
Pythagoras of Samos was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of Plato, Aristotle, and, through them, the West in general. Knowledge of his life is clouded by legend; modern scholars disagree regarding Pythagoras's education and influences, but they do agree that, around 530 BC, he travelled to Croton in southern Italy, where he founded a school in which initiates were sworn to secrecy and lived a communal, ascetic lifestyle.
Alastor refers to a number of people and concepts in Greek mythology:

Epimenides of Knossos was a semi-mythical 7th- or 6th-century BC Greek seer and philosopher-poet, from Knossos or Phaistos.

Aristoxenus of Tarentum was a Greek Peripatetic philosopher, and a pupil of Aristotle. Most of his writings, which dealt with philosophy, ethics and music, have been lost, but one musical treatise, Elements of Harmony, survives incomplete, as well as some fragments concerning rhythm and meter. The Elements is the chief source of our knowledge of ancient Greek music.

The sibyls were prophetesses or oracles in Ancient Greece.

Gaius Julius Solinus, better known simply as Solinus, was a Latin grammarian, geographer, and compiler who probably flourished in the early 3rd century AD. Historical scholar Theodor Mommsen dates him to the middle of the 3rd century.

Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the ancient Greek colony of Kroton, in modern Calabria (Italy) cirka 530 BC. Early Pythagorean communities spread throughout Magna Graecia.
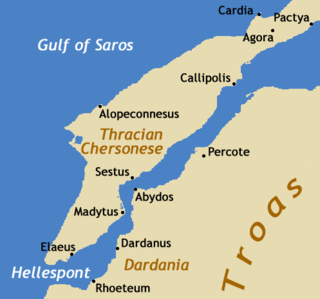
Sestos was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.

The Sibylline Oracles are a collection of oracular utterances written in Greek hexameters ascribed to the Sibyls, prophetesses who uttered divine revelations in a frenzied state. Fourteen books and eight fragments of Sibylline Oracles survive, in an edition of the 6th or 7th century AD. They are not to be confused with the original Sibylline Books of the ancient Etruscans and Romans which were burned by order of the Roman general Flavius Stilicho in the 4th century AD. Instead, the text is an "odd pastiche" of Hellenistic and Roman mythology interspersed with Jewish, Gnostic and early Christian legend.
Quintus Fabius Pictor was the earliest known Roman historian. His history, written in Greek and now mostly lost besides some surviving fragments, was highly influential on ancient writers and certainly participated in introducing Greek historiographical methods to the Roman world. However, the work was highly partisan towards Rome, blaming the Second Punic War on Carthage and idealizing the Roman Republic as a well-ordered state loyal to its allies. Fabius probably served as praetor, was a member of the Senate, and participated in a delegation sent to the oracle at Delphi in 216 BC. Some scholars consider him one of the earliest annalists, although this conclusion has been criticized.

Porphyry of Tyre was a Neoplatonic philosopher born in Tyre, Roman Phoenicia during Roman rule. He edited and published The Enneads, the only collection of the work of Plotinus, his teacher.
Oneiromancy is a form of divination based upon dreams, and also uses dreams to predict the future. Oneirogen plants may also be used to produce or enhance dream-like states of consciousness. Occasionally, the dreamer feels as if they are transported to another time or place, and this is offered as evidence they are in fact providing divine information upon their return.
Anastasius Bibliothecarius was the librarian (bibliothecarius) and chief archivist of the Church of Rome and also briefly a claimant to the Papacy.

Greek mathematics refers to mathematics texts and ideas stemming from the Archaic through the Hellenistic and Roman periods, mostly from the 5th century BC to the 6th century AD, around the shores of the Mediterranean. Greek mathematicians lived in cities spread over the entire region, from Anatolia to Italy and North Africa, but were united by Greek culture and the Greek language. The development of mathematics as a theoretical discipline and the use of deductive reasoning in proofs is an important difference between Greek mathematics and those of preceding civilizations.

The Greek Magical Papyri is the name given by scholars to a body of papyri from Graeco-Roman Egypt, written mostly in ancient Greek, which each contain a number of magical spells, formulae, hymns, and rituals. The materials in the papyri date from the 100s BCE to the 400s CE. The manuscripts came to light through the antiquities trade, from the 1700s onward. One of the best known of these texts is the Mithras Liturgy.

Scientific scholarship during the Byzantine Empire played an important role in the transmission of classical knowledge to the Islamic world and to Renaissance Italy, and also in the transmission of Islamic science to Renaissance Italy. Its rich historiographical tradition preserved ancient knowledge upon which splendid art, architecture, literature and technological achievements were built. Byzantines stood behind several technological advancements.

Ipse dixit is an assertion without proof, or a dogmatic expression of opinion.
The Medicina Plinii or Medical Pliny is an anonymous Latin compilation of medical remedies dating to the early 4th century AD. The excerptor, saying that he speaks from experience, offers the work as a compact resource for travelers in dealing with hucksters who sell worthless drugs at exorbitant prices or with know-nothings only interested in profit. The material is presented in three books in the conventional order a capite ad calcem, the first dealing with treatments pertaining to the head and throat, the second the torso and lower extremities, and the third systemic ailments, skin diseases, and poisons.
Philogelos, also titled or subtitled The Jests of Hierocles and Philagrius, is a Greek-language book published in late antiquity that is the oldest known surviving collection of jokes.

The Exhortation to the Greeks is an Ancient Greek Christian paraenetic or protreptic text in thirty-eight chapters.














