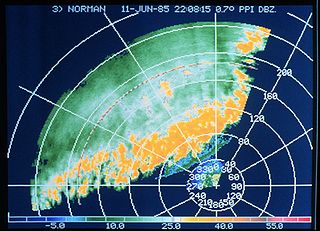
A rainband is a cloud and precipitation structure associated with an area of rainfall which is significantly elongated. Rainbands in tropical cyclones can be either stratiform or convective and are curved in shape. They consist of showers and thunderstorms, and along with the eyewall and the eye, they make up a tropical cyclone. The extent of rainbands around a tropical cyclone can help determine the cyclone's intensity.

Mesoscale meteorology is the study of weather systems and processes at horizontal scales of approximately 5 kilometres (3 mi) to several hundred kilometres. It is smaller than synoptic-scale systems but larger than microscale. At the small end, it includes storm-scale phenomena. Examples of mesoscale weather systems are sea breezes, squall lines, and mesoscale convective complexes.

The Monthly Weather Review is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Meteorological Society. It covers research related to analysis and prediction of observed and modeled circulations of the atmosphere, including technique development, data assimilation, model validation, and relevant case studies. This includes papers on numerical techniques and data assimilation techniques that apply to the atmosphere and/or ocean environment. The current editor-in-chief is Ron McTaggart-Cowan.

A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane, typhoon, tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of 65 kn or more.

The Kantō Plain, in the Kantō region of central Honshu, is the largest plain in Japan. Its 17,000 km2 covers more than half of the region extending over Tokyo, Saitama Prefecture, Kanagawa Prefecture, Chiba Prefecture, Gunma Prefecture, Tochigi Prefecture, and Ibaraki Prefecture.

Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The study of wind is called anemology.
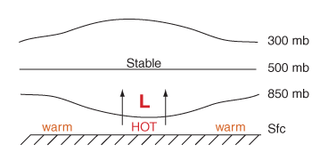
Thermal lows, or heat lows, are non-frontal low-pressure areas that occur over the continents in the subtropics during the warm season, as the result of intense heating when compared to their surrounding environments. Thermal lows occur near the Sonoran Desert, on the Mexican Plateau, in California's Great Central Valley, in the Sahara, in the Kalahari, over north-west Argentina, in South America, over the Kimberley region of north-west Australia, over the Iberian Peninsula, and over the Tibetan Plateau.

The Monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year from June through September, but it is only partly understood and notoriously difficult to predict. Several theories have been proposed to explain the origin, process, strength, variability, distribution, and general vagaries of the monsoon, but understanding and predictability are still evolving.
The Model for Prediction Across Scales (MPAS) is an Earth system modeling software that integrates atmospheric, oceanographic, and cryospheric modeling across scales from regional to planetary. It includes climate and weather modeling and simulations that were used initially by researchers in 2013. The atmospheric models were created by the Earth System Laboratory at the National Center for Atmospheric Research and the oceanographic models were created by the Climate, Ocean, and Sea Ice Modeling Group at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The software has been used to model real-time weather as well as seasonal forecasting of convection, tornadoes and tropical cyclones. The atmospheric modeling component of the software can be used with other atmospheric modeling software including the Weather Research and Forecasting Model, the Global Forecast System, and the Community Earth System Model.
References
- ↑ Frederick Sanders; Howard B. Bluestein (2008). "Solenoid (meteorology)". McGraw-Hill Companies. doi:10.1036/1097-8542.634300.
- ↑ Mike Pritchard (2011-02-04). "Notes on mountain plains solenoid literature from Koch et al., MWR, 2001".
- ↑ Eumetcal. "Sea Breeze".
- ↑ "Sea and Land Breezes" (PDF). University of Oklahoma. 2006.
- ↑ Jianhua Sun; Fuqing Zhang (February 2012). "Impacts of Mountain–Plains Solenoid on Diurnal Variations of Rainfalls along the Mei-Yu Front over the East China Plains". Monthly Weather Review . 140 (2). American Meteorological Society: 379–397. Bibcode:2012MWRv..140..379S. doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-11-00041.1 .