Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 163 million people, in an area of 148,560 square kilometres (57,360 sq mi), making it one of the most densely populated countries in the world. Bangladesh shares land borders with India to the west, north, and east, Myanmar to the southeast, and the Bay of Bengal to the south. It is narrowly separated from Nepal and Bhutan by the Siliguri Corridor, and from China by the Indian state of Sikkim in the north, respectively. The Bengalis make up 98% of the total population of Bangladesh. The large Muslim population of Bangladesh makes it the third-largest Muslim-majority country. Dhaka, the capital and largest city, is the nation's economic, political, and cultural hub. Chittagong, the largest seaport is the second-largest city.

Bengal is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predominantly covering present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal. Geographically, it is made up by the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta system, the largest such formation in the world, along with mountains in its north bordering the Himalayan states of Nepal and Bhutan, and east bordering Myanmar.

Dhaka, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and the largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the largest city in the Bengal region. It is the tenth-largest and the fourth-most densely populous city in the world with, as of 2011, a population of 8.9 million residents within the city limits, and a population of over 21 million residents in the Greater Dhaka Area. Dhaka is the economic, political, and cultural center of Bangladesh, and is one of the major cities in South Asia, the largest city in Eastern South Asia and among the Bay of Bengal countries; and one of the largest cities among OIC countries. As part of the Bengal plain, the city is bounded by the Buriganga River, Turag River, Dhaleshwari River and Shitalakshya River.

Bangladesh is the eighth-most populated country in the world with almost 2.2% of the world's population. The population is estimated by the 2019 revision of the World Population Prospects to have stood at 161,376,708 in 2018.

The Economy of Bangladesh is characterised as a developing market economy. It is the 37th largest in the world in nominal terms, and 31th largest by purchasing power parity. It is classified among the Next Eleven emerging market middle income economies and a frontier market. In the first quarter of 2019, Bangladesh's was the world's seventh fastest-growing economy with a rate of 8.3% real GDP annual growth. Dhaka and Chittagong are the principal financial centers of the country, being home to the Dhaka Stock Exchange and the Chittagong Stock Exchange. The financial sector of Bangladesh is the third largest in the Indian subcontinent. Bangladesh is one of the fastest growing economies in the world as well as the fastest growing economy in South Asia.

The foreign relations share the Bangladeshi government's policies in its external relations with the international community. The country pursues a moderate foreign policy that places heavy reliance on multinational diplomacy, especially at the United Nations and World Trade Organization (WTO). Since independence in 1971, the country has stressed its principle of "Friendship towards all, malice towards none" in dictating its diplomacy. As a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, Bangladesh has tended to not take sides with major powers. Since the end of the Cold War, the country has pursued better relations with regional neighbours.

The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. SAARC comprises 3% of the world's area, 21% of the world's population and 4.21% of the global economy, as of 2019.

The Bangladesh men's national cricket team, popularly known as The Tigers, is administered by the Bangladesh Cricket Board (BCB). It is a Full Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) with Test, One-Day International (ODI) and T20 International (T20I) status. It played its first Test match in November 2000 against India in Dhaka, becoming the tenth Test-playing nation.

Mohammed Rafique is a Bangladeshi cricket coach and former cricketer, who played all formats of the cricket. He is the first consistent cricketer of his national cricket team. He is the first Man Of the Match for Bangladesh in One Day Internationals. One of the best spinners to ever have played for Bangladesh, Rafique was the first Bangladesh bowler to take 100 wickets in Test matches.
The Bangladesh national football team is the national recognised football team of Bangladesh and is controlled by the Bangladesh Football Federation (BFF). It is a member of the Asian Football Confederation, and became a member of FIFA in 1974. Even though the Bangladesh Football Federation was first founded in 1972. Bangladesh was elected as a member of the AFC Executive Committee in 1982–1986 and 1998–2002. The current Executive Committee was elected democratically, under an AFC approved constitution and direct supervision of FIFA & AFC, in April 2008.

Mashrafe Bin Mortaza is a Bangladeshi international cricketer and politician who is the former captain in all three formats of the game for the Bangladesh national cricket team. Widely considered as the best captain for Bangladesh in ODI and T20 formats of all time, he became only the fifth bowler in the history to take 100 ODI wickets as a captain. Mortaza's career have been hampered by fifteen injuries as he has undergone a total of ten operations on his knees and ankles. Mashrafe is also the first pace bowler in Bangladesh who bowled a delivery clocking over 148 km/h during a Test against New Zealand at Hamilton in 2001.

Shakib Al Hasan, also known as Saqibul Hasan, is a Bangladeshi international cricketer. Regarded as one of the greatest all-rounders of all time, his aggressive left-handed batting style in the middle order, controlled slow left-arm orthodox bowling has made him a consistent player for Bangladesh. He was ranked as one of the world's most famous athletes by ESPN World Fame 100 in 2019.
The ICC Under-19 Cricket World Cup is an international cricket tournament organised by the International Cricket Council (ICC) contested by national under-19 teams. First contested in 1988, as the Youth World Cup, it was not staged again until 1998. Since then, the World Cup has been held as a biennial event, organised by the ICC. The first edition of the tournament had only eight participants, but every subsequent edition has included sixteen teams. India have won the World Cup on a record four occasions, while Australia have won three times, Pakistan twice, and Bangladesh, England, South Africa and the West Indies once each. Two other teams New Zealand and Sri Lanka have made it to tournament finals. Bangladesh are the current defending champion.
The South African cricket team toured Bangladesh for two Test matches and three One Day Internationals in February and March 2008. For South Africa, it represented the first tour after the retirement of bowler Shaun Pollock while Bangladesh were looking to rebuild after heavy defeats against New Zealand and Sri Lanka.

Football is the second-most popular sport in Bangladesh, after cricket, and is governed by the Bangladesh Football Federation (BFF).
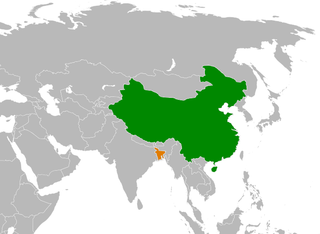
Bangladesh–China relations are the bilateral relations of Bangladesh and China. Bangladesh has an embassy in Beijing and consulates in Hong Kong and Kunming. China has an embassy in Dhaka. Both countries are members of the BCIM Forum. According to Chinese government designations, Bangladesh and China are "strategic partnership of cooperation".

Bangladesh–South Korea relations refer to the diplomatic and bilateral relations between the countries of Bangladesh and South Korea. Bangladesh is one of many countries that established diplomatic relationships with both Koreas. In 1974, South Korea opened its embassy in the capital Dhaka, with the latter nation opening its embassy in 1987.

South Asia is the southern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and the Maldives. Topographically, it is dominated by the Indian Plate and defined largely by the Indian Ocean on the south, and the Himalayas, Karakoram, and Pamir mountains on the north. The Amu Darya, which rises north of the Hindu Kush, forms part of the northwestern border. On land (clockwise), South Asia is bounded by Western Asia, Central Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia.