Sulawesi, also known as Celebes, is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's 11th-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago. Within Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra are more populous.

Central Sulawesi is a province of Indonesia located at the centre of the island of Sulawesi. The administrative capital and largest city is located in Palu. The province borders the provinces of Gorontalo to the east, Southeast Sulawesi, South Sulawesi, and West Sulawesi to the south, and sharing maritime borders with East Kalimantan to the west, North Maluku to the east, and Malaysia and the Philippines to the north.

Buginese or Bugis is a language spoken by about 4 million people mainly in the southern part of Sulawesi, Indonesia.
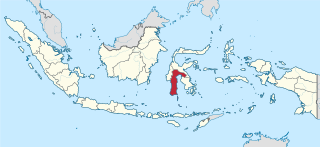
South Sulawesi is a province in the southern peninsula of Sulawesi, Indonesia. The Selayar Islands archipelago to the south of Sulawesi is also part of the province. The capital and largest city is Makassar. The province is bordered by Central Sulawesi and West Sulawesi to the north, the Gulf of Bone and Southeast Sulawesi to the east, Makassar Strait to the west, and Flores Sea to the south.

Makassar, formerly Ujung Pandang, is the capital of the Indonesian province of South Sulawesi. It is the largest city in the region of Eastern Indonesia and the country's fifth-largest urban center after Jakarta, Surabaya, Medan, and Bandung. The city is located on the southwest coast of the island of Sulawesi, facing the Makassar Strait.

The Bugis people, also known as Buginese, are an Austronesian ethnic group—the most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi, in the south-western province of Sulawesi, third-largest island of Indonesia. The Bugis in 1605 converted to Islam from Animism. Although the majority of Bugis are Muslim, a small minority adhere to Christianity as well as a pre-Islamic indigenous belief called Tolotang.

Bone was a sultanate in the south-west peninsula of what is now Sulawesi, a province of modern-day Indonesia. It came under Dutch rule in 1905, and was succeeded by the Bone Regency.

The Kingdom of Luwu was a polity located in the northern part of the modern-day South Sulawesi province of Indonesia, on the island of Sulawesi. It is considered one of the earliest known Buginese kingdoms in Sulawesi, founded between the 10th and 14th century. However, recent archaeological research has challenged this idea.
Wajoq, also spelled Wajo, Wajo', or Wajok, was a Bugis elective principality in the eastern part of the South Sulawesi peninsula. It was founded in the 15th century, and reached its peak in the 18th century, when it briefly became the hegemon of South Sulawesi replacing Boné. Wajoq retained its independence until it was subdued in the early 20th century by the Dutch colonial government. It continued to exist in some form up to the mid-20th century, when the self-governing entity was transformed into Wajo Regency in the newly independent Republic of Indonesia.

The Makassar people or Makassarese are an ethnic group that inhabits the southern part of the South Peninsula, Sulawesi in Indonesia. They live around Makassar, the capital city of the province of South Sulawesi, as well as the Konjo highlands, the coastal areas, and the Selayar and Spermonde islands. They speak Makassarese, which is closely related to Buginese, and also a Malay creole called Makassar Malay.

The caves in the Maros-Pangkep karst are situated in South Sulawesi, Indonesia, and contain paintings from the Paleolithic considered to be the earliest figurative art in the world, dated to at least 43,900 years ago.

The Sultanate of Gowa was one of the great kingdoms in the history of Indonesia and the most successful kingdom in the South Sulawesi region. People of this kingdom come from the Makassar tribe who lived in the south end and the west coast of southern Sulawesi.

Fort Somba Opu was a fortified commercial center of the Gowa Sultanate. Its ruins are located in Makassar, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. The fort was the center of the Gowa Sultanate in the 16th-century until its destruction by the Dutch East India Company in 1669. The conquest of Somba Opu citadel was one of the most difficult campaigns the Company had ever undertaken in the East.
The Makassar kingdom of Gowa emerged around 1300 CE as one of many agrarian chiefdoms in the Indonesian peninsula of South Sulawesi. From the sixteenth century onward, Gowa and its coastal ally Talloq became the first powers to dominate most of the peninsula, following wide-ranging administrative and military reforms, including the creation of the first bureaucracy in South Sulawesi. The early history of the kingdom has been analyzed as an example of state formation.

Sultan Saaduddin Arung Palakka, or La Tenritatta to Unru' was a 17th-century Bugis prince and warrior. He supported the Dutch East India Company (VOC) in the Makassar War (1666–1669) against the Gowa Sultanate in his native South Sulawesi. After the defeat of Gowa, he became the King of Bone and South Sulawesi's most powerful man.
Ajatappareng was a historical region in the western part of South Sulawesi consisting of five allied principalities: Sidenreng, Suppa, Rappang, Sawitto, Bacukiki and Alitta. They formed an alliance during the sixteenth century in response to the rise of Gowa and Tallo to the south and rivalling the Telumpoccoe alliance—consisting three Bugis kingdoms of Bone, Wajo, and Soppeng—to the east. The Ajatappareng confederation became a regional power and a major port thanks to its naval power and the exodus of traders fleeing the Portuguese capture of Malacca. The confederation's power declined in the seventeenth century, when it was subjugated by Gowa. The later invasion of South Sulawesi by the Dutch East India Company and its imposition of monopoly ended the region's status as a trade centre.
The Makasar script, also known as Ukiri' Jangang-jangang or Old Makasar script, is a historical Indonesian writing system that was used in South Sulawesi to write the Makassarese language between the 17th and 19th centuries until it was supplanted by the Lontara Bugis script.

The Toalean people were hunter-gatherers who inhabited the Indonesian island of Sulawesi during the Mid- to Late-Holocene period prior to the spread of Austronesian Neolithic farmers some 3,500 years ago from mainland Asia.